Neuron Structure and Function
... The neurotransmitter is released from vesicles in the axon. The neurotransmitter is released when the action potential reaches the ...
... The neurotransmitter is released from vesicles in the axon. The neurotransmitter is released when the action potential reaches the ...
neuron
... • transmit stimuli in the form of action potential to other neuron or effector cell • 1 neuron has 1 axon • metabolically dependent on perikaryon • Golgi type I neurons – motor neurons of CNS with long axon (up to 1 meter) terminate on skeletal muscle • Golgi type II neurons – short axons • axon hil ...
... • transmit stimuli in the form of action potential to other neuron or effector cell • 1 neuron has 1 axon • metabolically dependent on perikaryon • Golgi type I neurons – motor neurons of CNS with long axon (up to 1 meter) terminate on skeletal muscle • Golgi type II neurons – short axons • axon hil ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... The neurons are the nerve cells involved in the production and exchange of signals. They represent the functional unit of the nervous system. The majority of the neurons is characterized by 3 main areas: the cell body (also called soma), the dendrites and the axons. ...
... The neurons are the nerve cells involved in the production and exchange of signals. They represent the functional unit of the nervous system. The majority of the neurons is characterized by 3 main areas: the cell body (also called soma), the dendrites and the axons. ...
BOX 2.1 THE NEURON DOCTRINE The cell theory, which states
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
... The cell theory, which states that all organisms are composed of individual cells, was developed around the middle of the nineteenth century by Mattias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, this unitary vision of the cellular nature of life was not immediately applied to the nervous system, as mos ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... Nucleus – stores genes of the cell (DNA) Organelles – synthesize the proteins of the cell Cytosol – fluid inside cell Plasmic membrane – wall of the cell separating it from the fluid outside the cell. ...
... Nucleus – stores genes of the cell (DNA) Organelles – synthesize the proteins of the cell Cytosol – fluid inside cell Plasmic membrane – wall of the cell separating it from the fluid outside the cell. ...
Cells of the Nervous System
... in CNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = nuclei in PNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = ganglia processes: two types; axons and dendrites Dendrites shorter branching receptor regions contain all organelles (except nucleus) as in cell body large surface area for reception of sign ...
... in CNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = nuclei in PNS neuron cell bodies are clustered together = ganglia processes: two types; axons and dendrites Dendrites shorter branching receptor regions contain all organelles (except nucleus) as in cell body large surface area for reception of sign ...
Bridget Lecture 2 Notes The Neurons o Functional classes (CNS
... ● Active during inflammatory reaction due to brain damage ✓ Check your understanding o Trace from spine to spine of communication between cells o what are the three types of neurons? Blood Brain Barrier o selective permeability (only takes in what is needed) o active transport (e.g. glucose) ...
... ● Active during inflammatory reaction due to brain damage ✓ Check your understanding o Trace from spine to spine of communication between cells o what are the three types of neurons? Blood Brain Barrier o selective permeability (only takes in what is needed) o active transport (e.g. glucose) ...
The Nervous System
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
... The Nervous System: • is a rapid communication system using electrical signals. • enables movement, perception, thought, emotion and learning. • consists of a network of specialized cells called neurons. ...
Chapter 14
... which they then transmit to the CNS. 3. Astrocytes are the most numerous and largest glial cells in the CNS. They help form the blood-brain barrier, regulate tissue fluid composition, strengthen and reinforce the nervous tissue in the CNS, replace damaged neurons, and assist with neuronal developmen ...
... which they then transmit to the CNS. 3. Astrocytes are the most numerous and largest glial cells in the CNS. They help form the blood-brain barrier, regulate tissue fluid composition, strengthen and reinforce the nervous tissue in the CNS, replace damaged neurons, and assist with neuronal developmen ...
File
... • If a cell is incompetent to an inductive signal, will there be an effect? • No, because it does not have the machinery capable to induce the desired effect. • What was the main discovery of the Spemann Mangold ...
... • If a cell is incompetent to an inductive signal, will there be an effect? • No, because it does not have the machinery capable to induce the desired effect. • What was the main discovery of the Spemann Mangold ...
Synaptogenesis
... reach the astrocytic processes that delimit the surface of the spinal cord. Axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons also do not regenerate through the glia scars that form at lesion sites in the CNS white matter (red). ...
... reach the astrocytic processes that delimit the surface of the spinal cord. Axons of dorsal root ganglion neurons also do not regenerate through the glia scars that form at lesion sites in the CNS white matter (red). ...
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... 5. The telencephalon, or end-brain, contains two major structures in addition to neocortex. These structures, present in all vertebrates, are the ___________ _____________, which has some close connections with the olfactory bulb, and the ___________ ______________. 6. What are the kinds of function ...
... 5. The telencephalon, or end-brain, contains two major structures in addition to neocortex. These structures, present in all vertebrates, are the ___________ _____________, which has some close connections with the olfactory bulb, and the ___________ ______________. 6. What are the kinds of function ...
Notes Outline I (Part I)
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
... __________________ and in the PNS are called ___________________. 18. _____________________ receive imput from other neurons (axons). 19. Axons and dendrites are called ___________________ ________________. 20. Very long axons are otherwise know as ________________ _______________. 21. Movement of s ...
Slide ()
... The spinal cord varies slightly in diameter along its length but in cross section always shows bilateral symmetry around the small, CSF-filled central canal (C). Unlike the cerebrum and cerebellum, in the spinal cord the gray matter is internal, forming a roughly H-shaped structure that consists of ...
... The spinal cord varies slightly in diameter along its length but in cross section always shows bilateral symmetry around the small, CSF-filled central canal (C). Unlike the cerebrum and cerebellum, in the spinal cord the gray matter is internal, forming a roughly H-shaped structure that consists of ...
Slide ()
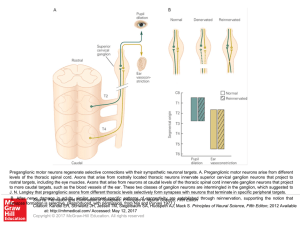
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
File - Mr. Haan`s Science
... change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
... change in and out of body b. Integration – processes and interprets data to see what to do c. Motor output – causes response of effector organs ...
Nervous System - EMTStudyCenter.com
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
... 5. All of the following are functions of the nervous system EXCEPT senses changes. analyzes changes. ...
Slide ()
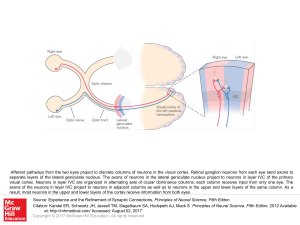
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
3-2_UniqueFt_of_Neurons
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
... dendrites: neurons have multiple dendrites (which also can branch multiple times) that connect them to other neurons’ axons, the collections of them make the dendritic trees, most of the incoming information from other neurons go through the dendritic spines (small membranous protrusions from the de ...
Roger Sperry`s Classic Experiment (1940`s)
... Frog behavior: Dangle a lure frog will grab it with its tongue. ...
... Frog behavior: Dangle a lure frog will grab it with its tongue. ...
Slide 1 - AccessPhysiotherapy
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
... dendrites and also on its cell body, the soma. The soma of this type of cell integrates the electrical information and also provides metabolic support for the cell as a whole. The place where the axon comes out of the soma is called the axon hillock, and this is where the information is encoded into ...
Nolte – Chapter 1 (Introduction to the Nervous
... o Neurofilaments Neruon’s version of the intermediate filaments found in most cells. They are ropelike assemblies of strands of polymers. o Serve as the substrate along which organelles are transported. o Microfilaments anchor membrane molecules in place (receptor molecules at synapses) o Transpor ...
... o Neurofilaments Neruon’s version of the intermediate filaments found in most cells. They are ropelike assemblies of strands of polymers. o Serve as the substrate along which organelles are transported. o Microfilaments anchor membrane molecules in place (receptor molecules at synapses) o Transpor ...
Target Selection
... topographically connected to motor neurons targets in the spinal cord.Particular areas of the motor cortex project to cervical and hindlimb spinal cord segments This specificity in the projections is maintained in vitro. Cultured explants from forelimb cortex prefer to send axons into explants of th ...
... topographically connected to motor neurons targets in the spinal cord.Particular areas of the motor cortex project to cervical and hindlimb spinal cord segments This specificity in the projections is maintained in vitro. Cultured explants from forelimb cortex prefer to send axons into explants of th ...