Neuron PowerPoint
... The firing of the message down the axon is called “action potential.” It occurs in an “all-or-none” process, which means either the message is sent or not sent. For example: imagine dominos are lined up perfectly, if you tap the first domino, they either all fall down or none of them ...
... The firing of the message down the axon is called “action potential.” It occurs in an “all-or-none” process, which means either the message is sent or not sent. For example: imagine dominos are lined up perfectly, if you tap the first domino, they either all fall down or none of them ...
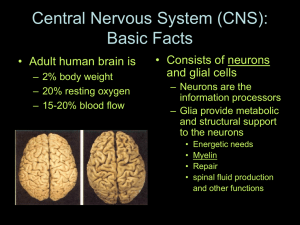
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
... Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow ...
Slide ()
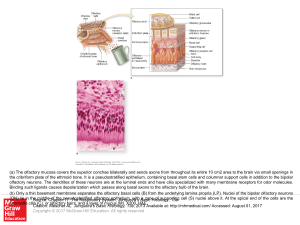
... the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition to the bipolar olfactory neurons. The dendrites of these neurons are at the luminal ends and have cilia specialized with many membrane receptors for odor ...
... the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. It is a pseudostratified epithelium, containing basal stem cells and columnar support cells in addition to the bipolar olfactory neurons. The dendrites of these neurons are at the luminal ends and have cilia specialized with many membrane receptors for odor ...
The Nervous System : communication
... own body temperature and to see other warning signs allowing the body to overheat without discomfort especially when dancing for hours in hot clubs. ...
... own body temperature and to see other warning signs allowing the body to overheat without discomfort especially when dancing for hours in hot clubs. ...
the brain: anatomical regions
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
... CEREBRUM is the largest portion of the brain Cerebellum is the second largest portion of the brain. Its function is for balance. ...
Document
... • One axon per cell arising from the axon hillock • Long axons (nerve fibers) • Occasional branches (axon collaterals) The Axon • Numerous terminal branches (telodendria) • Knoblike axon terminals (synaptic knobs or boutons) • Secretory region of neuron • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhib ...
... • One axon per cell arising from the axon hillock • Long axons (nerve fibers) • Occasional branches (axon collaterals) The Axon • Numerous terminal branches (telodendria) • Knoblike axon terminals (synaptic knobs or boutons) • Secretory region of neuron • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhib ...
The Neural Control of Behavior
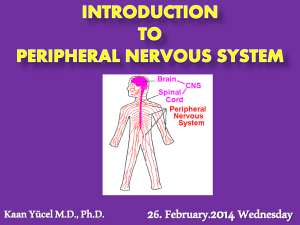
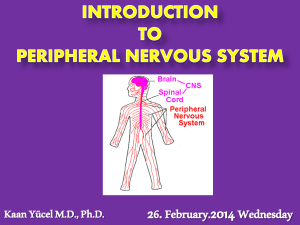
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
... chord •PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: the entire set of cranial and spinal nerves that connect the central nervous system (brain and spinal chord) to the body’s sensory organs, muscles, and glands. •NERVE: a large bundle containing the axons of many neurons. Located in the PNS, nerves connect the CNS wi ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
... • One axon per cell arising from the axon hillock • Long axons (nerve fibers) • Occasional branches (axon collaterals) The Axon • Numerous terminal branches (telodendria) • Knoblike axon terminals (synaptic knobs or boutons) • Secretory region of neuron • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhib ...
... • One axon per cell arising from the axon hillock • Long axons (nerve fibers) • Occasional branches (axon collaterals) The Axon • Numerous terminal branches (telodendria) • Knoblike axon terminals (synaptic knobs or boutons) • Secretory region of neuron • Release neurotransmitters to excite or inhib ...
Brains, Synapses and Neurotransmitters
... Well, the book is called Drugs and Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
... Well, the book is called Drugs and Behaviour, so, we had better know how the nervous system works The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells • Neurons ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
... To transmit information to other neurons, a brief electrical current impulses through its axon. ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ - This current causes the neuron to “fire” ...
Chapter 3
... The cells that line the inside of the neural tube, the ventricular zone, give rise to the cells of the CNS These cells divide and form into neurons and glia (founder cells) – The first phase of this division is called symmetrical division, because each cell splits into 2 identical new founder ce ...
... The cells that line the inside of the neural tube, the ventricular zone, give rise to the cells of the CNS These cells divide and form into neurons and glia (founder cells) – The first phase of this division is called symmetrical division, because each cell splits into 2 identical new founder ce ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in cluste ...
... • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in cluste ...
The Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
Laminar and Columnar organization of the cerebral cortex
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
... ◦ The appearance of the neocortex - the region of cerebral cortex nearest the surface of the brain - depends on what is used to stain it. The Golgi stain reveals a subset of neuronal cell bodies, axons, and dendritic trees. The Nissl method shows cell bodies and proximal dendrites. The Weigert stain ...
three basic functions of the nervous system
... Autonomic Nervous System - smooth muscles, glands (involuntary) ...
... Autonomic Nervous System - smooth muscles, glands (involuntary) ...
Presentation
... What fraction of regenerated serotonin axons survive long-term and do they attain normal morphology and spatial distribution? ~90% of the regenerated axons survive for 6 months after PCA treatment: They survive at the same rate as uninjured serotonin axons. Furthermore, their distribution and shape ...
... What fraction of regenerated serotonin axons survive long-term and do they attain normal morphology and spatial distribution? ~90% of the regenerated axons survive for 6 months after PCA treatment: They survive at the same rate as uninjured serotonin axons. Furthermore, their distribution and shape ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
... One thing that differentiates neurons from other body cells is that only neurons A. contain mitochondria. B. have a nucleus in their cell body. C. have an outer membrane that acts as a filter. D. have axons and dendrites. One difference between axons and dendrites is that A. axons carry signals to t ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a(n): a) independent variable. b) case study. c) hypothesis. d) operational definit ...
... d) set of principles that organizes observations and explains newly discovered facts. 9. In a written report of their research, psychologists specify exactly how anxiety is assessed, thus providing their readers with a(n): a) independent variable. b) case study. c) hypothesis. d) operational definit ...
Overview of the Day
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (carries info. to and from the CNS) somatic/skeletal nervous system (controls voluntary movement of skeletal muscles autonomic nervous system (controls glands and muscles of internal organs [e.g., heart]). The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems work together to k ...
Types of neurons
... Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
... Controls protein manufacturing Directs metabolism No role in neural signaling ...
Cardiovascular system
... “The Mysterious Butterflies of the Soul” Santiago Ramón y Cajal Nobel prize in physiology and medicine 1906 ...
... “The Mysterious Butterflies of the Soul” Santiago Ramón y Cajal Nobel prize in physiology and medicine 1906 ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimulation of the receptor cells, and spasms of muscles such as the heart. Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal glan ...
... memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimulation of the receptor cells, and spasms of muscles such as the heart. Norepinephrine: (NE) This compound is secreted principally from the adrenal glan ...