Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
Cell types: Muscle cell Adipocyte Liver cell Pancreatic cell Example
... Brain ischemia often results in necrotic cell death in the infarct core and cellular dysfunction in the peri-infarct zone. Neuronal necrosis results in extensive spreading of death to adjacent cells through complicated signaling pathways, including ROS, JNK, Eiger (Drosophila TNFα) and other unknown ...
... Brain ischemia often results in necrotic cell death in the infarct core and cellular dysfunction in the peri-infarct zone. Neuronal necrosis results in extensive spreading of death to adjacent cells through complicated signaling pathways, including ROS, JNK, Eiger (Drosophila TNFα) and other unknown ...
The Synaptic Cleft or Synapse
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
... The axon terminal at a synapse contains tiny vesicles filled with chemicals called neurotransmitters. If a nerve impulse takes place, vesicles fuse and release the neurotransmitter. A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine. ...
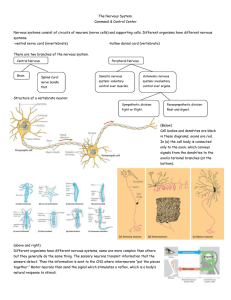
The Nervous System
... Nervous System The nervous system coordinates the activities of all of the body’s organ systems so that they work in concert with one another What systems must cooperate during exercise? What do we use to respond to changes in the external environment? Do the senses operate individually? ...
... Nervous System The nervous system coordinates the activities of all of the body’s organ systems so that they work in concert with one another What systems must cooperate during exercise? What do we use to respond to changes in the external environment? Do the senses operate individually? ...
Nervous Tissue
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core ...
... • White matter = myelinated processes (white in color) • Gray matter = nerve cell bodies, dendrites, axon terminals, bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... Neurons (Nerve Cells) • Structural units of the nervous system – Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites – Long-lived, amitotic, and have a high metabolic rate ...
... Neurons (Nerve Cells) • Structural units of the nervous system – Composed of a body, axon, and dendrites – Long-lived, amitotic, and have a high metabolic rate ...
RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology (CDB)
... odor molecules in the air; odorants inspired into the nasal cavity contact odorant receptors (ORs) expressed by olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) of the olfactory epithelium, and the OSNs then relay the information via the glomeruli in the olfactory bulb (OB) to the mitral and tufted cells, the secon ...
... odor molecules in the air; odorants inspired into the nasal cavity contact odorant receptors (ORs) expressed by olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) of the olfactory epithelium, and the OSNs then relay the information via the glomeruli in the olfactory bulb (OB) to the mitral and tufted cells, the secon ...
Chapter 14 Part 2
... DRGN enters dorsal horn at each spinal cord level Ascend/descend in Lissaur’s tract Synapse in Substantia Gelatinosa Decussate in ventral spinal cord Ascend ventrally in spinal cord as the Spinothalamic Tract • Synapse in thalamus (Ventral Posterior and intralaminar Nuclei) • Thalamic axons travel t ...
... DRGN enters dorsal horn at each spinal cord level Ascend/descend in Lissaur’s tract Synapse in Substantia Gelatinosa Decussate in ventral spinal cord Ascend ventrally in spinal cord as the Spinothalamic Tract • Synapse in thalamus (Ventral Posterior and intralaminar Nuclei) • Thalamic axons travel t ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Depolarization produced by the effect of a neurotransmitter Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
... Depolarization produced by the effect of a neurotransmitter Transient hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane Repolarization produced by the addition of multiple stimul Reflection of the activation of an opposing transmembrane potential ...
Neuron Labeling WS
... from a sense receptor to the brain or spinal cord. The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
... from a sense receptor to the brain or spinal cord. The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or gland ...
Slide ()
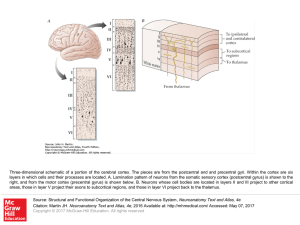
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
... Three-dimensional schematic of a portion of the cerebral cortex. The pieces are from the postcentral and and precentral gyri. Within the cortex are six layers in which cells and their processes are located. A. Lamination pattern of neurons from the somatic sensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) is shown ...
General Neurophysiology
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the removed flight muscles Motor pattern recorded in the absence of any movement of part of animal – fictive pattern Locust flight systém did not require sen ...
... Reduced the animal to a head and the floor of the thorax and the thoracic nerve cord Elecrodes on the stumps of the nerves that had innervated the removed flight muscles Motor pattern recorded in the absence of any movement of part of animal – fictive pattern Locust flight systém did not require sen ...
Slide ()
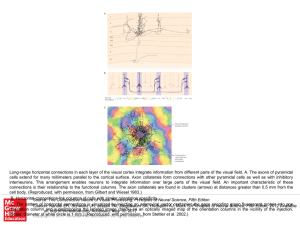
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM: Communication
... 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The ...
... 2. Integrative Function – information is “brought together,” interpreted, to create sensations, create thoughts, add to memory, make decisions, etc. Association neuron or interneuron 3. Motor Function – responses to signals (impulses). Signals sent from the CNS to effectors (muscles or glands). The ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – e.g., Motor cortex Golgi I: neurons with long-projecting axonal processes. Golgi II: neurons whose axonal process projects locally ...
... opposite ends of the soma. e.g., interneuron Multipolar; – Single axon & multiple dendrites – Most common type in men – e.g., Motor cortex Golgi I: neurons with long-projecting axonal processes. Golgi II: neurons whose axonal process projects locally ...
Nervous
... Modern brain–imaging techniques suggest that consciousness may be an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex. Nerve Cell Development Signal molecules direct an axon′s growth by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane of the growth cone. The genes and basic ev ...
... Modern brain–imaging techniques suggest that consciousness may be an emergent property of the brain based on activity in many areas of the cortex. Nerve Cell Development Signal molecules direct an axon′s growth by binding to receptors on the plasma membrane of the growth cone. The genes and basic ev ...
eprint_2_23793_166
... b. Pseudounipolar neurons: only one process arising from the soma. Developmentally, divides into two branches. Found in peripheral sensory ganglia, such as dorsal root ganglia. c. Bipolar neurons: single axon and dendrite arise at opposite poles of the cell body. Found only in sensory neurons, such ...
... b. Pseudounipolar neurons: only one process arising from the soma. Developmentally, divides into two branches. Found in peripheral sensory ganglia, such as dorsal root ganglia. c. Bipolar neurons: single axon and dendrite arise at opposite poles of the cell body. Found only in sensory neurons, such ...
File
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
... ________ The nerve cell that carriers impulses from a sense receptor to the brain and spinal cord. ________ The nerve cell that connects sensory and motor neurons. ________ The nerve cell that transmits impulses from the brain or spinal cord to a muscle or a gland. 3. There are three structural clas ...
Introduction
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of t ...
... • Identify and give functions for each of the following: dendrite, cell body, axon • Distinguish among sensory, motor and interneuron with respect to structure and function • Contrast the locations and functions of the central and peripheral nervous systems • Differentiate between the functions of t ...