O2-1 Significance of Premature Restriction or Closure of Foramen
... cavity imitating hypoplastic left heart, partial obstruction of left ventricular inflow, and premature atrial contractions were other additional findings. One fetus who was born prematurely at 26 weeks died after birth, two foetuses had to be delivered early at 37 weeks of gestation due to severe re ...
... cavity imitating hypoplastic left heart, partial obstruction of left ventricular inflow, and premature atrial contractions were other additional findings. One fetus who was born prematurely at 26 weeks died after birth, two foetuses had to be delivered early at 37 weeks of gestation due to severe re ...
Biochemistry - U
... Disease (CIHD) describes patients who develop progressive heart failure as a consequence of ischemic myocardial damage. In most instances, there's been a prior MI and sometimes previous coronary arterial bypass graft surgery or other interventions. Usually presents as insidious onset of CHF. 6) Defi ...
... Disease (CIHD) describes patients who develop progressive heart failure as a consequence of ischemic myocardial damage. In most instances, there's been a prior MI and sometimes previous coronary arterial bypass graft surgery or other interventions. Usually presents as insidious onset of CHF. 6) Defi ...
Emergency Department use of Esmolol in Refractory Ventricular
... difficult to treat and carries a high mortality rate • Treatment with epinephrine: – Activates α-1 receptors: this is probably helpful – Activates β-1 and β-2 receptors: this is probably harmful ...
... difficult to treat and carries a high mortality rate • Treatment with epinephrine: – Activates α-1 receptors: this is probably helpful – Activates β-1 and β-2 receptors: this is probably harmful ...
Left Ventricular Structure and Function in Aortic Stenosis: The Inner
... (LV) (r/h) with a normal sized cavity. If thicknessradius relationship and LV systolic pressure remain constant, the hypertrophy is appropriate. An increase in r/h represents an increase in wall stress and this is associated with an inappropriate hypertrophy. (1, 2) The increase in myocyte mass and ...
... (LV) (r/h) with a normal sized cavity. If thicknessradius relationship and LV systolic pressure remain constant, the hypertrophy is appropriate. An increase in r/h represents an increase in wall stress and this is associated with an inappropriate hypertrophy. (1, 2) The increase in myocyte mass and ...
Phases of the Cardiac Cycle Atrial systole begins: Atrial
... Side Note: Decreased Compliance leads to decreased stretch of the heart. As per Frank Starlings Law this means less force of contraction. With less force of contraction there will be a greater end systolic volume which will cause a decrease stroke volume. Since CO = Stroke Volume X HR a decreased St ...
... Side Note: Decreased Compliance leads to decreased stretch of the heart. As per Frank Starlings Law this means less force of contraction. With less force of contraction there will be a greater end systolic volume which will cause a decrease stroke volume. Since CO = Stroke Volume X HR a decreased St ...
cardiovascular mcq
... Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) is a disorder largely affecting cardiac myocytes. It is characterised by unexplained ventricular hypertrophy and histological evidence of myofibrillar disarray. With respect to the molecular genetic basis of HOCM, which of the following statements is true? ...
... Familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM) is a disorder largely affecting cardiac myocytes. It is characterised by unexplained ventricular hypertrophy and histological evidence of myofibrillar disarray. With respect to the molecular genetic basis of HOCM, which of the following statements is true? ...
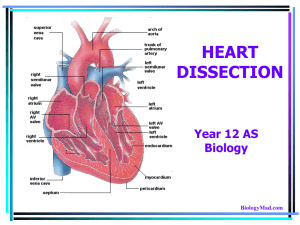
HEART DISSECTION
... The aorta is clearly visible at the top, with an atrium on either side, while the ventricles are in the bottom left. ...
... The aorta is clearly visible at the top, with an atrium on either side, while the ventricles are in the bottom left. ...
Jacksonville Fire and Rescue Department Rescue Division
... prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
... prompts the rescuer to deliver the shock, if necessary. An AED will NOT shock someone who does not ...
PDF
... one in 500 individuals [1]. Heart function in patients with HCM is characterized by hyperdynamic contraction [2] and impaired relaxation [3]. The clinical course is variable with some patients experiencing minimal symptoms and others developing exertional dyspnea, heart failure, atrial fibrillation ...
... one in 500 individuals [1]. Heart function in patients with HCM is characterized by hyperdynamic contraction [2] and impaired relaxation [3]. The clinical course is variable with some patients experiencing minimal symptoms and others developing exertional dyspnea, heart failure, atrial fibrillation ...
Definition: An extra abnormal heart sound usually detected while
... • Males, age > 45 • Presence of MR & leaflet thickening ...
... • Males, age > 45 • Presence of MR & leaflet thickening ...
Cardiomyopathy and anaesthesia
... condition. This important cause of sudden death in young adults affects significant numbers of the population who are unaware that they have the condition. The genetic associations are numerous and involve a number of different chromosomes, so screening is difficult to perform as not all mutations h ...
... condition. This important cause of sudden death in young adults affects significant numbers of the population who are unaware that they have the condition. The genetic associations are numerous and involve a number of different chromosomes, so screening is difficult to perform as not all mutations h ...
Heart Diseases
... • Also known as heart attack • Can occur at any age but the frequency rises progressively with increasing age • Approximately 10% of MIs occur before age 40 • Men are at significantly greater risk than women, and women tend to be protected against MI during their reproductive years • However, menopa ...
... • Also known as heart attack • Can occur at any age but the frequency rises progressively with increasing age • Approximately 10% of MIs occur before age 40 • Men are at significantly greater risk than women, and women tend to be protected against MI during their reproductive years • However, menopa ...
Phonocardiogram
... Aortic insufficiency (AI), also known as aortic regurgitation (AR), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle Aortic valve stenosis (AS) is a valvular heart disease caused by ...
... Aortic insufficiency (AI), also known as aortic regurgitation (AR), is the leaking of the aortic valve of the heart that causes blood to flow in the reverse direction during ventricular diastole, from the aorta into the left ventricle Aortic valve stenosis (AS) is a valvular heart disease caused by ...
S2006_74.DOC ENDOCARDIAL FIBROELASTOSIS
... both coronary arteries. At the age of 16 years, when we first saw her, she was asymptomatic, and was able to participate in high school activities and athletics without problems. Diagnostic tests: EKG at 24 years age showed a Q wave of 7mm and QR pattern in Lead 1. Echo at 32 years showed normal lef ...
... both coronary arteries. At the age of 16 years, when we first saw her, she was asymptomatic, and was able to participate in high school activities and athletics without problems. Diagnostic tests: EKG at 24 years age showed a Q wave of 7mm and QR pattern in Lead 1. Echo at 32 years showed normal lef ...
DOUBLE SITE LEFT HEART ENDOCARDITIS WITH VENTRICULAR
... The patient underwent, after 3 days of intensive medical and antibiotic therapy (Ampicillin and gentamicin), a double mitral and aortic valve prosthetic replacement associated with the resection of the mural vegetation. Intraoperative findings were concordant with the echographic data. The post oper ...
... The patient underwent, after 3 days of intensive medical and antibiotic therapy (Ampicillin and gentamicin), a double mitral and aortic valve prosthetic replacement associated with the resection of the mural vegetation. Intraoperative findings were concordant with the echographic data. The post oper ...
Eur J Heart Fail
... Doppler E/A ratio (p=0.01) increased in the CHF group, with no changes in left ventricular volumes. The healthy subjects had similar responses, but also displayed an increase in cardiac output (p<0.01) and left ventricular volumes (p<0.001). Exercise. Cardiac output and systolic blood pressure incre ...
... Doppler E/A ratio (p=0.01) increased in the CHF group, with no changes in left ventricular volumes. The healthy subjects had similar responses, but also displayed an increase in cardiac output (p<0.01) and left ventricular volumes (p<0.001). Exercise. Cardiac output and systolic blood pressure incre ...
EKG and blood pressure
... the number of “big boxes” between neighboring QRS complexes, and divide this into 300. The result will be approximately equal to the heart rate ►Although ...
... the number of “big boxes” between neighboring QRS complexes, and divide this into 300. The result will be approximately equal to the heart rate ►Although ...
Diseases of the Conduction System
... Diseases of the conduction system are numerous and varied. The authors have selected a few representative entities for this section: complete heart block as a consequence of primary tumor of the atrioventricular node [47], complete heart block associated with aortic stenosis and surgical replacement ...
... Diseases of the conduction system are numerous and varied. The authors have selected a few representative entities for this section: complete heart block as a consequence of primary tumor of the atrioventricular node [47], complete heart block associated with aortic stenosis and surgical replacement ...
After atrial excitation, impulse travels through the AV node
... volume, and ventricular systole includes both isovolumetric contraction and ventricular ejection. The ventricle does not empty completely during ejection, which is normally half diastole blood volume is pumped out. ...
... volume, and ventricular systole includes both isovolumetric contraction and ventricular ejection. The ventricle does not empty completely during ejection, which is normally half diastole blood volume is pumped out. ...
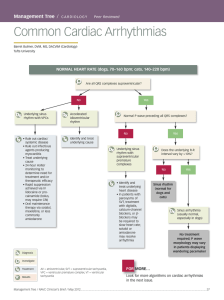
Common Cardiac Arrhythmias
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
... FOR MORE… Look for more algorithms on cardiac arrhythmias in the next issue. ...
Ventricular Assist Devices: - Vanderbilt University Medical Center
... • Utilized for LV support only; not appropriate to use with RV failure • Impella 2.5 can be inserted through the femoral artery during a standard catheterization procedure; provides up to 2.5 L of flow • Impella 5.0 inserted via femoral or axillary artery cut down; provides up to 5L of flow • The ...
... • Utilized for LV support only; not appropriate to use with RV failure • Impella 2.5 can be inserted through the femoral artery during a standard catheterization procedure; provides up to 2.5 L of flow • Impella 5.0 inserted via femoral or axillary artery cut down; provides up to 5L of flow • The ...
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
... They may predispose to bacterial endocarditis. ...
... They may predispose to bacterial endocarditis. ...
Valve Disease – From Bench to Bedside
... Aspirin 75 mg to 100 mg per day is reasonable in all patients with a bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve Anticoagulation with a VKA is reasonable for the first 3 months after bioprosthetic MVR or repair to achieve an INR of 2.5 ...
... Aspirin 75 mg to 100 mg per day is reasonable in all patients with a bioprosthetic aortic or mitral valve Anticoagulation with a VKA is reasonable for the first 3 months after bioprosthetic MVR or repair to achieve an INR of 2.5 ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.