* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EKG and blood pressure
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
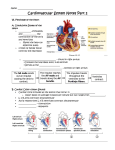
Cardiac Cycle ► The two atria contract at the same time, then they relax while the two ventricles simultaneously contract. ► The contraction phase of the ventricle chambers is called systole. ► The relaxation phase is called diastole. ► At a normal heart rate, one cardiac cycle last for 0.8 seconds! Electrocardiogram? The electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) is a graphic display of the electrical events of the cardiac cycle. Each event has a distinctive waveform, the study of which can lead to greater insight into a patient’s cardiac output. Wave Interpretation ►P Wave = contraction of atria ► PQ Wave = signal arrives at AV node slowing down a bit to allow ventricles to fill with blood ► Q Wave = signal moves to Bundle of His and divides into the bundles and Purkinje fibers ► R Wave = contraction of left ventricle ► S Wave = contraction of right ventricle ► T Wave = ventricles relaxing Rule of 300 (300 / 6) = 50 bpm ►Take the number of “big boxes” between neighboring QRS complexes, and divide this into 300. The result will be approximately equal to the heart rate ►Although rhythms. fast, this method only works for regular What is the heart rate? (300 / 1.5) = 200 bpm 10 Second Rule ►As most EKGs record 10 seconds of rhythm per page, one can simply count the number of beats present on the EKG and multiply by 6 to get the number of beats per 60 seconds. ►This method works well for irregular rhythms. What is the heart rate? 33 x 6 = 198 bpm Pulse “Heart Rate” ►Pulse Pressure wave of blood ►Monitored at “pressure points” in arteries where pulse is easily found ►Pulse averages 70–80 beats per minute at rest Blood Pressure ►Measurements by health professionals are made on the pressure in large arteries Systolic—pressure at the peak of ventricular contraction Diastolic—pressure when ventricles relax Write systolic pressure first and diastolic last (120/80 mm Hg) ►Pressure in blood vessels decreases as distance from the heart increases Measuring Arterial Blood Pressure Measuring Arterial Blood Pressure