Apical Heart View - University of Florida
... look Answer at is the apicallyCorrect located tricuspid valve on the Answer interventricular septum when compared to 1 valve. This will allow you to the mitral determine which is RV and which is LV ...
... look Answer at is the apicallyCorrect located tricuspid valve on the Answer interventricular septum when compared to 1 valve. This will allow you to the mitral determine which is RV and which is LV ...
FACT SHEET Facts About Sudden Cardiac Arrest Overview Sudden
... An estimated 92 percent of all people who suffer SCA die before reaching the hospital. 1 Defibrillation is the only definitive treatment for SCA, and survival decreases 7-10 percent for every minute without it.4 SCA victims range from young children to the elderly. The average response time to an em ...
... An estimated 92 percent of all people who suffer SCA die before reaching the hospital. 1 Defibrillation is the only definitive treatment for SCA, and survival decreases 7-10 percent for every minute without it.4 SCA victims range from young children to the elderly. The average response time to an em ...
Lecture 10. The mostly spread congenital heart diseases in children
... • Such circuitous route of blood causes volume overload on the LV. • The LV normally has a much higher systolic pressure (~100 mm Hg) than the RV (~85 mm Hg) and through VSD blood leaks into the RV and elevates RV pressure and volume, causing Pulm HTN. • These changes lead to elevated RV & pulmonary ...
... • Such circuitous route of blood causes volume overload on the LV. • The LV normally has a much higher systolic pressure (~100 mm Hg) than the RV (~85 mm Hg) and through VSD blood leaks into the RV and elevates RV pressure and volume, causing Pulm HTN. • These changes lead to elevated RV & pulmonary ...
Ch16 Summary
... pacemaker of the heart; it initiates impulses at the rate of 60 to 100 per minute. The A-V node is the back-up pacemaker of the heart; it initiates impulses if the S-A node fails to deliver an impulse. Normally, the cardiac impulse initiates in the S-A node, which travels to the A-V node, down the r ...
... pacemaker of the heart; it initiates impulses at the rate of 60 to 100 per minute. The A-V node is the back-up pacemaker of the heart; it initiates impulses if the S-A node fails to deliver an impulse. Normally, the cardiac impulse initiates in the S-A node, which travels to the A-V node, down the r ...
The Human Heart
... On the main floor are the two largest rooms—the left and right ventricles. The ventricles are the main pumping chambers of the heart. In a healthy heart, the left ventricle is the stronger pumping chamber where the internal pressures exceed those within the right ventricle. The wall separating the t ...
... On the main floor are the two largest rooms—the left and right ventricles. The ventricles are the main pumping chambers of the heart. In a healthy heart, the left ventricle is the stronger pumping chamber where the internal pressures exceed those within the right ventricle. The wall separating the t ...
Congenital Anomalies of the heart
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
medicare expands coverage of cardic rehab to chf
... • Decrease cardiac events In February, 2014 the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have expanded coverage of cardiac rehabilitation services to chronic heart failure patients. Patient Criteria Stable, chronic heart failure patients who can receive Medicare coverage are defined as patie ...
... • Decrease cardiac events In February, 2014 the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have expanded coverage of cardiac rehabilitation services to chronic heart failure patients. Patient Criteria Stable, chronic heart failure patients who can receive Medicare coverage are defined as patie ...
Heart failure Ventricular insufficiency Left heart failure (LHF
... ⇒ ALD ⇒ ↑ reabsorption of Na+ and H2O ⇒ Secondary hyperaldosteronism – ADH ⇒ vasoconstriction and resorption of H2O ...
... ⇒ ALD ⇒ ↑ reabsorption of Na+ and H2O ⇒ Secondary hyperaldosteronism – ADH ⇒ vasoconstriction and resorption of H2O ...
CVS Physiology
... 2. Cardiac muscle: decrease myocardial contractility by reduction of calcium fluxes across the cardiac cell ...
... 2. Cardiac muscle: decrease myocardial contractility by reduction of calcium fluxes across the cardiac cell ...
Heart and work Cardiac reserve - Energy Energy Force and pressure
... • Dilated cardiomyopathy involves enlargement of the heart muscle and is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. The heart muscle is weakened and cannot pump blood efficiently. Decreased heart function affects the lungs, liver, and other body systems. ...
... • Dilated cardiomyopathy involves enlargement of the heart muscle and is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. The heart muscle is weakened and cannot pump blood efficiently. Decreased heart function affects the lungs, liver, and other body systems. ...
Practical Approach to Anesthesia for Parturient with Cardiac Disease
... regurgitation, pulmonary artery pressure continues to increase and right heart failure occurs. ...
... regurgitation, pulmonary artery pressure continues to increase and right heart failure occurs. ...
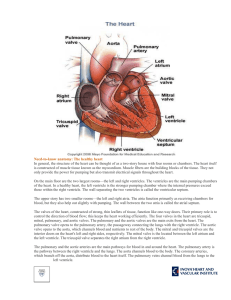
The Heart
... R.&L. bundle branches In interventricular septum Impulses transmit to myoconduction fibers Conduction myofibers (Pukinje fibers) • In ventricular walls • Impulses transmit to ventricular walls ...
... R.&L. bundle branches In interventricular septum Impulses transmit to myoconduction fibers Conduction myofibers (Pukinje fibers) • In ventricular walls • Impulses transmit to ventricular walls ...
Cardiac Cycle (PPT#4)
... ► R Wave = contraction of left ventricle ► S Wave = contraction of right ventricle ► T Wave = ventricles relaxing ...
... ► R Wave = contraction of left ventricle ► S Wave = contraction of right ventricle ► T Wave = ventricles relaxing ...
Review of Congenital Heart Disease
... mitral valve function. Most feline patients will have systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve which causes a left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. If the obstruction is moderate to severe, secondary left ventricular hypertrophy will develop. Patients with MVD have a variable amount of mit ...
... mitral valve function. Most feline patients will have systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve which causes a left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. If the obstruction is moderate to severe, secondary left ventricular hypertrophy will develop. Patients with MVD have a variable amount of mit ...
Rheumatic heart disease
... valvular structure will subsequently lead to Libman-Sacks vegetations, valve thickening, and valve regurgitation. Valvular stenosis is rarely seen. Involvement of the mitral valve is most frequently encountered. Valve disease for most patients is mild and asymptomatic, but patients in whom severe mi ...
... valvular structure will subsequently lead to Libman-Sacks vegetations, valve thickening, and valve regurgitation. Valvular stenosis is rarely seen. Involvement of the mitral valve is most frequently encountered. Valve disease for most patients is mild and asymptomatic, but patients in whom severe mi ...
CARDIOMYOPATHIES
... No specific laboratory blood tests are required in the workup. Genetic testing is not yet widely available but is becoming increasingly so. • Two-dimensional (2-D) echocardiography is diagnostic for HCM. Findings may be summarized as follows: • Abnormal systolic anterior leaflet motion of the mitral ...
... No specific laboratory blood tests are required in the workup. Genetic testing is not yet widely available but is becoming increasingly so. • Two-dimensional (2-D) echocardiography is diagnostic for HCM. Findings may be summarized as follows: • Abnormal systolic anterior leaflet motion of the mitral ...
Two Cardiology Zebras - Iowa Heart Foundation
... Absence of CAD • The majority of patients survive this problem • The only autopsy report is that of a patient who died of multiple organs system failure who also developed Takotsubo’s Syndrome. – The patient had no macroscopic signs of recent myocardial infarction or scars. ...
... Absence of CAD • The majority of patients survive this problem • The only autopsy report is that of a patient who died of multiple organs system failure who also developed Takotsubo’s Syndrome. – The patient had no macroscopic signs of recent myocardial infarction or scars. ...
Genetic Testing for Hereditary Cardiomyopathy
... (LVH) in the absence of predisposing cardiac or systemic diseases. The clinical features of HCM vary for each individual and range from asymptomatic to progressive heart failure to sudden cardiac death. Common symptoms include dyspnea on exertion, palpitations, chest pain, orthostatic hypotension, p ...
... (LVH) in the absence of predisposing cardiac or systemic diseases. The clinical features of HCM vary for each individual and range from asymptomatic to progressive heart failure to sudden cardiac death. Common symptoms include dyspnea on exertion, palpitations, chest pain, orthostatic hypotension, p ...
Heart Disease in cats
... The tests undertaken will help to establish the severity of an individual cat’s heart disease. In many cases no treatment will be needed, but monitoring will continue. In other cases a single medication, or combination of medications may be used. As with most illnesses, early detection and treatment ...
... The tests undertaken will help to establish the severity of an individual cat’s heart disease. In many cases no treatment will be needed, but monitoring will continue. In other cases a single medication, or combination of medications may be used. As with most illnesses, early detection and treatment ...
Heart Failure and Cardiomyopathy
... includes patients with structural heart disease (i.e., previous myocardial infarction [MI], asymptomatic valvular disease, and LV hypertrophy) but without symptoms of HF. Stage C HF is structural heart disease with prior or current symptoms of HF. Stage D HF is refractory or end-stage HF. HF should ...
... includes patients with structural heart disease (i.e., previous myocardial infarction [MI], asymptomatic valvular disease, and LV hypertrophy) but without symptoms of HF. Stage C HF is structural heart disease with prior or current symptoms of HF. Stage D HF is refractory or end-stage HF. HF should ...
pdf Sudden Cardiac Arrest Fact Sheet
... An estimated 92 percent of all people who suffer SCA die before reaching the hospital. 1 Defibrillation is the only definitive treatment for SCA, and survival decreases 7-10 percent for every minute without it.4 SCA victims range from young children to the elderly. The average response time ...
... An estimated 92 percent of all people who suffer SCA die before reaching the hospital. 1 Defibrillation is the only definitive treatment for SCA, and survival decreases 7-10 percent for every minute without it.4 SCA victims range from young children to the elderly. The average response time ...
Congenital Anomalies of the heart
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
... The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.