* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congenital Anomalies of the heart
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
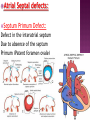
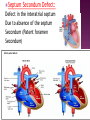
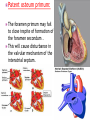
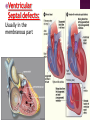
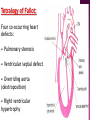
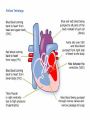
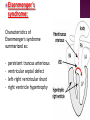
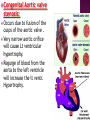
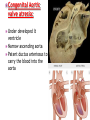
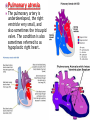
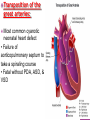
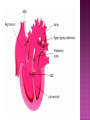
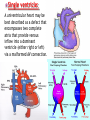
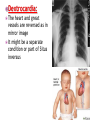
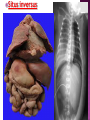
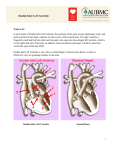
DR RANIA GABR Discuss the congenital anomalies related to the heart development. Congenital volume load Heart Defect Acyanotic pressure load Cyanotic ↑ pulmonary flow ↓ pulmonary flow left-to-right shunts obstr. ventric. outflow • atrial septal defect • pulmonary valve stenosis transpos. of gr. Vessels tetralogy of Fallot • ventricular septal defect aortic valve stenosis single ventricle pulmonary atresia • AV canal coarctation of aorta truncus arteriosus tricuspid atresia • patent ductus arteriosus total anomalous pulm. total anomalous pulm. return w/o obstruction return w/ obstruction Atrial Septal defects: Septum Primum Defect: Defect in the interatrial septum Due to absence of the septum Primum (Patent foramen ovale) Septum Secondum Defect: Defect in the interatrial septum Due to absence of the septum Secondum (Patent foramen Secondum) Complete absence of the interatrial septum (Core Triloculare Biventriculare): There is complete absence of both septum primum and septum secondum. i.e. there is a common atrium. Patent The osteum primum: foramen primum may fail to close inspite of formation of the foramen secondum . This will cause disturbance in the valvular mechanism of the interatrial septum. Patent foramen ovale: Mentioned before Premature closure of foramen ovale: Rarely , it is closed BEFORE birth. It results in marked enlargement of the Right atrium and ventricle. Persistent atrioventricular canal: The A-V cusions and the septum intermedium fail to develop. The A-V canal remains divided into rt and lt parts. There is usually: 1- Patent foramen primum 2- IV sepltal defect 3- Abnormalities in the leaflets of the valves guarding the A-V canal. Ventricular Septal defects: Usually in the membranous part Tetralogy of Fallot: Four co-occurring heart defects: • Pulmonary stenosis • Ventricular septal defect • Overriding aorta (dextroposition) • Right ventricular hypertrophy Eisenmenger's syndrome: Characteristics of Eisenmenger's syndrome summarized as: • • • • persistent truncus arteriosus ventricular septal defect left-right ventricular shunt right ventricle hypertrophy Congenital Aortic valve stenosis: Occurs due to fusion of the cusps of the aortic valve . Very narrow aortic orifice will cause Lt ventricular hypertrophy. Regurge of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle will increase the lt ventr. Hypertrophy. Congenital Aortic valve atresia: Under developed lt ventricle Narrow ascending aorta Patent ductus arteriosus to carry the blood into the aorta Pulmonary atresia The pulmonary artery is underdeveloped, the right ventricle very small, and also sometimes the tricuspid valve. The condition is also sometimes referred to as hypoplastic right heart. Transposition of the great arteries: Most common cyanotic neonatal heart defect • Failure of aorticopulmonary septum to take a spiraling course • Fatal without PDA, ASD, & VSD Single ventricle: A univentricular heart may be best described as a defect that encompasses two complete atria that provide venous inflow into a dominant ventricle (either right or left) via a malformed AV connection. Ectopia The Cordis: heart is bulging outside the chest due to wide separation in the 2 parts of the sternum Dextrocardia: The heart and great vessels are reversed as in mirror image It might be a separate condition or part of Situs inversus Situs inversus