The Olfactory–Limbic System and Multiple Chemical
... There are numerous examples of olfactory adaptation, for an example when you enter a restaurant you immediately perceive the aromas of the foods being cooked, but soon afterwards you become unaware of them. Two classic examples of olfactory adaptation, which pertain to MCS, occur with the use of pe ...
... There are numerous examples of olfactory adaptation, for an example when you enter a restaurant you immediately perceive the aromas of the foods being cooked, but soon afterwards you become unaware of them. Two classic examples of olfactory adaptation, which pertain to MCS, occur with the use of pe ...
Galanin-like peptide: a key player in the homeostatic regulation of
... in neurons in the ARC,36 with orexin-1 receptor immunoreactivity also being observed in a few GALP-positive neurons.38 We have previously reported that 3–12% of GALP-positive cells contain a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-like immunoreactivity.36 In spite of these findings, there are no other neurop ...
... in neurons in the ARC,36 with orexin-1 receptor immunoreactivity also being observed in a few GALP-positive neurons.38 We have previously reported that 3–12% of GALP-positive cells contain a-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-like immunoreactivity.36 In spite of these findings, there are no other neurop ...
Ethanol Facilitates Glutamatergic Transmission to Dopamine
... The cellular mechanisms underlying alcohol addiction are poorly understood. In several brain areas, ethanol depresses glutamatergic excitatory transmission, but how it affects excitatory synapses on dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a crucial site for the development of drug addi ...
... The cellular mechanisms underlying alcohol addiction are poorly understood. In several brain areas, ethanol depresses glutamatergic excitatory transmission, but how it affects excitatory synapses on dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a crucial site for the development of drug addi ...
Olfactory Learning in Drosophila: Learning from Models
... stimulus (US), e.g., electric shock, is paired with a conditioned stimulus (CS), e.g., an odor. Presenting the conditioned stimulus alone tests the associative strength. The timing between the two is characterized by the inter stimulus interval (ISI), which we define from onset of the shock to onset ...
... stimulus (US), e.g., electric shock, is paired with a conditioned stimulus (CS), e.g., an odor. Presenting the conditioned stimulus alone tests the associative strength. The timing between the two is characterized by the inter stimulus interval (ISI), which we define from onset of the shock to onset ...
The multifunctional lateral geniculate nucleus
... the LGN that is often promoted as the prototype dorsal thalamic nucleus (e.g. Sherman and Guillery, 2004). The LGN is that thalamic structure that receives from the retina and projects to visual cortex. Because the LGN neurons projecting to cortex are also retinal-recipient, because the retina drive ...
... the LGN that is often promoted as the prototype dorsal thalamic nucleus (e.g. Sherman and Guillery, 2004). The LGN is that thalamic structure that receives from the retina and projects to visual cortex. Because the LGN neurons projecting to cortex are also retinal-recipient, because the retina drive ...
Contents
... that the anatomical subdivisions will also provide a key to as yet unrecognized functional areas. That ‘cytoarchitectural differences reflect functional differences’ is a principle accepted now by every neuroanatomist: a cytoarchitectural difference in any nucleus is taken to reflect a functional di ...
... that the anatomical subdivisions will also provide a key to as yet unrecognized functional areas. That ‘cytoarchitectural differences reflect functional differences’ is a principle accepted now by every neuroanatomist: a cytoarchitectural difference in any nucleus is taken to reflect a functional di ...
table of contents
... Contrary to peripheral fatigue, central fatigue is derived from central factors such as motivation, central nervous system transmission, and motor unit recruitment and occurs proximal to the neuromuscular junction (14). The central fatigue model suggests that the decline in muscle tension or force p ...
... Contrary to peripheral fatigue, central fatigue is derived from central factors such as motivation, central nervous system transmission, and motor unit recruitment and occurs proximal to the neuromuscular junction (14). The central fatigue model suggests that the decline in muscle tension or force p ...
1 - BrainMaster
... only be the primary source for neuroscientists interested in the initial discoveries in adult neurogenesis and how they came about, but should also be of value to those interested in science history, funding, and policy. Novel methods for labeling new neurons – new thymidine analogs such as BrdU, i ...
... only be the primary source for neuroscientists interested in the initial discoveries in adult neurogenesis and how they came about, but should also be of value to those interested in science history, funding, and policy. Novel methods for labeling new neurons – new thymidine analogs such as BrdU, i ...
Structure and Function of the Brain Serotonin System
... and caudal to the SCD (Fig. 2). The group has a rostrocaudal oblique orientation (34,305), and the paramedian columns are separated by as much as 400 pm in cats and monkeys. Rostrally, the cells from this group end around and within the caudal and lateral aspects of the interpeduncular nucleus. Caud ...
... and caudal to the SCD (Fig. 2). The group has a rostrocaudal oblique orientation (34,305), and the paramedian columns are separated by as much as 400 pm in cats and monkeys. Rostrally, the cells from this group end around and within the caudal and lateral aspects of the interpeduncular nucleus. Caud ...
Topographically Specific Hippocampal Projections Target Functionally Distinct Prefrontal Areas in the
... CA1’ and CA1 fields rostrally, but originated in the subicular fields caudally. In contrast, labeled neurons which innervated orbital cortices were considerably more focal, emanating from the same relative position within a field throughout the rostrocaudal extent of the hippocampal formation. In ma ...
... CA1’ and CA1 fields rostrally, but originated in the subicular fields caudally. In contrast, labeled neurons which innervated orbital cortices were considerably more focal, emanating from the same relative position within a field throughout the rostrocaudal extent of the hippocampal formation. In ma ...
Learned Movements Elicited by Direct Stimulation of Cerebellar
... antidromic activation of mossy fibers, we blocked the mossy fiber transmission ventral to the stimulation electrode in two animals. If the CS information is transmitted via the mossy fibers, this should abolish responses to the forelimb CS but leave responses to MCP stimulation unaffected. A micropi ...
... antidromic activation of mossy fibers, we blocked the mossy fiber transmission ventral to the stimulation electrode in two animals. If the CS information is transmitted via the mossy fibers, this should abolish responses to the forelimb CS but leave responses to MCP stimulation unaffected. A micropi ...
Chapter 9 The Nervous System
... than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a nerve impulse (action potential) – The stimulated section of membrane immediately repolarizes, but by that time the depolarization has already triggered the next section of membrane to depolarize, thus propagating a wave of electrica ...
... than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a nerve impulse (action potential) – The stimulated section of membrane immediately repolarizes, but by that time the depolarization has already triggered the next section of membrane to depolarize, thus propagating a wave of electrica ...
Chapter 9 The Nervous System
... than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a nerve impulse (action potential) – The stimulated section of membrane immediately repolarizes, but by that time the depolarization has already triggered the next section of membrane to depolarize, thus propagating a wave of electrica ...
... than the outside at the stimulated point; this depolarization is a nerve impulse (action potential) – The stimulated section of membrane immediately repolarizes, but by that time the depolarization has already triggered the next section of membrane to depolarize, thus propagating a wave of electrica ...
The Role of the Terminal Nerve and GnRH in Olfactory System
... external environments, which is accomplished in part via centrifugal modulatory pathways. In the olfactory sensory system, responsiveness is regulated by neuromodulators released from centrifugal fibers into the olfactory epithelium and bulb. Among the modulators known to modulate neural activity of ...
... external environments, which is accomplished in part via centrifugal modulatory pathways. In the olfactory sensory system, responsiveness is regulated by neuromodulators released from centrifugal fibers into the olfactory epithelium and bulb. Among the modulators known to modulate neural activity of ...
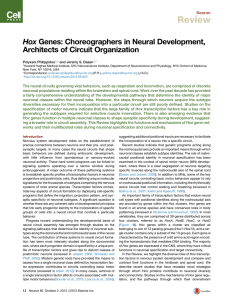
Hox Genes: Choreographers in Neural Development, Architects of
... generating the subtypes required for selective muscle innervation. There is also emerging evidence that Hox genes function in multiple neuronal classes to shape synaptic specificity during development, suggesting a broader role in circuit assembly. This Review highlights the functions and mechanisms ...
... generating the subtypes required for selective muscle innervation. There is also emerging evidence that Hox genes function in multiple neuronal classes to shape synaptic specificity during development, suggesting a broader role in circuit assembly. This Review highlights the functions and mechanisms ...
For Peer Review - diss.fu
... basal ganglia. The LHb is implicated in various biological functions, such as reward, sleepwake cycle, feeding, pain processing and memory formation. The modulatory role of the LHb is partly assumed by putative spontaneously active LHb neurons projecting to the ...
... basal ganglia. The LHb is implicated in various biological functions, such as reward, sleepwake cycle, feeding, pain processing and memory formation. The modulatory role of the LHb is partly assumed by putative spontaneously active LHb neurons projecting to the ...
Examination of Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH)
... is also present in the cerebral cortex with relatively low activity, but in humans, D1 is absent from the CNS [21, 22]. The main source of extra-thyroidal T3 is type 2 deiodinase (D2) that converts T4 to T3 by 5’-monodeiodination of the outer ring of the molecule [14, 18]. In addition to regulating ...
... is also present in the cerebral cortex with relatively low activity, but in humans, D1 is absent from the CNS [21, 22]. The main source of extra-thyroidal T3 is type 2 deiodinase (D2) that converts T4 to T3 by 5’-monodeiodination of the outer ring of the molecule [14, 18]. In addition to regulating ...
... Neuronal cell death programmes are counteracted by survival signals during development in order to maintain the tissue homeostasis. Neuronal differentiation is a mechanism generating functionally integrated neuronal cells from their progenitors. These processes appear to be mediated via activation o ...
Projections from the brain to the spinal cord in the mouse Huazheng
... identified at 10× magnification. Each labeled cell was marked by a dot on the drawing. Labeled cells were identified on the basis that they contained a nucleus. In many cases a nucleolus was seen, but no attempt was make to ensure that each counted cell contained a nucleolus. For this reason, the co ...
... identified at 10× magnification. Each labeled cell was marked by a dot on the drawing. Labeled cells were identified on the basis that they contained a nucleus. In many cases a nucleolus was seen, but no attempt was make to ensure that each counted cell contained a nucleolus. For this reason, the co ...
the human entorhinal cortex
... calcium-binding protein immunohistochemistry (e.g., parvalbumin, calretinin, and calbindin D28k, hereafter referred to as calbindin) and lucifer yellow microinjections. Moreover, the changes in the entorhinal neuronal populations containing the three calcium-binding proteins are described for AD. Th ...
... calcium-binding protein immunohistochemistry (e.g., parvalbumin, calretinin, and calbindin D28k, hereafter referred to as calbindin) and lucifer yellow microinjections. Moreover, the changes in the entorhinal neuronal populations containing the three calcium-binding proteins are described for AD. Th ...
Coincidence Detection or Temporal Integration?
... In cats, SII cortex receives direct projections from the ventrobasal complex (Spreafico et al., 1981; Burton and Kopf, 1984). We recorded neurons in SII cortex instead of primary somatosensory (SI) cortex because receptive fields in SII cortex are larger, and this increased the probability of encoun ...
... In cats, SII cortex receives direct projections from the ventrobasal complex (Spreafico et al., 1981; Burton and Kopf, 1984). We recorded neurons in SII cortex instead of primary somatosensory (SI) cortex because receptive fields in SII cortex are larger, and this increased the probability of encoun ...
Plasticity of Binocularity and Visual Acuity Are Differentially Limited
... blocking solution of 3% normal horse serum (Vector Laboratories S-2000) in TBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 (TBS-T; Sigma-Aldrich T9284) for 1 h at room temperature. The primary antibodies goat antiNogo Receptor (R&D Systems; AF1440), mouse anti-PV (Sigma; P3088), and sheep anti- PV (R&D Systems; AF ...
... blocking solution of 3% normal horse serum (Vector Laboratories S-2000) in TBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 (TBS-T; Sigma-Aldrich T9284) for 1 h at room temperature. The primary antibodies goat antiNogo Receptor (R&D Systems; AF1440), mouse anti-PV (Sigma; P3088), and sheep anti- PV (R&D Systems; AF ...
Review Getting Formal with Dopamine and Reward
... [this issue of Neuron]) . The structures included the dopamine system, as many of the stimulation sites were in close proximity to axons of dopamine neurons or to axons presynaptic to them (Wise, 1996a). Finally, major drugs of abuse influence dopamine neurotransmission (Wise and Hoffman, 1992; Wise ...
... [this issue of Neuron]) . The structures included the dopamine system, as many of the stimulation sites were in close proximity to axons of dopamine neurons or to axons presynaptic to them (Wise, 1996a). Finally, major drugs of abuse influence dopamine neurotransmission (Wise and Hoffman, 1992; Wise ...
Decreased cohesin in the brain leads to defective synapse
... In Drosophila melanogaster, Nipped-B, which is required to load cohesin onto DNA, mediates long-range activation of the homeobox genes cut and ultrabithorax (Rollins et al., 1999). Previous studies have indicated that cohesin functions in axon pruning of the Drosophila mushroom-body γ neurons. Its d ...
... In Drosophila melanogaster, Nipped-B, which is required to load cohesin onto DNA, mediates long-range activation of the homeobox genes cut and ultrabithorax (Rollins et al., 1999). Previous studies have indicated that cohesin functions in axon pruning of the Drosophila mushroom-body γ neurons. Its d ...
Peripheral Nerve Segment Defect Repair
... -Provide insulation by the envelopment of the nerve with lipid-rich myelin sheath. -Potentiate conduction ...
... -Provide insulation by the envelopment of the nerve with lipid-rich myelin sheath. -Potentiate conduction ...