the koniocellular pathway in primate vision
... and well understood. In studies conducted by Casagrande and her colleagues, the aggregation of K cells into two wide layers was exploited to determine the connectional and physiological properties of these neurons (Casagrande & DeBruyn 1982, Casagrande 1994). As is described below, much of this work ...
... and well understood. In studies conducted by Casagrande and her colleagues, the aggregation of K cells into two wide layers was exploited to determine the connectional and physiological properties of these neurons (Casagrande & DeBruyn 1982, Casagrande 1994). As is described below, much of this work ...
Anatomy - Nervous System Test Chpt 9
... 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in its environment? a. a threshold b. an action potential c. a nerve signal d. a dendrite 4. Sense organs are part of ...
... 2. What is the smallest structural and functional unit of the nervous system? a. nerve b. neuron c. brain d. spinal cord 3. What begins when a neuron is stimulated by another neuron in its environment? a. a threshold b. an action potential c. a nerve signal d. a dendrite 4. Sense organs are part of ...
The Living World - Chapter 28 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Nerve impulses jump from node to node Multiple sclerosis and Tay-Sachs disease result from degeneration of the myelin sheath Copyright ©The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
DEPARTAMENTO DE CIÊNCIAS DA VIDA
... identified glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), heat shock protein 40 (Hsp40) and Rhoassociated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (RockII) as signals increased after a dorsal root injury that may act as potential regeneration inhibitors. Both GSK3β and RockII were already described in the ...
... identified glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), heat shock protein 40 (Hsp40) and Rhoassociated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase 2 (RockII) as signals increased after a dorsal root injury that may act as potential regeneration inhibitors. Both GSK3β and RockII were already described in the ...
Segundo trabajo
... Animal handling procedures were approved by the Local Committee (99/1 University of Barcelona) and the Generalitat de Catalunya (1094/99), in accordance with the Directive 86/609/EU of the European Commission. Certified time-pregnant Sprague–Dawley dams (Charles River Laboratories, France) were deep ...
... Animal handling procedures were approved by the Local Committee (99/1 University of Barcelona) and the Generalitat de Catalunya (1094/99), in accordance with the Directive 86/609/EU of the European Commission. Certified time-pregnant Sprague–Dawley dams (Charles River Laboratories, France) were deep ...
Poly(A) Binding Protein Nuclear 1 regulates the
... Pabpn1 knock down interferes with homeostatic plasticity Given the above regulation of both Camk2a and Gria2, we next determined whether Pabpn1 and polyadenylation play a role in homeostatic plasticity. We elicited homeostatic plasticity using a 24 hours treatment of bicuculline a gammaaminobutyric ...
... Pabpn1 knock down interferes with homeostatic plasticity Given the above regulation of both Camk2a and Gria2, we next determined whether Pabpn1 and polyadenylation play a role in homeostatic plasticity. We elicited homeostatic plasticity using a 24 hours treatment of bicuculline a gammaaminobutyric ...
Biomimetic approaches to the control of underwater walking machines
... central pattern generator (CPG) model of the organization of innate motor systems (Kennedy & Davis 1977; Pearson 1993). The basis of this model is that the locomotory movements of different limbs are controlled by segmental CPGs resident in the spinal cord or ganglionic chain (Sillar et al. 1986; Se ...
... central pattern generator (CPG) model of the organization of innate motor systems (Kennedy & Davis 1977; Pearson 1993). The basis of this model is that the locomotory movements of different limbs are controlled by segmental CPGs resident in the spinal cord or ganglionic chain (Sillar et al. 1986; Se ...
17. Pathways and Integrative Functions
... The CNS communicates with peripheral body structures through pathways. These pathways conduct either sensory or motor information; processing and integration occur continuously along them. These pathways travel through the white matter of the brainstem and/or spinal cord as they connect various CNS ...
... The CNS communicates with peripheral body structures through pathways. These pathways conduct either sensory or motor information; processing and integration occur continuously along them. These pathways travel through the white matter of the brainstem and/or spinal cord as they connect various CNS ...
Review Early Steps in the Development of the Forebrain
... this region of our CNS that confers many uniquely human attributes. Despite this, the general organization of the forebrain is conserved in all vertebrates. What makes the brain of each species unique is not the initial presence or absence of different subdomains of the CNS; rather, it is the extent ...
... this region of our CNS that confers many uniquely human attributes. Despite this, the general organization of the forebrain is conserved in all vertebrates. What makes the brain of each species unique is not the initial presence or absence of different subdomains of the CNS; rather, it is the extent ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
The Peripheral Nervous System
... • Although the somatic nervous system is generally under conscious control, some actions of the system occur automatically. • For example, if you accidentally step on a tack with your bare foot, your leg may recoil before you are even aware of the pain. • This rapid response (a reflex) is caused by ...
... • Although the somatic nervous system is generally under conscious control, some actions of the system occur automatically. • For example, if you accidentally step on a tack with your bare foot, your leg may recoil before you are even aware of the pain. • This rapid response (a reflex) is caused by ...
Layer-Specific Markers as Probes for Neuron Type Identity in
... across cortical areas (30, 31, 40, 42) and developmental stages (22, 26, 33). Finally, some layer-specific markers can be actively regulated in response to neural activity (51). All of these factors must be carefully controlled when molecular markers are used as probes for laminar identity. In human ...
... across cortical areas (30, 31, 40, 42) and developmental stages (22, 26, 33). Finally, some layer-specific markers can be actively regulated in response to neural activity (51). All of these factors must be carefully controlled when molecular markers are used as probes for laminar identity. In human ...
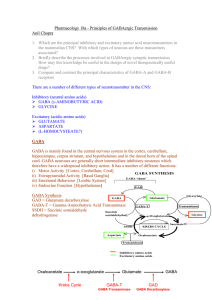
Pharmacology 18a – Priciples of GABAergic Transmission
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
... GABA is stored in vesicles in nerve terminals (like any other neurotransmitter) and is released by exocytosis upon influx of calcium ions. GABA Receptors There are 2 types of GABA receptor: GABAA Generally POSTsynaptic When activated by GABA cause influx of Cl- ions This causes the cell to hyp ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
... in particular, in orbital frontal cortex (OFC). For example, imaging studies in human stimulant users have found persistent basal and drug-induced changes in metabolic activity (Volkow et al., 1992; Paulus et al., 2002; Adinoff et al., 2003; Bolla et al., 2003), DA receptor levels (Volkow et al., 19 ...
Molecular and morphological analyses of basal forebrain
... can be distinguished by their molecular and morphological characteristics. These phenotypic traits are established by specific gene expression profiles which direct the differentiation and maturation of individual neuronal subclasses. For example, basal forebrain cholinergic neurons can be distingui ...
... can be distinguished by their molecular and morphological characteristics. These phenotypic traits are established by specific gene expression profiles which direct the differentiation and maturation of individual neuronal subclasses. For example, basal forebrain cholinergic neurons can be distingui ...
the medial division of the medial geniculate body of the cat
... body of the cat with the Golgi methods. The results show that the medial division consists of morphologically heterogeneous neurons. The main types, in descending order of frequency, are medium-sized neurons with (1) radiate, (2) tufted, or (3) elongate dendrites; (4) small stellate or radiate neuro ...
... body of the cat with the Golgi methods. The results show that the medial division consists of morphologically heterogeneous neurons. The main types, in descending order of frequency, are medium-sized neurons with (1) radiate, (2) tufted, or (3) elongate dendrites; (4) small stellate or radiate neuro ...
Temporal fate specification and neural progenitor competence
... (FIG. 1b). Hb is necessary and sufficient to specify the earliest-born neural identity in multiple neuroblast lineages, including NB7‑1, NB7‑3 and NB3‑1 (REFS 5,7,10,12–15). Although the specific characteristics of the first-born progeny differ between neuroblast lineages, in each case cells specifi ...
... (FIG. 1b). Hb is necessary and sufficient to specify the earliest-born neural identity in multiple neuroblast lineages, including NB7‑1, NB7‑3 and NB3‑1 (REFS 5,7,10,12–15). Although the specific characteristics of the first-born progeny differ between neuroblast lineages, in each case cells specifi ...
Neutrophil Contribution in Facilitating Optic Nerve Regeneration
... interact to sustain the prolonged regenerative response induced by inflammation? For example, the numbers of regenerating axons were significantly higher 2 weeks after inflammation-induced regeneration, despite the greatly reduced number of neutrophils in the eye after 3 d (Kurimoto et al., 2013). I ...
... interact to sustain the prolonged regenerative response induced by inflammation? For example, the numbers of regenerating axons were significantly higher 2 weeks after inflammation-induced regeneration, despite the greatly reduced number of neutrophils in the eye after 3 d (Kurimoto et al., 2013). I ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
... Interneurons are organized into functional groups of interconnected neurons called neuronal pools, each with a limited number of input sources and output destinations. An entire neuronal pool may stimulate or depress activity in other parts of the brain or spinal cord. ...
... Interneurons are organized into functional groups of interconnected neurons called neuronal pools, each with a limited number of input sources and output destinations. An entire neuronal pool may stimulate or depress activity in other parts of the brain or spinal cord. ...
Pyramidal (Voluntary Motor) System
... The corticobulbar tract originates from lamina V large pyramidal neurons in the head region of the motor cortex (ventrolateral precentral gyrus), and descends into the brainstem, projecting bilaterally (ie. crossed and uncrossed) to all cranial nerve motor nuclei. ...
... The corticobulbar tract originates from lamina V large pyramidal neurons in the head region of the motor cortex (ventrolateral precentral gyrus), and descends into the brainstem, projecting bilaterally (ie. crossed and uncrossed) to all cranial nerve motor nuclei. ...
The Role of Spasticity in Functional Neurorehabilitation
... human and quadruped animal, having been observed during at rest and functional tests [2]. Several experiments have shown that the muscle spasms indicate an increase in motoneural firing rate, causing a strong muscle contraction [21]. The enhancement in motoneuronal excitability is attributed to chan ...
... human and quadruped animal, having been observed during at rest and functional tests [2]. Several experiments have shown that the muscle spasms indicate an increase in motoneural firing rate, causing a strong muscle contraction [21]. The enhancement in motoneuronal excitability is attributed to chan ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal in response to an action potential into the synapse – The molecules diffuse across the synapse – NT molecules interact with receptors to alter the potential of the ...
... • The synapse is the junction between an axon terminal and an adjacent dendrite • Neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal in response to an action potential into the synapse – The molecules diffuse across the synapse – NT molecules interact with receptors to alter the potential of the ...
AP150 PATHWAYS ASSIGNMENT
... An action potential begins on a ____________________________ neurons that leaves the __________________ lobe of the brain and passes through the _________________ of the midbrain and then the ___________________ of the medulla oblongata where it then decussates and travels down a ___________________ ...
... An action potential begins on a ____________________________ neurons that leaves the __________________ lobe of the brain and passes through the _________________ of the midbrain and then the ___________________ of the medulla oblongata where it then decussates and travels down a ___________________ ...
Electrophysiological Identification of Tonic and Phasic Neurons in
... and melittin inflammation treatments significantly decreased rheobase and AP durations (depolarization and repolarization), enhanced amplitudes of overshoot and afterhyperpolarization (AHP) and increased the number of action potential firings. In phasic neurons, however, the same treatments caused l ...
... and melittin inflammation treatments significantly decreased rheobase and AP durations (depolarization and repolarization), enhanced amplitudes of overshoot and afterhyperpolarization (AHP) and increased the number of action potential firings. In phasic neurons, however, the same treatments caused l ...