Presentation Tuesday
... Conceptually: all proteins that are directly descended from one protein in the last common ancestor of the species one is interested in are considered orthologous to each other Operationally in a “graph-based approach”: Combine all connected “best triangular hits” into Clusters of Orthologous Groups ...
... Conceptually: all proteins that are directly descended from one protein in the last common ancestor of the species one is interested in are considered orthologous to each other Operationally in a “graph-based approach”: Combine all connected “best triangular hits” into Clusters of Orthologous Groups ...
ap® biology 2015 scoring guidelines
... Overview This question focused on using evidence to support biological evolution. Students were asked to evaluate amino acid sequences from five related species to construct a phylogenetic tree reflecting the evolutionary relationships among them, and justify the placement on the tree of the species ...
... Overview This question focused on using evidence to support biological evolution. Students were asked to evaluate amino acid sequences from five related species to construct a phylogenetic tree reflecting the evolutionary relationships among them, and justify the placement on the tree of the species ...
Chuanlong (Ben) Du
... Communicated with non-statisticians, learned their problems, understood their intensions and explained statistical concepts and analysis results to them. Analyzed data using generalized/mixed linear models; adapted methods and solved problems of low expression, dependency structure, heterogeneou ...
... Communicated with non-statisticians, learned their problems, understood their intensions and explained statistical concepts and analysis results to them. Analyzed data using generalized/mixed linear models; adapted methods and solved problems of low expression, dependency structure, heterogeneou ...
Sample.pdf
... Below is a list of data structures and three applications. Select two data structures that you think would be the most useful for the particular application. Of the two data structures that you selected, pick the better of the two and explain why it is better for that particular application. State a ...
... Below is a list of data structures and three applications. Select two data structures that you think would be the most useful for the particular application. Of the two data structures that you selected, pick the better of the two and explain why it is better for that particular application. State a ...
such as for example in pairwise distance methods
... – they search for each column of the alignment, the simplest explanation for how the characters evolved. – For instance, MP involves a search for a tree with the fewest number of amino acid (or nucleotide character changes that account for the observed differences between the protein (gene) sequence ...
... – they search for each column of the alignment, the simplest explanation for how the characters evolved. – For instance, MP involves a search for a tree with the fewest number of amino acid (or nucleotide character changes that account for the observed differences between the protein (gene) sequence ...
The role of positive selection in molecular evolution
... on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed distributions for within-locus selection coefficients, specifically a double-exponential and a Student's t distribution. Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods on a set of coding sequences from 91 autosomal ge ...
... on aligned DNA sequence data from two closely related species. We investigate heavy-tailed distributions for within-locus selection coefficients, specifically a double-exponential and a Student's t distribution. Using Markov Chain Monte Carlo methods on a set of coding sequences from 91 autosomal ge ...
ICDM04Stream
... Idea 1: using observable statistical traits from the model itself to guess the error on unlabeled streaming data. Idea 2: using very small number of specifically acquired examples to statistically estimate the error – similar to estimate poll to estimate Bush or Kerry will win the presidency. ...
... Idea 1: using observable statistical traits from the model itself to guess the error on unlabeled streaming data. Idea 2: using very small number of specifically acquired examples to statistically estimate the error – similar to estimate poll to estimate Bush or Kerry will win the presidency. ...
BIOLOGY - Learner
... By selecting a particular class of morphological characters, researchers may also bias the analysis in such a way that groups with certain characteristics cluster with others for reasons other than homology. For instance, if the set of characters were weighted toward those involved in carnivory, car ...
... By selecting a particular class of morphological characters, researchers may also bias the analysis in such a way that groups with certain characteristics cluster with others for reasons other than homology. For instance, if the set of characters were weighted toward those involved in carnivory, car ...
Mine Microarray Gene Expression Data, Predict Cancers
... • Single gene (zyxin), single branch tree 38/38 correct on training cases 31/34 correct on test cases, 3 errors X*5735_at <=(8+1)38: ALL • Tree size up to 3 genes 1 decision tree with 1 error 7 decision trees with 2 errors 7 decision trees with 3 errors ...
... • Single gene (zyxin), single branch tree 38/38 correct on training cases 31/34 correct on test cases, 3 errors X*5735_at <=(8+1)38: ALL • Tree size up to 3 genes 1 decision tree with 1 error 7 decision trees with 2 errors 7 decision trees with 3 errors ...
powerpoint slides - Central Web Server 2
... The following is based on observation and not on an a priori truth: ...
... The following is based on observation and not on an a priori truth: ...
BioE/MCB/PMB C146/246, Spring 2005 Problem Set 1
... The graphs for A and B1 should look very similar. Differences are due only to the random process of choosing which bases mutate. The graph for B2 should show fewer mutations overall, with many positions ...
... The graphs for A and B1 should look very similar. Differences are due only to the random process of choosing which bases mutate. The graph for B2 should show fewer mutations overall, with many positions ...
Whippo - cloudfront.net
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
... All vertebrates have genes that make hemoglobin Like many other genes, hemoglobin genes mutates at a fairly constant rate, even if they are in different animal groups Rate of change can be used to estimate how long ago groups or organisms diverged from one another! ...
Bot3404_11_week6.2 - Ecological Evolution – E
... High levels of genetic diversity but slow mutation and speciation rates. High local genetic diversity with high rates of gene flow. (paradox?) Species integrity despite apparent interspecific gene flow. ...
... High levels of genetic diversity but slow mutation and speciation rates. High local genetic diversity with high rates of gene flow. (paradox?) Species integrity despite apparent interspecific gene flow. ...
CLASSIFICATION Chapter 18
... Modern Systematic Taxonomists construct a Phylogenetic tree, or family tree to show these relationships. A phylogenetic tree shows the evolutionary relationships between different groups of organisms. ...
... Modern Systematic Taxonomists construct a Phylogenetic tree, or family tree to show these relationships. A phylogenetic tree shows the evolutionary relationships between different groups of organisms. ...
Microbial Taxonomy Traditional taxonomy or the classification
... • Terminal nodes NOT all the same length, so not constant for all organisms either! ...
... • Terminal nodes NOT all the same length, so not constant for all organisms either! ...
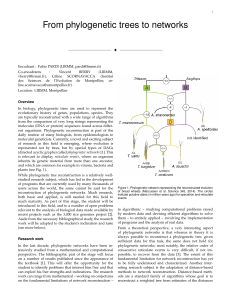
Networks: expanding evolutionary thinking
... manatees, hyraxes), Xenarthra (e.g., armadillos, anteaters), or Boreoplacentalia (e.g., human, mouse, dog), represents the first divergence among placental mammals has long vexed mammalian systematics. Different sets of molecular data have placed each of the three major groups as a sister group to t ...
... manatees, hyraxes), Xenarthra (e.g., armadillos, anteaters), or Boreoplacentalia (e.g., human, mouse, dog), represents the first divergence among placental mammals has long vexed mammalian systematics. Different sets of molecular data have placed each of the three major groups as a sister group to t ...