A common ancestor
... Pairwise Sequence Alignment • Methods – Global alignment • Closely related sequences • Similar length ...
... Pairwise Sequence Alignment • Methods – Global alignment • Closely related sequences • Similar length ...
Phylogeny slides
... Brute force algorithm: consider all possible alignments, then determine the one that results in a best score (time complexity?) Common Heuristic: Use regular (two-string) alignment and then repeatedly add a string to a growing alignment ...
... Brute force algorithm: consider all possible alignments, then determine the one that results in a best score (time complexity?) Common Heuristic: Use regular (two-string) alignment and then repeatedly add a string to a growing alignment ...
Phylogenetic targeting
... Summary • Bayesian approach is time-consuming, but works well, even though data matrix is very sparse ...
... Summary • Bayesian approach is time-consuming, but works well, even though data matrix is very sparse ...
Slides of Barbara`s talk - School of Mathematical Sciences
... *More generally, this could be a set of Q matrices ...
... *More generally, this could be a set of Q matrices ...
A method for paralogy trees reconstruction
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
... Genes belonging to the same organism are called paralogs when they show a significant similarity in the sequences, even if they have a different biological function. It is an emergent biological paradigm that the families of paralogs derive from a mechanism of gene duplication with modification, rep ...
Step 3. Construction of the phylogenetic tree Distance methods
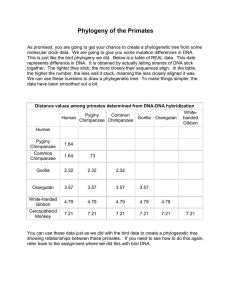
... Therefore, methods have been developed to compensate for this. ...
... Therefore, methods have been developed to compensate for this. ...
Phylogenetic tree estimation
... Synteny & collinearity • Synteny gene loci are on the same chromosome ...
... Synteny & collinearity • Synteny gene loci are on the same chromosome ...
An Introduction to Phylogenetics
... All of these representations depict the same topology Branch lengths are indicated in blue Red lengths are meaningless ...
... All of these representations depict the same topology Branch lengths are indicated in blue Red lengths are meaningless ...
CSCE590/822 Data Mining Principles and Applications
... Assumptions fail when Highly dependent on evolution is rapid assumed evolution model ...
... Assumptions fail when Highly dependent on evolution is rapid assumed evolution model ...
Concept Check Questions
... Phylogenetic systematic informs the construction of phylogenetic trees based on shared characteristics ...
... Phylogenetic systematic informs the construction of phylogenetic trees based on shared characteristics ...
Phylogenetics Molecular Phylogenetics
... means that it lacks the common ancestor of (A) the species in the group. Furthermore, a valid taxon that includes the extant species G, H, J, and K would necessarily also contain D and E, which are also descended from A. ...
... means that it lacks the common ancestor of (A) the species in the group. Furthermore, a valid taxon that includes the extant species G, H, J, and K would necessarily also contain D and E, which are also descended from A. ...
Day6
... • Phylogenetic analysis is one of the most controversial areas in bioinformatics. There are a wide variety of different methods for analyzing the data, and even the experts often disagree on the best method for analyzing the data. ...
... • Phylogenetic analysis is one of the most controversial areas in bioinformatics. There are a wide variety of different methods for analyzing the data, and even the experts often disagree on the best method for analyzing the data. ...
Creating Phylogenetic Trees with MEGA
... – At each site, the likelihood is determined by evaluating the probability that a certain evolutionary model (eg. BLOSSUM or PAM matrices) has generated the observed data. – The likelihood’s for each site are then multiplied to provide likelihood for each tree – Choose the tree with maximum like ...
... – At each site, the likelihood is determined by evaluating the probability that a certain evolutionary model (eg. BLOSSUM or PAM matrices) has generated the observed data. – The likelihood’s for each site are then multiplied to provide likelihood for each tree – Choose the tree with maximum like ...
Diapositiva 1
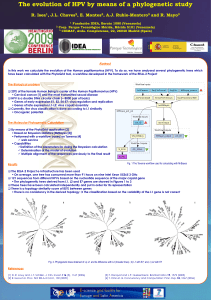
... Distance trees were constructed using Neighbor-Joining with a maximum likelihood distance matrix using the model selected by MODELTEST. The standard errors of branch lengths were estimated using PAUP . Divergence dates with low and high confidence intervals and associated evolutionary rates were est ...
... Distance trees were constructed using Neighbor-Joining with a maximum likelihood distance matrix using the model selected by MODELTEST. The standard errors of branch lengths were estimated using PAUP . Divergence dates with low and high confidence intervals and associated evolutionary rates were est ...
Phylogenetic - Nematode bioinformatics. Analysis tools and data
... Are mathematical and/or statistical methods for inferring the divergence order of taxa, as well as the lengths of the branches that connect them. There are many phylogenetic methods available today, each having strengths and weaknesses. Most can be classified as follows: Characters (bp, aa) Distance ...
... Are mathematical and/or statistical methods for inferring the divergence order of taxa, as well as the lengths of the branches that connect them. There are many phylogenetic methods available today, each having strengths and weaknesses. Most can be classified as follows: Characters (bp, aa) Distance ...