PHYLOGENY AND EVOLUTION OF CORNALES: INTEGRATING
... excellent fossil records and provides an exceptional system for testing macroevolutionary hypotheses. The major goal of the project is to reconstruct the phylogeny of Cornales using evidence from extensive DNA sequences, morphology, and fossils. The phylogeny will serve as the basis for definitive t ...
... excellent fossil records and provides an exceptional system for testing macroevolutionary hypotheses. The major goal of the project is to reconstruct the phylogeny of Cornales using evidence from extensive DNA sequences, morphology, and fossils. The phylogeny will serve as the basis for definitive t ...
AP Biology Name Cladistics and Bioinformatics Questions 2013 The
... An outgroup is a species of organism that acts as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships between three or more other species of organisms. It is hypothesized to be related to the species in question but less closely than any of the other species are to each other. Outgroup ...
... An outgroup is a species of organism that acts as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships between three or more other species of organisms. It is hypothesized to be related to the species in question but less closely than any of the other species are to each other. Outgroup ...
Evolution Cladistics Questions 2013
... An outgroup is a species of organism that acts as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships between three or more other species of organisms. It is hypothesized to be related to the species in question but less closely than any of the other species are to each other. Outgroup ...
... An outgroup is a species of organism that acts as a reference group when determining the evolutionary relationships between three or more other species of organisms. It is hypothesized to be related to the species in question but less closely than any of the other species are to each other. Outgroup ...
Eleven species are distinguished in the genus Oxythyrea Mulsant
... recolonized it back including new areas in northern regions. Master thesis is focused on resolving population structure of O. funesta and partial phylogeny of the genus Oxythyrea using molecular genetic methods. 145 individuals of O. funesta and 15 individuals of five other species of the genus Oxyt ...
... recolonized it back including new areas in northern regions. Master thesis is focused on resolving population structure of O. funesta and partial phylogeny of the genus Oxythyrea using molecular genetic methods. 145 individuals of O. funesta and 15 individuals of five other species of the genus Oxyt ...
tree - Tecfa
... Paralogs = Genes resulting from gene duplication Inparalogs = Paralogs resulting from lineage-specific duplication(s) subsequent to a particular speciation event Outparalogs = Paralogs resulting from gene duplication(s) preceding a ...
... Paralogs = Genes resulting from gene duplication Inparalogs = Paralogs resulting from lineage-specific duplication(s) subsequent to a particular speciation event Outparalogs = Paralogs resulting from gene duplication(s) preceding a ...
PHYLOGENETIC NETWORKS
... – Decide whether SPR(T1,T2)=m in O(mn) time, and – Construct network N from T1 and T2 in O(mn) time ...
... – Decide whether SPR(T1,T2)=m in O(mn) time, and – Construct network N from T1 and T2 in O(mn) time ...
A Phase Transition in Molecular Evolution with Applications to the Assembly of the Tree of Life
... between statistical accuracy and computational efficiency. In this talk I will describe a fruitful connection between standard models of molecular evolution and a class of spin systems from probability theory that sheds light on this issue. I will show how this probabilistic perspective produces a f ...
... between statistical accuracy and computational efficiency. In this talk I will describe a fruitful connection between standard models of molecular evolution and a class of spin systems from probability theory that sheds light on this issue. I will show how this probabilistic perspective produces a f ...
ISVEE/181 Molecular characterization of indigenous peste des petits
... and nucleoprotein (N) gene segments and phylogenetic analysis, so as to focus on genetic variation in the field viruses. A total of 64 clinical samples collected from sheep and goats. The samples were positive with IcELISA were also found positive with RT-PCR. Selected regions of PPRV genome were am ...
... and nucleoprotein (N) gene segments and phylogenetic analysis, so as to focus on genetic variation in the field viruses. A total of 64 clinical samples collected from sheep and goats. The samples were positive with IcELISA were also found positive with RT-PCR. Selected regions of PPRV genome were am ...
3000_2013_1e
... • when and how were complex eyes evolved? in what species are they lost? are the genes required to develop eyes still there? can they be expressed in different ways? ...
... • when and how were complex eyes evolved? in what species are they lost? are the genes required to develop eyes still there? can they be expressed in different ways? ...
Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis: Design and Implementation of
... difference in lengths can appear due to sequencing errors (digitalizing the biological sample), mutations (insertions or deletions of one or more sites along the sequence) or because the researcher also wants to include fragments of the same genetic region that were used in other experiments. The se ...
... difference in lengths can appear due to sequencing errors (digitalizing the biological sample), mutations (insertions or deletions of one or more sites along the sequence) or because the researcher also wants to include fragments of the same genetic region that were used in other experiments. The se ...
Slides
... • Models of ribosome binding site and promoter regions • Non – geometric length distributions of exons • Pseudo higher order EHMM can be constructed. • Idea of pair HMM to multiple sequences ...
... • Models of ribosome binding site and promoter regions • Non – geometric length distributions of exons • Pseudo higher order EHMM can be constructed. • Idea of pair HMM to multiple sequences ...
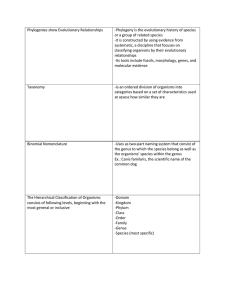
Phylogenies show Evolutionary Relationships
... -As new evidence about organisms becomes available through biochemical analysis, phylogenetic trees are constantly being revised ...
... -As new evidence about organisms becomes available through biochemical analysis, phylogenetic trees are constantly being revised ...
Lecture5
... Only differences can be observed directly – not distances All distance methods rely (crucially) on this A great many models used for nucleotide sequences (e.g. JC, K2P, HKY, Rev, Maximum ...
... Only differences can be observed directly – not distances All distance methods rely (crucially) on this A great many models used for nucleotide sequences (e.g. JC, K2P, HKY, Rev, Maximum ...
Diagrams Nov 8
... Phenetic: classification of the organisms based on their similarities, trees obtained using a phenetic approach may not reflect evolutionary relationships. A tree based on this method is called a phenogram Cladistic (Hennig 1966): study of the different pathways of evolution, the most parsimonious p ...
... Phenetic: classification of the organisms based on their similarities, trees obtained using a phenetic approach may not reflect evolutionary relationships. A tree based on this method is called a phenogram Cladistic (Hennig 1966): study of the different pathways of evolution, the most parsimonious p ...