Recursive partitioning for tumor classification with gene
... Expression profiles of 2,000 genes using an Affymetrix oligonucleotide array in 22 normal and 40 colon cancer tissues The response is binary indicating normal or cancer tissue and the predictor variables are the 2000 genes ...
... Expression profiles of 2,000 genes using an Affymetrix oligonucleotide array in 22 normal and 40 colon cancer tissues The response is binary indicating normal or cancer tissue and the predictor variables are the 2000 genes ...
Apr7
... Furthermore, disagreements regarding the divergence times have also placed in question any uniformity in evolution rates that are promised by a “molecular clock.” See as one example the article on the time of divergence of the human and the chimp. One of the hypotheses there is that humans, because ...
... Furthermore, disagreements regarding the divergence times have also placed in question any uniformity in evolution rates that are promised by a “molecular clock.” See as one example the article on the time of divergence of the human and the chimp. One of the hypotheses there is that humans, because ...
Testing for Natural Selection on Conserved Non-genic Sequences in Mammals
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
... The observation of high DNA sequence conservation across long periods of evolutionary time is thought to be a good signal of important regions. Otherwise, the similarity between sequences of species would have eroded by neutral mutation processes. This is also why, in general, higher conservation is ...
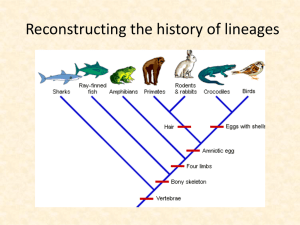
12-History of Lineages
... How can the history of evolution be reconstructed without seeing speciation events? 1) Identification of key characters (heritable parts or attributes of an organism) 2) Transform characters into transformation series 3) Compare these characters to an outgroup 4) Construct a cladogram based on the o ...
... How can the history of evolution be reconstructed without seeing speciation events? 1) Identification of key characters (heritable parts or attributes of an organism) 2) Transform characters into transformation series 3) Compare these characters to an outgroup 4) Construct a cladogram based on the o ...
20 years and 22 papers with Bernard Moret
... Phylogeny reconstruction in 1999 • Distance-based – Breakpoint (BP) distances [Blanchette, Kunisawa, Sankoff 1999] – fast but high error • Breakpoint tree (NP-hard, even for three taxa) – BPAnalysis: [Sankoff & Blanchette 1998]: exhaustive search through treespace to find the minimum breakpoint len ...
... Phylogeny reconstruction in 1999 • Distance-based – Breakpoint (BP) distances [Blanchette, Kunisawa, Sankoff 1999] – fast but high error • Breakpoint tree (NP-hard, even for three taxa) – BPAnalysis: [Sankoff & Blanchette 1998]: exhaustive search through treespace to find the minimum breakpoint len ...
Lecture 7. Data Stream Mining. Building decision trees
... No “magic” parameters. Self-adapts to change Always as accurate as CVFDT, and sometimes much better Less memory - no example window Moderate overhead in time (<50%). Working on it Rigorous guarantees possible ...
... No “magic” parameters. Self-adapts to change Always as accurate as CVFDT, and sometimes much better Less memory - no example window Moderate overhead in time (<50%). Working on it Rigorous guarantees possible ...
Lectures 11 Friday, October 22, 2010 Phylogenetic tree (phylogeny
... Different genes evolve at different rates, which makes them useful for analyzing species that diverged at different times in the past. Ribosomal RNA evolves very slowly. The recognition that Archaea and Bacteria were quite different first came from the analysis of ribosomal RNA sequences. Once the g ...
... Different genes evolve at different rates, which makes them useful for analyzing species that diverged at different times in the past. Ribosomal RNA evolves very slowly. The recognition that Archaea and Bacteria were quite different first came from the analysis of ribosomal RNA sequences. Once the g ...
PowerPoint
... Similarity criterion for phylogeny • A number of methods (e.g. ClustalW) use sequence identity with Kimura (1983) correction: Corrected K = - ln(1.0-K-K2/5.0), where K is percentage divergence (expressed as sequence identity difference) corresponding to two aligned sequences (often only taking the ...
... Similarity criterion for phylogeny • A number of methods (e.g. ClustalW) use sequence identity with Kimura (1983) correction: Corrected K = - ln(1.0-K-K2/5.0), where K is percentage divergence (expressed as sequence identity difference) corresponding to two aligned sequences (often only taking the ...
Pi kur, 2004
... A: For yeast, a minimum of 20 genes is required to recover 95% bootstrap values for each branch of the species tree (Rokas et al. 2003, Nature) ...
... A: For yeast, a minimum of 20 genes is required to recover 95% bootstrap values for each branch of the species tree (Rokas et al. 2003, Nature) ...
Chapter 19
... amino acid that is replaced and what it is replaced with Most mutations that affect phenotype are selected against, some may prove adaptive Similarities in proteins do not always equal similarity in DNA sequence because of the redundancy in the genetic code ...
... amino acid that is replaced and what it is replaced with Most mutations that affect phenotype are selected against, some may prove adaptive Similarities in proteins do not always equal similarity in DNA sequence because of the redundancy in the genetic code ...
Investigating Sequences - BioQUEST Curriculum Consortium
... To maximise the benefits to the scientific community of Plasmodium genome sequencing, the Pathogen Genomics group is committed to the curation of Plasmodium spp. This will ensure that annotation is updated and maintained, and will form a framework that underpins global efforts to understand the para ...
... To maximise the benefits to the scientific community of Plasmodium genome sequencing, the Pathogen Genomics group is committed to the curation of Plasmodium spp. This will ensure that annotation is updated and maintained, and will form a framework that underpins global efforts to understand the para ...
Link to Powerpoint
... – PCR amplify a gene of interest – Tells you what types of organisms are there – Bacteria/Archaea (16S rRNA), Microbial Euks (18S rRNA), Fungi (ITS), Virus (no good marker) ...
... – PCR amplify a gene of interest – Tells you what types of organisms are there – Bacteria/Archaea (16S rRNA), Microbial Euks (18S rRNA), Fungi (ITS), Virus (no good marker) ...