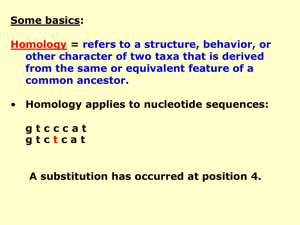
Nuclear Gene Trees and the Phylogenetic Relationships of the
... Phylogenetic relationships of mangabeys within the Old World monkey tribe Papionini are inferred from analyses of nuclear DNA sequences from five unlinked loci. The following conclusions are strongly supported, based on congruence among trees derived for the five separate gene regions: (1) mangabeys ...
... Phylogenetic relationships of mangabeys within the Old World monkey tribe Papionini are inferred from analyses of nuclear DNA sequences from five unlinked loci. The following conclusions are strongly supported, based on congruence among trees derived for the five separate gene regions: (1) mangabeys ...
Causes, consequences and solutions of
... include understanding genome organization, epidemiological investigations, predicting protein functions, and deciding the genes to be analyzed in comparative studies. Despite immense progress in recent years, phylogenetic reconstruction involves many challenges that create uncertainty with respect t ...
... include understanding genome organization, epidemiological investigations, predicting protein functions, and deciding the genes to be analyzed in comparative studies. Despite immense progress in recent years, phylogenetic reconstruction involves many challenges that create uncertainty with respect t ...
Phylogenomics: improving functional predictions for uncharacterized
... evolutionary relationships than similarity methods (including clustering) because they allow for evolutionary branches to have different lengths. Thus, in those cases in which gene function correlates with gene phylogeny and in which amounts or rates of change vary between lineages, similarity-based ...
... evolutionary relationships than similarity methods (including clustering) because they allow for evolutionary branches to have different lengths. Thus, in those cases in which gene function correlates with gene phylogeny and in which amounts or rates of change vary between lineages, similarity-based ...
Species tree
... • “supertree” The supertree approach estimates phylogenies for subsets of genes with good overlap, then combines these subtree estimates into a supertree. • Depends on the ability to distinguish between orthologs and paralogs; • Supertree approaches are controversial, in part because the methodology ...
... • “supertree” The supertree approach estimates phylogenies for subsets of genes with good overlap, then combines these subtree estimates into a supertree. • Depends on the ability to distinguish between orthologs and paralogs; • Supertree approaches are controversial, in part because the methodology ...
Station 1: Double Bubbles Directions: Make a double bubble
... 90% of their population due to a tornado. ...
... 90% of their population due to a tornado. ...
seq.
... find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest probability under this model. This approach can also be use ...
... find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest probability under this model. This approach can also be use ...
Supplementary Methods Sampling and sequencing Five adult C
... z measures, for a given GO-slim term, the contrast in selective pressure between the two species accounting for the overall genomic trends. z is expected to be high and positive when the term-specific N/S ratio is substantially higher than the genomic average in C. nigra, and/or substantially lo ...
... z measures, for a given GO-slim term, the contrast in selective pressure between the two species accounting for the overall genomic trends. z is expected to be high and positive when the term-specific N/S ratio is substantially higher than the genomic average in C. nigra, and/or substantially lo ...
ppt - Chair of Computational Biology
... * need to know how to search among all possible trees for the most parsimonious ones, and how to infer branch lengths. * sofar only considered simple model of 0/1 characters. DNA sequences have 4 states, protein sequences 20 states. * Justification: is it reasonable to use the parsimony criterion? I ...
... * need to know how to search among all possible trees for the most parsimonious ones, and how to infer branch lengths. * sofar only considered simple model of 0/1 characters. DNA sequences have 4 states, protein sequences 20 states. * Justification: is it reasonable to use the parsimony criterion? I ...
LIGNUM: Towards Forest Scientist`s Workbench
... 1. The Finnish Forest Research Institute 2. Dept. of Forest Ecology, University of Helsinki ...
... 1. The Finnish Forest Research Institute 2. Dept. of Forest Ecology, University of Helsinki ...
seq.
... find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest probability under this model. This approach can also be use ...
... find that tree that explains sequence data with minimum number of substitutions (tree includes hypothesis of sequence at each of the nodes) Maximum Likelihood analyses given a model for sequence evolution, find the tree that has the highest probability under this model. This approach can also be use ...
Applied Bayesian Inference for Agricultural Statisticians
... • Formal tests are based on asymptotic (“large sample”) approximations. – Nice properties when n is “large” When is n large enough? – Quasi-likelihood (PROC GENMOD)…what’s that? • “vacuous” (Walt Stroup) for repeated measures specs.→ can’t even simulate data generation process. ...
... • Formal tests are based on asymptotic (“large sample”) approximations. – Nice properties when n is “large” When is n large enough? – Quasi-likelihood (PROC GENMOD)…what’s that? • “vacuous” (Walt Stroup) for repeated measures specs.→ can’t even simulate data generation process. ...
Inference of a Phylogenetic Tree: Hierarchical Clustering
... Caminalcules. Although these techniques have a superficial similarity, in that they both use agglomeration as their construction method, their origin and approaches are antithetical. For a small problem space of the original species proposed by Camin (1965) the genetic algorithm was able to produce ...
... Caminalcules. Although these techniques have a superficial similarity, in that they both use agglomeration as their construction method, their origin and approaches are antithetical. For a small problem space of the original species proposed by Camin (1965) the genetic algorithm was able to produce ...
Comparing data sets It is possible to collect multiple different data
... less than 1 in a 1000 chance that two partitions would yield optimal trees that are this close by chance. This is an important point to stress. Even when partitions differ in the optimal tree they support, they generally yield trees that are more similar to each other than would be expected by chanc ...
... less than 1 in a 1000 chance that two partitions would yield optimal trees that are this close by chance. This is an important point to stress. Even when partitions differ in the optimal tree they support, they generally yield trees that are more similar to each other than would be expected by chanc ...
comparing dna sequences to determine evolutionary relationships
... the same species, while there is significant variation in COI sequences of organisms from different species. Therefore, a COI sequence provides a unique sequence signature for a particular species. For the same reasons, the COI gene is suitable for comparing phylogenetic relationships between specie ...
... the same species, while there is significant variation in COI sequences of organisms from different species. Therefore, a COI sequence provides a unique sequence signature for a particular species. For the same reasons, the COI gene is suitable for comparing phylogenetic relationships between specie ...
Estimating cancer survival and clinical outcome based on genetic
... Measure of genetic progression = number of events that have occurred All events are independent and impact on progression is cumulative ...
... Measure of genetic progression = number of events that have occurred All events are independent and impact on progression is cumulative ...