Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Basic pathways involved in the medullary control of blood pressure. The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) is one of the major sources of excitatory input to sympathetic nerves controlling the vasculature. These neurons receive inhibitory input from the baroreceptors via an inhibitory neuron in th ...
... Basic pathways involved in the medullary control of blood pressure. The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) is one of the major sources of excitatory input to sympathetic nerves controlling the vasculature. These neurons receive inhibitory input from the baroreceptors via an inhibitory neuron in th ...
Chapter Three Study Guide
... Controls muscles used in speech Controls sequence of movements Spontaneous speaking and writing Memory for words and numbers Understanding speech and writing ...
... Controls muscles used in speech Controls sequence of movements Spontaneous speaking and writing Memory for words and numbers Understanding speech and writing ...
Chapter 3
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
... 1. Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. 2. Know the main types of glia and their functions. 3. Be able to describe the advantages and disadvantages of the blood-brain barrier. Module 2.2 The Nerve Impulse 4. Understand why the neuron uses considerable ene ...
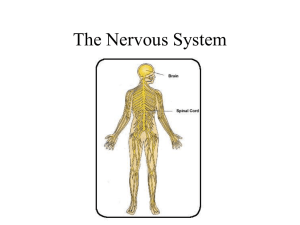
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... • Generally inhibitory • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect ...
... • Generally inhibitory • Prevents the receptor nerve from being overstimulated • When it accumulates it has a sedative effect ...
File
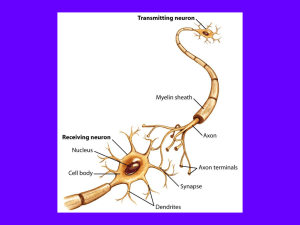
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
... -- an axon carries nerve impulses AWAY from the cell body. -- if an action potential is generated, it will originate within the axon hillock, which will then pass the signal on to the axon. -- the axon carries the action potential from the cell body/axon hillock to its bulb-like synaptic endings (lo ...
Anatomy and Physiology 241 Lecture Objectives The Nervous
... the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location and function of preganglionic and postganglionic fibers and general number of each. Be able to classify neurons as bipolar, ...
... the PNS and the CNS. Describe the synapse in detail. Define sensory neuron, motor neuron, interneuron and give the function and location of each. Know the difference, location and function of preganglionic and postganglionic fibers and general number of each. Be able to classify neurons as bipolar, ...
CH 48 Nervous systemnotes2010
... 2. bipolar disorder- mood swings from high to low ; can cause increased bouts of energy with creative ideas, overtalking, increased risk behaviors ( some famous artists and musicians were believed to have p produced their best work during this manic phase). The depressive stage lowers ability to fee ...
... 2. bipolar disorder- mood swings from high to low ; can cause increased bouts of energy with creative ideas, overtalking, increased risk behaviors ( some famous artists and musicians were believed to have p produced their best work during this manic phase). The depressive stage lowers ability to fee ...
Name: Date: Period: _____ Unit 9 Textbook Notes: The Nervous
... the pre-synaptic cell, or is degraded by enzymes in the synaptic cleft _____Calcium ions rush into the axon terminal and are packaged in synaptic vesicles _____Synaptic vesicles fuse with the axon terminal membrane and release calcium ions (the neurotransmitter) into the synaptic cleft. _____Calcium ...
... the pre-synaptic cell, or is degraded by enzymes in the synaptic cleft _____Calcium ions rush into the axon terminal and are packaged in synaptic vesicles _____Synaptic vesicles fuse with the axon terminal membrane and release calcium ions (the neurotransmitter) into the synaptic cleft. _____Calcium ...
The nervous system - Mr T Pities the Fool
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
... neurone: 1. Sensory neurone – carry impulse from receptor to CNS 2. Relay – connects sensory to motor 3. Motor – connects CNS to effector which makes a response. (muscle, gland) ...
Neural Communication
... is recycled in a process called reuptake, in which the neurotransmitter is taken back up into the presynaptic membrane and repackaged, to be released again. In the case of one type of neurotransmitter acetylcholine (Ach), the neurotransmitter is broken down into constituent parts by an enzyme called ...
... is recycled in a process called reuptake, in which the neurotransmitter is taken back up into the presynaptic membrane and repackaged, to be released again. In the case of one type of neurotransmitter acetylcholine (Ach), the neurotransmitter is broken down into constituent parts by an enzyme called ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... 3) D 4) C 5) C 6) B 7) D 8) A 9) D 10) A 11) D 12) D 13) C 14) B 15) B ...
... 3) D 4) C 5) C 6) B 7) D 8) A 9) D 10) A 11) D 12) D 13) C 14) B 15) B ...
Nervous System
... • Gaps in myelin sheath cells called Nodes of Ranvier – allow impulses to move more quickly down neurons ...
... • Gaps in myelin sheath cells called Nodes of Ranvier – allow impulses to move more quickly down neurons ...
How specific is ligand
... Second messengers from lipids Calcium is a second messenger Nitric oxide is a second messenger more neat things about receptors and their signaling pathways • Do the things that you have learned about affect ...
... Second messengers from lipids Calcium is a second messenger Nitric oxide is a second messenger more neat things about receptors and their signaling pathways • Do the things that you have learned about affect ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ peripheral nervous system. 8. What part of the nervous system would neurons of the spinal cord b ...
... chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ peripheral nervous system. 8. What part of the nervous system would neurons of the spinal cord b ...
The Nervous System
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
Anatomy and Physiology 121: The Nervous System General
... ~ 100,000 presynaptic terminals lie on dendrites of a cell Synaptic Transmission ...
... ~ 100,000 presynaptic terminals lie on dendrites of a cell Synaptic Transmission ...
Introduction to the physiology of perception
... • A synapse is a process that releases neurotransmitters, chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles (cavities) of the sending neuron • In a synapse, an action potential cause neurotransmitters to be: - released by the presynaptic neuron - received by the postsynaptic neuron on receptor sites, areas ...
... • A synapse is a process that releases neurotransmitters, chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles (cavities) of the sending neuron • In a synapse, an action potential cause neurotransmitters to be: - released by the presynaptic neuron - received by the postsynaptic neuron on receptor sites, areas ...
AP Biology - Pleasantville High School
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
... membrane in a lock and key manner. (Inhibitor substances stop the impulse because they can fit into the receptor sites and block the normal neurotransmitter.) -this generates an action potential in the postsynaptic membrane and the nerve impulse continues on -after their release the neurotransmitter ...
Airgas template - Morgan Community College
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
... The parasympathetic nervous system functions in maintaining vital functions and responding when there is a critical threat to the integrity of the individual—the “fight-or-flight” response. ...
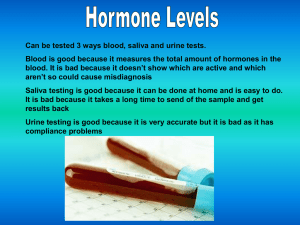
Hormone Levels and EEG (Ashanti)
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
... EEG is useful because the time resolution is very high. As other methods for researching brain activity have time resolution between seconds and minutes, the EEG has a resolution down to sub-millisecond. It is also good because other methods for exploring functions in the brain rely on blood flow or ...
Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells
... – Spatial summation—adding together the effects of several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects ...
... – Spatial summation—adding together the effects of several knobs being activated simultaneously and stimulating different locations on the postsynaptic membrane, producing an action potential – Temporal summation—when synaptic knobs stimulate a postsynaptic neuron in rapid succession, their effects ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... Motor/Efferent Div. • send impulses away from the CNS + effectors - voluntary and involuntary muscles ...
... Motor/Efferent Div. • send impulses away from the CNS + effectors - voluntary and involuntary muscles ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... “Band-Aid” of cells called Schwann Cells. Multiple layers of these cells create a sheath, or covering, around the axon called a myelin sheath. •The myelin sheath, allows for the super-fast conduction of nerve impulses. Nerves that are mylenated appear white. Mylenated nerves are used to send signals ...
... “Band-Aid” of cells called Schwann Cells. Multiple layers of these cells create a sheath, or covering, around the axon called a myelin sheath. •The myelin sheath, allows for the super-fast conduction of nerve impulses. Nerves that are mylenated appear white. Mylenated nerves are used to send signals ...