Neural Conduction - U
... Activation of Receptors (2) It can act at a metabotropic receptor associated with a signal protein that is attached to a G-protein inside the neuron; this G-protein can either move to a nearby ion channel, activate it, and cause a change in the membrane potential OR it can lead to the production of ...
... Activation of Receptors (2) It can act at a metabotropic receptor associated with a signal protein that is attached to a G-protein inside the neuron; this G-protein can either move to a nearby ion channel, activate it, and cause a change in the membrane potential OR it can lead to the production of ...
Biological explanation of schizophrenia (1)
... • Rats behaviour changed – psychotic behaviour consistent with that shown in patients with schizophrenia • Research has suggested that the presence of an excess of dopamine receptors and synapses in the brain contributes to schizophrenia ...
... • Rats behaviour changed – psychotic behaviour consistent with that shown in patients with schizophrenia • Research has suggested that the presence of an excess of dopamine receptors and synapses in the brain contributes to schizophrenia ...
NERVOUS and ENDOCRINE SYSTEMS TEST PREVIEW
... 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an impulse? 6. What is the pathway of an impulse from stimulus ...
... 3. What part of a neuron receives impulses and carries it to the cell body? Which part carries impulses away from the cell body? 4. What is the difference between intensity and strength of a nerve impulse? 5. What determines the rate of an impulse? 6. What is the pathway of an impulse from stimulus ...
It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
... It is known that in humans, as in all vertebrates, the central and peripheral nervous systems play essential roles in the transmission and assimilation of the information of our environment. This information is processed through neuronal synaptic communications, mediated by excitatory and inhibitory ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in defining complex technical terms for an audience of non-technical readers. In particular, the intended audience for these definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given f ...
... The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in defining complex technical terms for an audience of non-technical readers. In particular, the intended audience for these definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given f ...
Technical Definitions
... The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in defining complex technical terms for an audience of non-technical readers. In particular, the intended audience for these definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given f ...
... The objective of this assignment is to gain experience in defining complex technical terms for an audience of non-technical readers. In particular, the intended audience for these definitions is a person who is taking an introductory level psychology class. Three types of definitions will be given f ...
File
... Neurotransmitters (chemicals) released from the sending neuron travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron generating an action potential ...
... Neurotransmitters (chemicals) released from the sending neuron travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron generating an action potential ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Know the similarities and differences between twins in terms of biological psychology and social-cultural psychology. Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolution ...
... Know the similarities and differences between twins in terms of biological psychology and social-cultural psychology. Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolution ...
How Neurons Talk to Each Other
... The presynaptic nerve endings contain signal molecules known as neurotransmitters, which are stored in small membrane-enclosed vesicles. Each nerve ending in the central nervous system contains an average of several hundred synaptic vesicles. However, synapses vary significantly. For example, some s ...
... The presynaptic nerve endings contain signal molecules known as neurotransmitters, which are stored in small membrane-enclosed vesicles. Each nerve ending in the central nervous system contains an average of several hundred synaptic vesicles. However, synapses vary significantly. For example, some s ...
Slide () - AccessEmergency Medicine
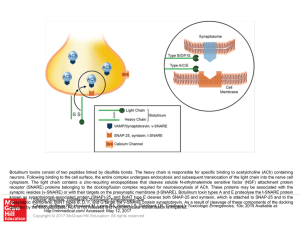
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... • There is a small gap between neurons called a synaptic cleft. That region or junction is called synapses. – This is where neurons communicate – The signaling activity of the nervous system is made up of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons. • These synapses do not c ...
... • There is a small gap between neurons called a synaptic cleft. That region or junction is called synapses. – This is where neurons communicate – The signaling activity of the nervous system is made up of electrical activity within neurons and chemical flow between neurons. • These synapses do not c ...
Slide 1
... Source: Modeling Future Heroes, A Practical Application of Heroic Values, By Roger F. Cram Source: NAMI–Family to Family Course, Class 6, Handout 2–Basic Neuro-transmission at the Synapse–page 6.23 Paragraph 3 ...
... Source: Modeling Future Heroes, A Practical Application of Heroic Values, By Roger F. Cram Source: NAMI–Family to Family Course, Class 6, Handout 2–Basic Neuro-transmission at the Synapse–page 6.23 Paragraph 3 ...
Neuroscience & Behavior
... between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
... between neurons when released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether it will generate a neural impulse ...
Nervous System
... • Action Potential jumps from node to node • Speeds up signal from 5 m/sec to 150 m/sec ...
... • Action Potential jumps from node to node • Speeds up signal from 5 m/sec to 150 m/sec ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fit ...
... locks. In this case, the “locks” are special receptor sites in the dendrites of the receiving neuron. These sites accept only one kind of chemical. For the nerve signal to pass on, the neurotransmitter must be the right chemical that fits, or “unlocks”, the receptor site. If the neurotransmitter fit ...
Module 4 - Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receives messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branche ...
... Parts of a Neuron Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receives messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branche ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ Unit 7, Part 2 Notes: The Nervous
... 20. A nerve cell is not always at resting potential, however. An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. Neuroscientists use other words, such as a "spike" or an "impulse" for the action potential. The action potential is an explosion of electr ...
... 20. A nerve cell is not always at resting potential, however. An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. Neuroscientists use other words, such as a "spike" or an "impulse" for the action potential. The action potential is an explosion of electr ...
15-1 Section Summary
... and motor neurons. Together they make up the chain of nerve cells that carry an impulse through the nervous system. A sensory neuron picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse. An interneuron is a neuron that carries nerve impulses from ...
... and motor neurons. Together they make up the chain of nerve cells that carry an impulse through the nervous system. A sensory neuron picks up stimuli from the internal or external environment and converts each stimulus into a nerve impulse. An interneuron is a neuron that carries nerve impulses from ...
10-1
... 23. This is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene. It acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre and postsynaptic neuronal processes. The primary role of this neurotransmitter is to slow down the neuron ...
... 23. This is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABRA1 gene. It acts at inhibitory synapses in the brain by binding to specific transmembrane receptors in the plasma membrane of both pre and postsynaptic neuronal processes. The primary role of this neurotransmitter is to slow down the neuron ...
mechanisms of neurotransmitter receptor biogenesis and trafficking
... whereby neurons exchange information between each other is called neurotransmission. This remarkable feat is achieved through membrane bound neurotransmitter receptors that bind neurotransmitters with high specificity. The brain utilises a variety of neurotransmitter/ neurotransmitter receptor partn ...
... whereby neurons exchange information between each other is called neurotransmission. This remarkable feat is achieved through membrane bound neurotransmitter receptors that bind neurotransmitters with high specificity. The brain utilises a variety of neurotransmitter/ neurotransmitter receptor partn ...
Slide ()
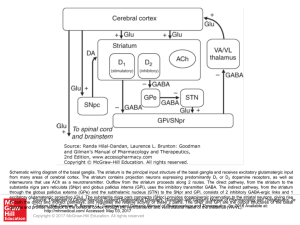
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
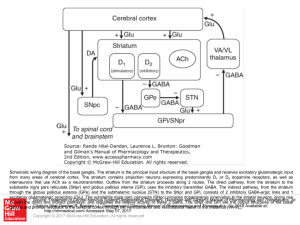
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Study Guide for Chapter 7 - Neuron Function Be familiar with the
... action potential (“nerve impulse”), afferent, astrocyte, axon, axonal end bulbs (synaptic end bulbs, boutons, axon endings, synaptic knobs), bipolar neuron, blood-brain barrier, central nervous system (CNS), chemically-gated (ligand-gated) channel, dendrite, depolarization, efferent, electrochemical ...
... action potential (“nerve impulse”), afferent, astrocyte, axon, axonal end bulbs (synaptic end bulbs, boutons, axon endings, synaptic knobs), bipolar neuron, blood-brain barrier, central nervous system (CNS), chemically-gated (ligand-gated) channel, dendrite, depolarization, efferent, electrochemical ...
Leaving Certificate Biology Topic iQuiz
... Which of the following structures of a reflex arc transmits impulses toward the central nervous system? Receptor ...
... Which of the following structures of a reflex arc transmits impulses toward the central nervous system? Receptor ...