too low levels
... of which are then sent to different parts of the brain while others are reabsorbed by the sending neuron in a process called reuptake ...
... of which are then sent to different parts of the brain while others are reabsorbed by the sending neuron in a process called reuptake ...
The Nervous System Ch. 12 & 13
... before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action potential is reached , it starts to move back to -70 mV (resting potential). This is called repolarization. The reaching of the threshold potential causes voltage-gated K+ channels ...
... before they close. Action potentials are all-or-none, either they will occur or not at all. Once the peak of the action potential is reached , it starts to move back to -70 mV (resting potential). This is called repolarization. The reaching of the threshold potential causes voltage-gated K+ channels ...
Information Processing in Motor Learning
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
... Transport the information necessary for all activities we carry out The language of the nervous system Relay of impulse within neuron: ...
Ch10 Reading Guide
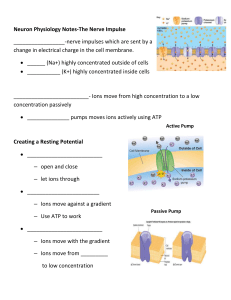
... 3. The cell uses ATP to actively transport ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. Volts are ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. A volt is called ...
... 3. The cell uses ATP to actively transport ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. Volts are ________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. A volt is called ...
CHAPTER 3
... inhibition of pain and feelings of elation, followed by anxiety, pain, and overresponsiveness to stimulation. The brain produces chemicals known as endorphins that bind to opiate receptors, helping to inhibit pain. d) Marijuana: Marijuana (cannabis) produces a variety of effects including drowsiness ...
... inhibition of pain and feelings of elation, followed by anxiety, pain, and overresponsiveness to stimulation. The brain produces chemicals known as endorphins that bind to opiate receptors, helping to inhibit pain. d) Marijuana: Marijuana (cannabis) produces a variety of effects including drowsiness ...
Neurons
... system. Neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are specialized to transmit information throughout the body. These highly specialized nerve cells are responsible for communicating information i ...
... system. Neurons are similar to other cells in the human body in a number of ways, but there is one key difference between neurons and other cells. Neurons are specialized to transmit information throughout the body. These highly specialized nerve cells are responsible for communicating information i ...
for research use only. not for use in diagnostic procedures. product
... Species Reactivity: The antibody has been directly tested for reactivity in Western blots with rat tissue. It is anticipated that the antibody will react with bovine, canine, chicken, human, mouse and nonhuman primate based on the fact that these species have 100% homology with the amino acid sequen ...
... Species Reactivity: The antibody has been directly tested for reactivity in Western blots with rat tissue. It is anticipated that the antibody will react with bovine, canine, chicken, human, mouse and nonhuman primate based on the fact that these species have 100% homology with the amino acid sequen ...
Option E: Neurobiology and behaviour
... E.3.5 Outline Pavlov’s experiments into conditioning of dogs. E.3.6 Outline the role of inheritance and learning in the development of birdsong in young birds. ...
... E.3.5 Outline Pavlov’s experiments into conditioning of dogs. E.3.6 Outline the role of inheritance and learning in the development of birdsong in young birds. ...
10.6: Cell Membrane Potential
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation • More EPSPs lead to greater probability of an action potential ...
... • EPSPs and IPSPs are added together in a process called summation • More EPSPs lead to greater probability of an action potential ...
Neurology, Neurons, and EEG
... Neurology is a study of the nervous system. The nervous system is categorized into two physical parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is most easily described by what it is not…it is everything BUT the spinal cord and brain. The central ne ...
... Neurology is a study of the nervous system. The nervous system is categorized into two physical parts: the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is most easily described by what it is not…it is everything BUT the spinal cord and brain. The central ne ...
Biology 231
... synapse – site of communication between a neuron and another cell neuromuscular junction – synapse between neuron and muscle fiber neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending ...
... synapse – site of communication between a neuron and another cell neuromuscular junction – synapse between neuron and muscle fiber neuroglandular junction – synapse between neuron and gland most synapses are between one neuron and another neuron Synapses Between Neurons presynaptic neuron – sending ...
Nervous System - Gordon State College
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
... either excite or inhibit firing of the receiving neuron. Excitatory messages increase the probability of an action potential. Inhibitory messages reduce the likelihood of neural firing. ...
Addiction and the Brain
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
Introducing Your Brain
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
... tiny gap, or synapse, to other neurons. Specialized molecules called receptors on the receiving neuron pick up the chemical. The branches on the receiving end of a neuron are called dendrites. Receptors there have special shapes so they can only collect one kind of neurotransmitter. In the dendrite, ...
Neuron Physiology Notes
... polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) ...
... polarized with a resting potential of (-70 mv) 2.) Neuron is stimulated by the influx of a neurotransmitters that causes sodium channels to open. Sodium moves inward causing neuron to depolarize. (-62mv) 3.) Threshold is reached when enough sodium enters the neuron to change the potential to (-55mv) ...
Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior
... • Motor Neurons (efferent) ~ 2-3 million – Sends messages from brain muscles, organs, glands ...
... • Motor Neurons (efferent) ~ 2-3 million – Sends messages from brain muscles, organs, glands ...
The Nervous System
... Synaptic Vesicles: contain the neurotransmitters. Contained near surface of synaptic endings. Acetylcholine (Ach), Noradrenalin (NA), Serotonin, Adrenalin (epinephrine) are some important neurotransmitters. Transmission across a synapse is one-way because only the ends of axons have synaptic v ...
... Synaptic Vesicles: contain the neurotransmitters. Contained near surface of synaptic endings. Acetylcholine (Ach), Noradrenalin (NA), Serotonin, Adrenalin (epinephrine) are some important neurotransmitters. Transmission across a synapse is one-way because only the ends of axons have synaptic v ...
The Nervous System
... Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
... Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Figure 48.10 Propagation of the action potential Figure 48.11 Saltatory conduction ...
Chapter 3 Neuroscience and Behavior
... (including messages from internal organs and skin) 2. motor (efferent) neurons: transmit information from brain or spinal cord to muscles and glands; help us move our arms, legs, etc. 3. interneurons: transmit messages between neurons Most neurons are interneurons (in the nervous system) 3 Parts of ...
... (including messages from internal organs and skin) 2. motor (efferent) neurons: transmit information from brain or spinal cord to muscles and glands; help us move our arms, legs, etc. 3. interneurons: transmit messages between neurons Most neurons are interneurons (in the nervous system) 3 Parts of ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...
... Na ions are transferred out into extracellular fluid. K ions are transferred into cell within cytoplasm. This is threshold potential. The permeability of the cell membrane increases, allowing Na to rush into the cell. Cells interior takes a positive charge. (Called depolarization) Depolarization swe ...