The Nervous System
... What are the two major divisions of the nervous system? What structures comprise each of these ...
... What are the two major divisions of the nervous system? What structures comprise each of these ...
LTP
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
... Synaptic Plasticity Synaptic efficacy (strength) is changing with time. Many of these changes are activity-dependent, i.e. the magnitude and direction of change depend on the activity of pre- and post-synaptic neuron. Some of the mechanisms involved: ...
Unit – M Neuron, Impulse Generation, and Reflex Arc Structures and
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
... When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, sodium gates open which allows some Na+ to enter the axoplasm (interior). Now, the inside becomes more positive than the outside by 40 mv. This is called the Upswing Phase of the action potential. The charge changes from –60 mv to +40 mv. The change is calle ...
Electrochemical Impulses
... • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
... • The wave of depolarization is followed by a wave of re-polarization • The action potential moves along the axon by jumping from one node of Ranvier to another ...
Document
... __B__12. Which description does not apply to nerve impulses? a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They travel from neuron to neuron. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. __C__13. The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are a. unconscious control b. ...
... __B__12. Which description does not apply to nerve impulses? a. They follow an all-or-none principle. c. They travel from neuron to neuron. b. They flow at various speeds. d. They flow in only one direction. __C__13. The somatic nervous system regulates activities that are a. unconscious control b. ...
Biology 360: Sensory Systems and Development 1) Describe the
... (GR). These inhibitory connections modify and sharpen the input information from the olfactory receptor neurons (ORN). The M/T output is less broad and more refined as a result of lateral inhibition than it would have been in the absence of these lateral inhibitory connections. Lateral inhibition is ...
... (GR). These inhibitory connections modify and sharpen the input information from the olfactory receptor neurons (ORN). The M/T output is less broad and more refined as a result of lateral inhibition than it would have been in the absence of these lateral inhibitory connections. Lateral inhibition is ...
The postsynaptic NMDA-receptor–PSD-95
... General Hospital, 50 Blossom Street, Boston, MA 02114, USA ...
... General Hospital, 50 Blossom Street, Boston, MA 02114, USA ...
Nervous System - Calgary Christian School
... The blood-brain barrier protects the neurons and glial cells in the brain from substances that could harm them. Unlike blood vessels in other parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons ...
... The blood-brain barrier protects the neurons and glial cells in the brain from substances that could harm them. Unlike blood vessels in other parts of the body that are relatively leaky to a variety of molecules, the blood-brain barrier keeps many substances, including toxins, away from the neurons ...
Biology and Behavior note frame
... b. All action potentials are ___________________________________________. c. A neuron does NOT fire at _______________, _______________ or _______________ but at _______________ each time it _______________. ...
... b. All action potentials are ___________________________________________. c. A neuron does NOT fire at _______________, _______________ or _______________ but at _______________ each time it _______________. ...
Slide 1
... MAPK, which regulates CREB2. Whereas CREB1 acts as an initiator of gene transcription, CREB2 acts as a repressor of gene transcription. The combined effects of activation of CREB1 and suppression of CREB2 lead to regulation of the synthesis of at least 10 proteins, only some of which are shown. ApTB ...
... MAPK, which regulates CREB2. Whereas CREB1 acts as an initiator of gene transcription, CREB2 acts as a repressor of gene transcription. The combined effects of activation of CREB1 and suppression of CREB2 lead to regulation of the synthesis of at least 10 proteins, only some of which are shown. ApTB ...
No Slide Title
... How do we study this?--- examine what ‘should’ happen and look for changes from that ‘standard’ ...
... How do we study this?--- examine what ‘should’ happen and look for changes from that ‘standard’ ...
Ch 35 PowerPoint - Damien Rutkoski
... the fluid-filled cochlea. The cochlea is lined with tiny hair cells that are pushed back and forth by these pressure waves. In response to these movements, the hair cells produce nerve impulses that are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve. ...
... the fluid-filled cochlea. The cochlea is lined with tiny hair cells that are pushed back and forth by these pressure waves. In response to these movements, the hair cells produce nerve impulses that are sent to the brain through the auditory nerve. ...
Chapter 11 Marieb
... There are over 50 NEUROTRANSMITTERS! Most neurons release two or more, and they are released differentially by stimulation rate. One NT is released at a slow rate, and another is released at a faster rate. This increases the versatility of the neuron. CLASSIFICATION of NEUROTRANSMITTERS is by chemic ...
... There are over 50 NEUROTRANSMITTERS! Most neurons release two or more, and they are released differentially by stimulation rate. One NT is released at a slow rate, and another is released at a faster rate. This increases the versatility of the neuron. CLASSIFICATION of NEUROTRANSMITTERS is by chemic ...
lecture-4-post
... the cell, all or none Myelin Sheath: contains electrical signal (prevents crossover & facilitates transmission Dendrites: receives information from other cells, multiple signals are then combined ...
... the cell, all or none Myelin Sheath: contains electrical signal (prevents crossover & facilitates transmission Dendrites: receives information from other cells, multiple signals are then combined ...
Neurotransmitter Systems
... Serotonergic Neurons The amine neurotransmitter serotonin, also called 5hydroxytryptamine and abbreviated 5-HT, is derived from the amino acid tryptophan. Serotonergic neurons are relatively few in number, but they appear to play an important role in the brain systems that regulate mood, emotional ...
... Serotonergic Neurons The amine neurotransmitter serotonin, also called 5hydroxytryptamine and abbreviated 5-HT, is derived from the amino acid tryptophan. Serotonergic neurons are relatively few in number, but they appear to play an important role in the brain systems that regulate mood, emotional ...
The Human Nervous System
... and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
... and other organelles typical of eukaryotic cells 3. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... • Read the front page of today’s activity • What is the difference between a dendrite and an axon? ...
... • Read the front page of today’s activity • What is the difference between a dendrite and an axon? ...
9.2 Electrochemical Impulses
... neurotransmitters from the end plate which will diffuse into the dendrites of an adjacent neuron and create a depolarization of the dendrites. The neuron that releases the neurotransmitters is the ...
... neurotransmitters from the end plate which will diffuse into the dendrites of an adjacent neuron and create a depolarization of the dendrites. The neuron that releases the neurotransmitters is the ...
Chapter 48 - cloudfront.net
... fuse with the terminal membrane which results in the release of neurotransmitters to the postsynaptic cells. 14. The postsynaptic cells contain ligand-gated ion channels that allow the binding of transmitted neurotransmitters. The binding of neurotransmitters may cause the opening of certain ion cha ...
... fuse with the terminal membrane which results in the release of neurotransmitters to the postsynaptic cells. 14. The postsynaptic cells contain ligand-gated ion channels that allow the binding of transmitted neurotransmitters. The binding of neurotransmitters may cause the opening of certain ion cha ...
Nerve activates contraction - Silver Falls School District
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
... stimulus depolarizes the neuron’s membrane allows Na+ to flow inside membrane exchange of ions initiates an action potential in neuron ...
Chapter 11
... 1. Most neurons release only one neurotransmitter, but some may release two or more 2. more than100 neurotransmitters known 3. Neurotransmitters may be synthesized in the axon terminal, or in the cell body and then transported. In either case, the synthesizing enzymes are made in the cell body. B. C ...
... 1. Most neurons release only one neurotransmitter, but some may release two or more 2. more than100 neurotransmitters known 3. Neurotransmitters may be synthesized in the axon terminal, or in the cell body and then transported. In either case, the synthesizing enzymes are made in the cell body. B. C ...
Slide ()
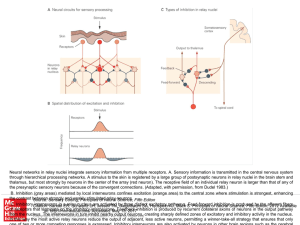
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...