teacher`s guide teacher`s guide teacher`s guide
... Martin Luther, Francesco Petrarca, Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon, Henry VII, Pope Leo X, Louis XI, the Medici family and Johannes Gutenberg were some of the movers and shakers of the Renaissance; people who, each in his or her own way, contributed to an era that changed the European la ...
... Martin Luther, Francesco Petrarca, Isabella of Castile and Ferdinand of Aragon, Henry VII, Pope Leo X, Louis XI, the Medici family and Johannes Gutenberg were some of the movers and shakers of the Renaissance; people who, each in his or her own way, contributed to an era that changed the European la ...
03. Flemish Art and European Culture
... away from the traditional medieval technique of portraying the human figure as a stiff, flat, two-dimensional character. An artist far ahead of his time, Giotto began to protray humans as rounded, proportioned, and naturalistic. His work influenced the development of Renaissance art more than a cent ...
... away from the traditional medieval technique of portraying the human figure as a stiff, flat, two-dimensional character. An artist far ahead of his time, Giotto began to protray humans as rounded, proportioned, and naturalistic. His work influenced the development of Renaissance art more than a cent ...
The Renaissance
... surronded Italians and remined them of their past. It was natural that they became interested in Greek and Roman art and tried to make their own art as good. 2.By 1300s , Italy’s cities had become were wealthy. They could afford to pay painters, sculptors , architects and other artists to produce ne ...
... surronded Italians and remined them of their past. It was natural that they became interested in Greek and Roman art and tried to make their own art as good. 2.By 1300s , Italy’s cities had become were wealthy. They could afford to pay painters, sculptors , architects and other artists to produce ne ...
Recovery and Rebirth: The Age of the Renaissance
... popes, the papal residency in Avignon and the Great Schism enabled cities such as Urbino, Bologna, and Ferrara to become independent Renaissance popes of the 15th century spent much time attempting to reestablish their control over the Papal States ...
... popes, the papal residency in Avignon and the Great Schism enabled cities such as Urbino, Bologna, and Ferrara to become independent Renaissance popes of the 15th century spent much time attempting to reestablish their control over the Papal States ...
Renaissance_Times_IP.. - Medieval Fantasies Company
... work did they do? What kind of education did they have? What was it like to be a peasant, middle class or member of a noble family? 2. Explore the literature of the Renaissance period. Select an author and read a book or watch a video from one of his/her works. Compare the dialogue of then to today’ ...
... work did they do? What kind of education did they have? What was it like to be a peasant, middle class or member of a noble family? 2. Explore the literature of the Renaissance period. Select an author and read a book or watch a video from one of his/her works. Compare the dialogue of then to today’ ...
World History
... Luther created the modern Church service with Bible readings, preaching, and songs to replace the Catholic mass. Many politicians and noblemen supported Luther because they were tired of the Church meddling in their affairs. June 1524- German peasants revolt. Luther supports the nobles because he fe ...
... Luther created the modern Church service with Bible readings, preaching, and songs to replace the Catholic mass. Many politicians and noblemen supported Luther because they were tired of the Church meddling in their affairs. June 1524- German peasants revolt. Luther supports the nobles because he fe ...
Recovery and Rebirth: The Age of the Renaissance
... popes, the papal residency in Avignon and the Great Schism enabled cities such as Urbino, Bologna, and Ferrara to become independent Renaissance popes of the 15th century spent much time attempting to reestablish their control over the Papal States ...
... popes, the papal residency in Avignon and the Great Schism enabled cities such as Urbino, Bologna, and Ferrara to become independent Renaissance popes of the 15th century spent much time attempting to reestablish their control over the Papal States ...
к½Â·°l¬F
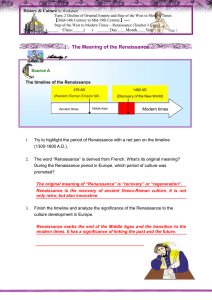
... With reference to Source A, analyze the important influence of Renaissance on Europe. i) Advocated new thoughts and broke the constraint on thoughts in the Middle Ages; ii) Weakened the authorities of the Roman Catholic Church and promoted the religious reform; iii) Paid attention to human’s value, ...
... With reference to Source A, analyze the important influence of Renaissance on Europe. i) Advocated new thoughts and broke the constraint on thoughts in the Middle Ages; ii) Weakened the authorities of the Roman Catholic Church and promoted the religious reform; iii) Paid attention to human’s value, ...
***DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM*** UNIT 1 EXAM AGE OF
... Match the person (letter) with the number that describes what they are known for: A. Shakespeare B. Michelangelo C. Da Vinci 15. ___ Playwright and poet whose work changed the way people thought about and interacted with literature 16. ___ Painter and sculptor close with the Medici family famous for ...
... Match the person (letter) with the number that describes what they are known for: A. Shakespeare B. Michelangelo C. Da Vinci 15. ___ Playwright and poet whose work changed the way people thought about and interacted with literature 16. ___ Painter and sculptor close with the Medici family famous for ...
Renaissance and Reformation
... • Gutenberg: invented a new type of printing press. Used movable type.1st Book printed= Bible • Books suddenly within reach of ordinary person. ...
... • Gutenberg: invented a new type of printing press. Used movable type.1st Book printed= Bible • Books suddenly within reach of ordinary person. ...
Humanism
... .themselves as ushering in the modern age, as distinct from the ancient and medieval eras Study of the Renaissance might well center on five interrelated issues. First, although Renaissance thinkers often tried to associate themselves with classical antiquity and to dissociate themselves from the Mi ...
... .themselves as ushering in the modern age, as distinct from the ancient and medieval eras Study of the Renaissance might well center on five interrelated issues. First, although Renaissance thinkers often tried to associate themselves with classical antiquity and to dissociate themselves from the Mi ...
r enaissance t imes - Girl Scout Council`s Own Badges
... work did they do? What kind of education did they have? What was it like to be a peasant, middle class or member of a noble family? 2. Explore the literature of the Renaissance period. Select an author and read a book or watch a video from one of his/her works. Compare the dialogue of then to today’ ...
... work did they do? What kind of education did they have? What was it like to be a peasant, middle class or member of a noble family? 2. Explore the literature of the Renaissance period. Select an author and read a book or watch a video from one of his/her works. Compare the dialogue of then to today’ ...
The Renaissance - Cabarrus County Schools
... to the fact that a number of lords became increasingly powerful. They brought peace and stability to numerous regions. As a result, people felt more safe and secure. Merchants began to travel more freely and trade their goods. Wherever merchants settled, builders and other tradespeople gathered arou ...
... to the fact that a number of lords became increasingly powerful. They brought peace and stability to numerous regions. As a result, people felt more safe and secure. Merchants began to travel more freely and trade their goods. Wherever merchants settled, builders and other tradespeople gathered arou ...
Florence - International School of Sosua
... • Renaissance ideas were most gloriously expressed in its paintings, sculpture, and architecture. • Wealthy patrons played a major role in this artistic growth. • Popes, Princes, and wealthy merchants supported the work of hundreds of artists. ...
... • Renaissance ideas were most gloriously expressed in its paintings, sculpture, and architecture. • Wealthy patrons played a major role in this artistic growth. • Popes, Princes, and wealthy merchants supported the work of hundreds of artists. ...
Renaissance notes
... The Invention of Printing: Encourages Literature 1. ca. 1450: printing with movable type was invented by a German, Johan Gutenberg. 2. During the Middle Ages books had to be hand copied (time consuming and expensive) on parchment (goat skin). 3. 12th Century: Europeans discovered paper from the Mosl ...
... The Invention of Printing: Encourages Literature 1. ca. 1450: printing with movable type was invented by a German, Johan Gutenberg. 2. During the Middle Ages books had to be hand copied (time consuming and expensive) on parchment (goat skin). 3. 12th Century: Europeans discovered paper from the Mosl ...
Northern Ren Art
... The Northern Renaissance ended with a Mannerist phase, which lasted a generation longer in the North than it did in Italy, where it was outmoded by 1600. ...
... The Northern Renaissance ended with a Mannerist phase, which lasted a generation longer in the North than it did in Italy, where it was outmoded by 1600. ...
The Renaissance
... • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas and allowed more people to become educated. ...
... • The movable type printing press and the production and sale of books (Gutenberg Bible) helped disseminate ideas and allowed more people to become educated. ...
Renaissance Big Book
... The important thing about the Renaissance is that new inventions and trade routes brought new ideas to Europe that changed the way people thought and lived. • As new ideas spread throughout Europe, a group of resourceful, talented people made important contributions to the arts, science, medicine, ...
... The important thing about the Renaissance is that new inventions and trade routes brought new ideas to Europe that changed the way people thought and lived. • As new ideas spread throughout Europe, a group of resourceful, talented people made important contributions to the arts, science, medicine, ...
The Renaissance
... Johann Gutenberg printed the Bible using the first printing press and printing inks. • Impact: • Printed books were cheaper and easier to produce. • With books more readily available, more people learned to read. (vernacular) • Readers gained access to a broad range of knowledge and ideas. ...
... Johann Gutenberg printed the Bible using the first printing press and printing inks. • Impact: • Printed books were cheaper and easier to produce. • With books more readily available, more people learned to read. (vernacular) • Readers gained access to a broad range of knowledge and ideas. ...
Sejarah Senibina Barat
... parts of the body are related to one another in ratios of whole numbers, and these ratios should be used in the design of architecture. ...
... parts of the body are related to one another in ratios of whole numbers, and these ratios should be used in the design of architecture. ...
Chapter 15: The Renaissance
... In Northern Europe the most emotionally-charged images were made in ____________ {{Germany}} ...
... In Northern Europe the most emotionally-charged images were made in ____________ {{Germany}} ...
Chapter 15: The Renaissance
... In Northern Europe the most emotionally-charged images were made in ____________ {{Germany}} ...
... In Northern Europe the most emotionally-charged images were made in ____________ {{Germany}} ...
How Did Artists Help Spread the Ideas of the Renaissance?
... nobles paid artists to create portraits of them and their families. Since photography did not yet exist, this was the only way to record the likeness of a person. Now that it was important for good artists to be recognized for their work, and art became a marketable commodity, artists began to sign ...
... nobles paid artists to create portraits of them and their families. Since photography did not yet exist, this was the only way to record the likeness of a person. Now that it was important for good artists to be recognized for their work, and art became a marketable commodity, artists began to sign ...
World History Chapter 13 Section 1
... - He dissected corpses to learn about muscles and bones and he made sketches of nature and of models in his studio. - The Mona Lisa, which is a portrait of a woman with a mysterious smile. - The Last Supper, shows Jesus and his apostles on the night before the crucifixion. - His talents and accompli ...
... - He dissected corpses to learn about muscles and bones and he made sketches of nature and of models in his studio. - The Mona Lisa, which is a portrait of a woman with a mysterious smile. - The Last Supper, shows Jesus and his apostles on the night before the crucifixion. - His talents and accompli ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.