Reticular formation
... states .In REM sleep without atonia, lesions to locus ceruleus disrupt the excitatory connection to mangocellular column disable the hyperpolarization of the alpha spinal motorneurons. In humans after extensive neurologic evaluations who have suffering from both idiopathic and symptomatic forms have ...
... states .In REM sleep without atonia, lesions to locus ceruleus disrupt the excitatory connection to mangocellular column disable the hyperpolarization of the alpha spinal motorneurons. In humans after extensive neurologic evaluations who have suffering from both idiopathic and symptomatic forms have ...
neurons
... Biological psychology is the scientific study of the biological bases of behavior and mental processes. This area of research is also called biopsychology. Both terms emphasize the idea of a biological approach to the study of psychological processes. Biological psychology is one of the scientific d ...
... Biological psychology is the scientific study of the biological bases of behavior and mental processes. This area of research is also called biopsychology. Both terms emphasize the idea of a biological approach to the study of psychological processes. Biological psychology is one of the scientific d ...
THE NEUROBIOLOGY OF ADDICTION: USING EASTERN
... • What new research shows: A review of more than a dozen massage studies conducted by the Touch Research Institute at the University of Miami School of Medicine concludes that massage therapy relieves depression and anxiety by affecting the body's biochemistry. • In a series of studies including abo ...
... • What new research shows: A review of more than a dozen massage studies conducted by the Touch Research Institute at the University of Miami School of Medicine concludes that massage therapy relieves depression and anxiety by affecting the body's biochemistry. • In a series of studies including abo ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Parkinson’s Disease: wide-eyed, unblinking expression, involuntary tremor, muscle rigidity, shuffling gait - due to dopamine deficiency, or the malfunction of dopamine receptors Alzheimer’s Disease: characterized by loss of memory, senility, deterioration of cells in the basal nuclei, presence of ta ...
... Parkinson’s Disease: wide-eyed, unblinking expression, involuntary tremor, muscle rigidity, shuffling gait - due to dopamine deficiency, or the malfunction of dopamine receptors Alzheimer’s Disease: characterized by loss of memory, senility, deterioration of cells in the basal nuclei, presence of ta ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... The fibrous tunic, the external layer of the eye wall, is composed of the anterior cornea and the posterior sclera. The cornea refracts incoming light rays into the interior of the eye, while the tough, white sclera provides for eye shape and protects its delicate internal components. The vascular t ...
... The fibrous tunic, the external layer of the eye wall, is composed of the anterior cornea and the posterior sclera. The cornea refracts incoming light rays into the interior of the eye, while the tough, white sclera provides for eye shape and protects its delicate internal components. The vascular t ...
Answers to WHAT DID YOU LEARN questions
... The fibrous tunic, the external layer of the eye wall, is composed of the anterior cornea and the posterior sclera. The cornea refracts incoming light rays into the interior of the eye, while the tough, white sclera provides for eye shape and protects its delicate internal components. The vascular t ...
... The fibrous tunic, the external layer of the eye wall, is composed of the anterior cornea and the posterior sclera. The cornea refracts incoming light rays into the interior of the eye, while the tough, white sclera provides for eye shape and protects its delicate internal components. The vascular t ...
File
... ____________________________ are feelings that occur when the brain interprets sensory impulses. What does the term projection mean when referring to the brain and sensations? During sensory ____________________, sensory impulses are sent at decreasing rates until receptors fail to send impulses unl ...
... ____________________________ are feelings that occur when the brain interprets sensory impulses. What does the term projection mean when referring to the brain and sensations? During sensory ____________________, sensory impulses are sent at decreasing rates until receptors fail to send impulses unl ...
Five basic concepts illustrate the usefulness of neuroscience to
... particularly helpful in mitigating depression. If clients are sad, encourage them to walk or run. Not only will they feel better, but their brains will be expanding as well. 3) The importance of attention and focus: Our basic concepts of attending behavior and attention — required for the learning p ...
... particularly helpful in mitigating depression. If clients are sad, encourage them to walk or run. Not only will they feel better, but their brains will be expanding as well. 3) The importance of attention and focus: Our basic concepts of attending behavior and attention — required for the learning p ...
The Body and the Brain
... Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the axon are called axon terminals. Messages are se ...
... Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the axon are called axon terminals. Messages are se ...
L3 Drugs-Psychoactive drugs
... of relieving severe pain, narcotics are commonly abused drugs because of their euphoric effect and highly addictive quality ...
... of relieving severe pain, narcotics are commonly abused drugs because of their euphoric effect and highly addictive quality ...
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM - Tamalpais Union High School District
... Dopamine - cont’d • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
... Dopamine - cont’d • Dopamine also sends signals that help coordinate your skeletal muscle movements • Parkinson’s Disease – deficient dopamine production – tremors ...
intro to psych brain and behavior
... Firing is an all or nothing event The neuron either fires, or doesn’t fire ...
... Firing is an all or nothing event The neuron either fires, or doesn’t fire ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
... certain stimulus (you have NO control over it). ...
White blood cells play important roles in protecting us from infections
... spontaneous recovery. I hypothesize that the migrated white blood cells serve to recover neuronal damage. In this project, I focus on this interesting phenomenon, which can be detected rarely, but occurs spontaneously, and aim to clarify the physiological significance. 4. Anticipated effects and fut ...
... spontaneous recovery. I hypothesize that the migrated white blood cells serve to recover neuronal damage. In this project, I focus on this interesting phenomenon, which can be detected rarely, but occurs spontaneously, and aim to clarify the physiological significance. 4. Anticipated effects and fut ...
Development & Neuroplasticity - U
... • Regions of several different chromosomes have been implicated in the vulnerability to schizophrenia ...
... • Regions of several different chromosomes have been implicated in the vulnerability to schizophrenia ...
Now!
... including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. b. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subd ...
... including parts of the neuron and the process of transmission of a signal between neurons. b. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subd ...
Nervous System
... Sensory receptors on finger reacts to stimulus (heat) Impulse is carried to the spinal cord by a sensory neuron In the spinal cord, the impulse is transferred by an interneuron to motor neuron Motor neurons conducts the impulse to an effector (arm ...
... Sensory receptors on finger reacts to stimulus (heat) Impulse is carried to the spinal cord by a sensory neuron In the spinal cord, the impulse is transferred by an interneuron to motor neuron Motor neurons conducts the impulse to an effector (arm ...
UNIT XI
... Parkinson’s Disease • Destruction of the pars compacta in the substantia nigra • Prevents activity of dopamine-secreting nerve fibers to the caudate nucleus. • Dopamine = Inhibitor • Causes – Rigidity of musculature – Involuntary tremor (3-6 Hz) – Difficulty initiating movements ...
... Parkinson’s Disease • Destruction of the pars compacta in the substantia nigra • Prevents activity of dopamine-secreting nerve fibers to the caudate nucleus. • Dopamine = Inhibitor • Causes – Rigidity of musculature – Involuntary tremor (3-6 Hz) – Difficulty initiating movements ...
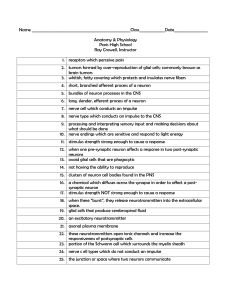
Name
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
... 10. nerve endings which are sensitive and respond to light energy 11. stimulus strength strong enough to cause a response 12. when one pre-synaptic neuron affects a response in two post-synaptic neurons 13. ovoid glial cells that are phagocytic 14. not having the ability to reproduce 15. clusters of ...
Learning, Memory and Perception.
... result from natural selection (evolutionary “learning”), and the means to sculpt each individual brain with its own, unique, life history. Brains contain two main cell types: neurons, and support cells or glia. We will focus here mainly on neurons, even though it is clear that glia play many fundame ...
... result from natural selection (evolutionary “learning”), and the means to sculpt each individual brain with its own, unique, life history. Brains contain two main cell types: neurons, and support cells or glia. We will focus here mainly on neurons, even though it is clear that glia play many fundame ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
... • Memory loss • Confusion • Problems speaking, understanding • Time/place? • Misplacing things • Mood swings • Personality change (suspiciousness) • Lack of interest ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 40.1 Periodic activation in sleep cycles
... are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular pathways remain to be demonstrated, and, in many cases, the neuronal archit ...
... are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular pathways remain to be demonstrated, and, in many cases, the neuronal archit ...
Common Neurotransmitters: Criteria for Neurotransmitters, Key
... Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule must be present in the brain and distributed unevenly and enzymes that help to create the neurotransmitter must be present in ...
... Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule must be present in the brain and distributed unevenly and enzymes that help to create the neurotransmitter must be present in ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.