1 - PBL Group 14
... cell and transiently increases its permeability to particular ions. Most excitatory neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction cause an increase in Na+ and K+ permeability. This results in a net inward current carried mainly by Na+, which depolarizes the cell and increase ...
... cell and transiently increases its permeability to particular ions. Most excitatory neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction cause an increase in Na+ and K+ permeability. This results in a net inward current carried mainly by Na+, which depolarizes the cell and increase ...
Early Brain Development
... Parts of the Brain The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information ...
... Parts of the Brain The brain has different sections, each section controls a specific function. One of the most important parts is the cortex. The cortex is the part of the brain that its growth permits more complex learning. Neurons in the baby’s brain are tiny messengers that transmit information ...
Gene Mutation Story
... Gene Mutation Story -Alzheimer’s It was just a typical day in the brain, no different than it always was, all cells seemed to be in order working in tip top shape, blood was being pumped through the brain, and the host William who was 60 years old was sound asleep. But there was a subtle disturbance ...
... Gene Mutation Story -Alzheimer’s It was just a typical day in the brain, no different than it always was, all cells seemed to be in order working in tip top shape, blood was being pumped through the brain, and the host William who was 60 years old was sound asleep. But there was a subtle disturbance ...
cocaine
... the central nervous system. Stimulant- A class of drugs that enhance brain activity. Prescription stimulants were used historically to treat asthma, obesity, neurological disorders, & a variety of other ailments, before their potential for abuse and addiction became apparent. ...
... the central nervous system. Stimulant- A class of drugs that enhance brain activity. Prescription stimulants were used historically to treat asthma, obesity, neurological disorders, & a variety of other ailments, before their potential for abuse and addiction became apparent. ...
Review for Quiz 2 Fixed Action Pattern Types of neurons Anatomy of
... Worm Grunting Facial Fusiform Sulcus Hippocampal functions ...
... Worm Grunting Facial Fusiform Sulcus Hippocampal functions ...
Neurotransmitters: Acetylcholine (Ach) transmitter plays a role in
... *A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often…But it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed* ...
... *A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often…But it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed* ...
Option E: Neurobiology and behaviour
... E.4.2 Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. E.4.4 ...
... E.4.2 Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. E.4.4 ...
Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior
... Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
... Synaptic gap or cleft-a tiny gap between the receiving neuron and sending neuron ...
Nerve Notes
... A. Cell body - cell organelles, nuclei B. Dendrites – branched extensions that receive information from other neurons or receptors C. Axon – tube that carries action potential D. Myelin Sheath – insulation along axon, made by Schwan cells 1. Nodes of Ranvier – gaps between Myelin 2. White matter – a ...
... A. Cell body - cell organelles, nuclei B. Dendrites – branched extensions that receive information from other neurons or receptors C. Axon – tube that carries action potential D. Myelin Sheath – insulation along axon, made by Schwan cells 1. Nodes of Ranvier – gaps between Myelin 2. White matter – a ...
Carrie Heath
... the heart slowed down as well as the second heart that was connected to the first by ringers solution. What was the cause of this? What type of drug that we have discussed in class could be used as a cholinergic antagonist, and what would be the effect on the two hearts? 7. What are SNARE proteins a ...
... the heart slowed down as well as the second heart that was connected to the first by ringers solution. What was the cause of this? What type of drug that we have discussed in class could be used as a cholinergic antagonist, and what would be the effect on the two hearts? 7. What are SNARE proteins a ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... The Hippocampus and Neurons are parts of the brain that fascinate me. This is an amazing organ in which electricity (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus a ...
... The Hippocampus and Neurons are parts of the brain that fascinate me. This is an amazing organ in which electricity (synapses) coupled with this organ’s ability to control every function in the human body make this organ a never-ending source of research. I narrowed this project to the hippocampus a ...
A1984SR69800001
... noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit then current notions about transmitters. By the end of the 1960s, however, in ...
... noradrenaline, would have a prominent role in the central nervous system (CNS). Amino acids, with well-identified roles in cellular metabolism, protein synthesis, etc.—and found abundantly throughout the brain—did not fit then current notions about transmitters. By the end of the 1960s, however, in ...
Runx1t1- Exploring its role as a transcriptional regulator in the
... diversity in the nervous system is created. A classic model system in which to address this question is the peripheral nervous system. Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion are located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into m ...
... diversity in the nervous system is created. A classic model system in which to address this question is the peripheral nervous system. Sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion are located along the spinal cord; they derive during development from common progenitor cells which differentiate into m ...
An Update on Alzheimer`s Disease by Dr. David L. (“Woody
... disease, with current estimates of over five million sufferers in the United States alone. It is the nation’s sixth leading cause of death. The causes and underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s are not known. Although it is typically diagnosed in people over 65 years of age, researchers do understand ...
... disease, with current estimates of over five million sufferers in the United States alone. It is the nation’s sixth leading cause of death. The causes and underlying mechanisms of Alzheimer’s are not known. Although it is typically diagnosed in people over 65 years of age, researchers do understand ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... The neuron consists of a cell body containing the nucleus, cytoplasm, and an electrically excitable output fiber, the axon. Most axons also give rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. Synapses, from the Greek word meaning “to clasp together,” are the contact points where one ...
... The neuron consists of a cell body containing the nucleus, cytoplasm, and an electrically excitable output fiber, the axon. Most axons also give rise to many smaller branches before ending at nerve terminals. Synapses, from the Greek word meaning “to clasp together,” are the contact points where one ...
Chapter 10 Somatic and Special Senses
... ________________ cavity, which is filled with a fluid called _____________________ humor. Lens: What is the ability of the lens to change its shape called? Why is this important? Adjusting for light and dark conditions: The ______________________ is a thin, smooth muscle that adjusts the amount of l ...
... ________________ cavity, which is filled with a fluid called _____________________ humor. Lens: What is the ability of the lens to change its shape called? Why is this important? Adjusting for light and dark conditions: The ______________________ is a thin, smooth muscle that adjusts the amount of l ...
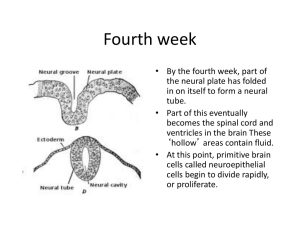
Fourth week
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
... in short-term memory, and other structures involved in the olfactory pathways Next, the telencephalon produces the basal ganglia, which will eventually contain structures that control movement, sensory information, and some types of learning. The amygdala will eventually help the brain attach emotio ...
Document
... cord and form dorsal root of spinal nerve -Cell bodies are grouped outside the spinal cord in dorsal root ganglia Motor neurons: -Axons leave from the ventral surface and form ventral root of spinal nerve -Cell bodies are located in the spinal cord ...
... cord and form dorsal root of spinal nerve -Cell bodies are grouped outside the spinal cord in dorsal root ganglia Motor neurons: -Axons leave from the ventral surface and form ventral root of spinal nerve -Cell bodies are located in the spinal cord ...
Gene Section CMKOR1 (chemokine orphan receptor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Local order: Telomeric to IQCA. Centromeric to COPS8. Note: RDC1 was originally thought to be the receptor for VIP. ...
... Local order: Telomeric to IQCA. Centromeric to COPS8. Note: RDC1 was originally thought to be the receptor for VIP. ...
Sensory systems
... somatosensory cortex (SI) in the parietal lobe • it is located caudally to the sulcus centralis on the gyrus postcentralis (Br3a, Br3b, Br2, Br1) • the secondary somatosensory area (SII) is located laterally; input from the SI • behind SI, posterior parietal cortex (Br5, Br7) also has somatosensory ...
... somatosensory cortex (SI) in the parietal lobe • it is located caudally to the sulcus centralis on the gyrus postcentralis (Br3a, Br3b, Br2, Br1) • the secondary somatosensory area (SII) is located laterally; input from the SI • behind SI, posterior parietal cortex (Br5, Br7) also has somatosensory ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... principle of nerve cells. What we feel is dependent on the amount of neurons that fire. ...
... principle of nerve cells. What we feel is dependent on the amount of neurons that fire. ...
Psych 9A. Lec. 05 PP Slides: Brain and Nervous System
... central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
... central nervous system: CNS) Efferent (away from or out of the CNS) Many simple reflexes rely on circuits within the spine: no need for brain involvement. ...
The Mechanical Senses: Vestibular and Somatosensation
... SOMATOSENSATION: sensation of the body/skin Sensory Neuron (or “Sensory Receptor”) Types 1) Tactile: response to being touched (“light” and “deep” touch) Ruffini ending, Meissner’s corpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle The axons from these receptors are myelinated! 2) Pain: response to noxious stimulus 3) ...
... SOMATOSENSATION: sensation of the body/skin Sensory Neuron (or “Sensory Receptor”) Types 1) Tactile: response to being touched (“light” and “deep” touch) Ruffini ending, Meissner’s corpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle The axons from these receptors are myelinated! 2) Pain: response to noxious stimulus 3) ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.