Nolte – Chapter 1 (Introduction to the Nervous
... o Unipolar Only one axon that emits from one cell body. Nothing else. An example of this would be sensory neurons with cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia. Usually developmental. o PseduoUnipolar Cell body is pinched off and there are no dendrites. Carries axon potentials back from skin ...
... o Unipolar Only one axon that emits from one cell body. Nothing else. An example of this would be sensory neurons with cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglia. Usually developmental. o PseduoUnipolar Cell body is pinched off and there are no dendrites. Carries axon potentials back from skin ...
1 1. The central nervous system (CNS) includes the A. brain and
... 39. A chronic progressive movement disorder caused by the death of neurons in the substantia nigra which would normally produce dopamine. Diagnosis must include the presence of one of more of the four most common primary motor symptoms: resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instabilit ...
... 39. A chronic progressive movement disorder caused by the death of neurons in the substantia nigra which would normally produce dopamine. Diagnosis must include the presence of one of more of the four most common primary motor symptoms: resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instabilit ...
OL Chapter 2
... • Stage 1 sleep: slowed breathing, irregular brain waves, hallucinations/images • Stage 2 sleep: more fully asleep but still could be awakened; “spindles” of activity in brain waves • Stage 3 sleep: a transition to Stage 4 (omitted in some models) • Stage 4 sleep: Such deep sleep that many kids wet ...
... • Stage 1 sleep: slowed breathing, irregular brain waves, hallucinations/images • Stage 2 sleep: more fully asleep but still could be awakened; “spindles” of activity in brain waves • Stage 3 sleep: a transition to Stage 4 (omitted in some models) • Stage 4 sleep: Such deep sleep that many kids wet ...
My Secret Role in True Happiness: A Story of a Neuron
... My creation began from an original stem cell, which was produced from a collection of cells called an embryonic disk. The stem cell eventually developed into precursor cells for neurons. My precursor cell then produced what is called a neuroblast, or a neuron with an unknown fate. It was at this poi ...
... My creation began from an original stem cell, which was produced from a collection of cells called an embryonic disk. The stem cell eventually developed into precursor cells for neurons. My precursor cell then produced what is called a neuroblast, or a neuron with an unknown fate. It was at this poi ...
AAAS Summary
... Obstetric and pediatric patients sometimes have to undergo complex surgical procedures that require prolonged anesthesia. In essence, the nervous system must be put to sleep, sometimes for many hours, by drugs that suppress neuronal activity. All drugs that have proven useful for this purpose are ei ...
... Obstetric and pediatric patients sometimes have to undergo complex surgical procedures that require prolonged anesthesia. In essence, the nervous system must be put to sleep, sometimes for many hours, by drugs that suppress neuronal activity. All drugs that have proven useful for this purpose are ei ...
Slide 1
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
... The Nervous System • The control center for the entire body. • Made up of brain, spinal cord, and neurons. ...
Nerve Cell Impulses
... individuals may find it impossible to move forward voluntarily. Low dopamine may also be implicated in mental stasis. Some drugs (LSD + hallucinogens) are thought to work on the dopamine system. ...
... individuals may find it impossible to move forward voluntarily. Low dopamine may also be implicated in mental stasis. Some drugs (LSD + hallucinogens) are thought to work on the dopamine system. ...
Chapter 48: The Nervous System
... Parietal- reading, somatosensory association, speech, taste ...
... Parietal- reading, somatosensory association, speech, taste ...
Synaptic Transmission and Neurotransmitters
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
... – Principal excitatory NT in central nervous system – Critical for learning: it is Glutamate and the NMDA receptors that allow for long term potentiation – May play significant role in schizophrenia: disrupts regulation of DA, NE, Ach, 5HT. • Affects memory formation • Affects arousal • Affects proc ...
Serotonin, also known as 5-HT (5
... found at the synapses of certain neurons. That is, it is released by the tip of one stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neuro ...
... found at the synapses of certain neurons. That is, it is released by the tip of one stimulated neuron, and recognized by an adjacent neuron, causing it to fire and so on. In this way, the nerve impulse is propagated throughout the nervous system. Note that after a nerve fires at a synapse, the neuro ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... • Dendrite: receives info from neighboring neurons. • Cell body: living portion of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles. • Axon: sends info to neighboring neurons. ...
... • Dendrite: receives info from neighboring neurons. • Cell body: living portion of the neuron; contains the nucleus and organelles. • Axon: sends info to neighboring neurons. ...
Chapter 3 (part 2) – Protein Function
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
... • Enzymes and bound ligand go through a number of intermediate forms of different geometry. They are all called transition states. • The energy that it takes to get to the most unstable transition state is called the activation energy. • Enzymes speed reactions by selectively stabilizing the transi ...
Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... Neurons: nerve cells- send and receive information • Glial cells: support and protect the neurons • Myelination: coats the neural pathways, allows for efficient and fast signals to travel • Reflex behavior: controlled by lower brain centers, ...
... Neurons: nerve cells- send and receive information • Glial cells: support and protect the neurons • Myelination: coats the neural pathways, allows for efficient and fast signals to travel • Reflex behavior: controlled by lower brain centers, ...
Chapter 7 States of Consciousness II
... growth hormone. Older people release less of this hormone and sleep less. ...
... growth hormone. Older people release less of this hormone and sleep less. ...
mechanisms of neurotransmitter receptor biogenesis and trafficking
... little is known. For example, we now know that GABA is found in the endoplasmic reticulum. We do not know how it gets inside this cell organelle but assume it is transported there by a protein. Because it has been known for decades that GABA is present inside mitochondria, a cell organelle involved ...
... little is known. For example, we now know that GABA is found in the endoplasmic reticulum. We do not know how it gets inside this cell organelle but assume it is transported there by a protein. Because it has been known for decades that GABA is present inside mitochondria, a cell organelle involved ...
BIOL 241 Autonomic Nervous System 1 I. Visceral Reflexes A. All
... 2. cardiac muscle 3. smooth muscle B. Autonomic neurons 1. not somatic 2. requires two neurons a. preganglionic b. postganglionic C. Somatic vs. visceral effectors 1. skeletal muscle (somatic) 2. visceral effectors a. heartb. smooth musclec. ANS activity d. denervation hypersensitivity D. Receptors ...
... 2. cardiac muscle 3. smooth muscle B. Autonomic neurons 1. not somatic 2. requires two neurons a. preganglionic b. postganglionic C. Somatic vs. visceral effectors 1. skeletal muscle (somatic) 2. visceral effectors a. heartb. smooth musclec. ANS activity d. denervation hypersensitivity D. Receptors ...
A.1 Neural Development
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
... An axon grows from each immature neuron in response to chemical stimuli Some axons extend beyond the neural tube to reach other parts of the body A developing neuron forms multiple synapses Synapses that are nut used do not persist Neural pruning involves the loss of unused neurons The plasticity of ...
NPLEX Combination Review Introductory Chapter – Concepts
... – Actions of the drug mimic parasympathetic activity to the extent that receptors are activated ...
... – Actions of the drug mimic parasympathetic activity to the extent that receptors are activated ...
PPT Guide Brain Development
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
... Brain growth and development There is a fivefold increase in the number of dendrites in cortex from birth to age 2 years, as a result approximately ___________________ new connections may be established per neuron. This is called “___________________________” These connections are necessary because ...
Gamma band activity in the nuclei of the Reticular Activating System
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
... characterized by low amplitude, high frequency oscillatory activity in the gamma band range (~20-100 Hz). Gamma frequency oscillations have been proposed to participate in conscious perception, problem solving, memory, and rapid eye movement (REM) sleep. It has been suggested that such coherent acti ...
Biology and Behaviour
... Key opens an ion channel Causes an action potential in the next neuron…. Great place for drug interactions ...
... Key opens an ion channel Causes an action potential in the next neuron…. Great place for drug interactions ...
Slide ()
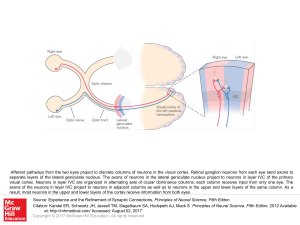
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
... Afferent pathways from the two eyes project to discrete columns of neurons in the visual cortex. Retinal ganglion neurons from each eye send axons to separate layers of the lateral geniculate nucleus. The axons of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus project to neurons in layer IVC of the prima ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.