Previous lecture
... Bi / CNS 150 Lecture 10 Synaptic inhibition; cable properties of neurons; electrical integration in cerebellum Monday, October 19, 2015 Henry Lester Chapter 2 (p. 22-30); Chapter 10 (223-234) ...
... Bi / CNS 150 Lecture 10 Synaptic inhibition; cable properties of neurons; electrical integration in cerebellum Monday, October 19, 2015 Henry Lester Chapter 2 (p. 22-30); Chapter 10 (223-234) ...
Nervous System - APBio
... • Sensory Neurons – transmit info from sensors (that detect internal or external stimuli) to interneurons (the CNS) • Interneurons – either the spinal cord or brain, integrate the sensory input and send message the motor neurons • Motor Neurons – send message from interneurons to effector cells (mus ...
... • Sensory Neurons – transmit info from sensors (that detect internal or external stimuli) to interneurons (the CNS) • Interneurons – either the spinal cord or brain, integrate the sensory input and send message the motor neurons • Motor Neurons – send message from interneurons to effector cells (mus ...
biopharmaceutical and bioproducts
... BIOPHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOPRODUCTS BY PUAN AZDUWIN BINTI KHASRI 6 DECEMBER 2012 ...
... BIOPHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOPRODUCTS BY PUAN AZDUWIN BINTI KHASRI 6 DECEMBER 2012 ...
Development of a paradigm to investigate mechanisms of divided
... In Alzheimer’s disease impaired attention can be detected almost immediately after the first signs of memory loss and is considered to be a major cause of difficulties in the patients everyday life in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Several types of attention are recognized such as divided, ...
... In Alzheimer’s disease impaired attention can be detected almost immediately after the first signs of memory loss and is considered to be a major cause of difficulties in the patients everyday life in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Several types of attention are recognized such as divided, ...
Awakenings and Neurotransmitters
... • 100 years later it was thought to involve a chemical deficiency • In the 1960s, scientists traced the problem to nerve cells failing to produce dopamine ...
... • 100 years later it was thought to involve a chemical deficiency • In the 1960s, scientists traced the problem to nerve cells failing to produce dopamine ...
Design principles of sensory receptors
... the 7-TM protein does not couple to a G protein. Instead, it functions as an ionotropic receptor (Figure 1B) since its activation gates an ion channel (Nagel et al., 2005). GPCRs may form homomeric (Figure 1C) as well as heteromeric dimers (Figure 1D). For class A GPCRs instable homodimerization ha ...
... the 7-TM protein does not couple to a G protein. Instead, it functions as an ionotropic receptor (Figure 1B) since its activation gates an ion channel (Nagel et al., 2005). GPCRs may form homomeric (Figure 1C) as well as heteromeric dimers (Figure 1D). For class A GPCRs instable homodimerization ha ...
Ch 2 neurotrans and nervous sys
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
Chapter 2 figures 2.7 to 2.12
... Figure 2.7. Number of neural impulses in selected single cells of the monkey brain when shown differing pictures. These neurons fire the most when a face is present (Washmuth et al. 1994). ...
... Figure 2.7. Number of neural impulses in selected single cells of the monkey brain when shown differing pictures. These neurons fire the most when a face is present (Washmuth et al. 1994). ...
Mechanism of hormone action
... • How do we know that cAMP is a secondary messenger? – Changes in production of cAMP after hormonal treatment – Correlation between amount of cAMP being produced and cellular response to the hormone – Inhibition of phosphodiesterase activity • Presence of ligand but no effects ...
... • How do we know that cAMP is a secondary messenger? – Changes in production of cAMP after hormonal treatment – Correlation between amount of cAMP being produced and cellular response to the hormone – Inhibition of phosphodiesterase activity • Presence of ligand but no effects ...
File
... Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic and muscular fuctions Sarin Gas ...
... Acetylcholine (often abbreviated ACh) is the most common neurotransmitter. It is located in both the central nervous and peripheral nervous system Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter be identified in 1914 As a neuromodulator it acts on basic autonomic and muscular fuctions Sarin Gas ...
Slide 1
... (depicted in tracings on the right). Postulated inhibitory connections are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular path ...
... (depicted in tracings on the right). Postulated inhibitory connections are shown as red circles; postulated excitatory connections as green circles; and cholinergic pontine nuclei are shown as blue circles. It should be noted that the actual synaptic signs of many of the aminergic and reticular path ...
Lecture 2 (Neurons)
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
... communicate information quickly by using ionic currents and chemical signals called neurotransmitters. Nerve - Many neurons that are bundled together and covered by a connective tissue sheath. Nervous System – The entire network of interconnecting neurons. ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
... Plays a key role in maintaining homeostasis during stress, it is the “flight-or-fight” system of the body. This is done by accelerating heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and raising the blood pressure. For this information to be communicated, it uses pre/post-ganglionic neurons. -Preganglionic ...
Neurochemistry of Dementias
... thalamus (not cortex) D4 - despite high affinity for clozapine, & links to ADHD, receptor protein has very low density in human - many polymorphisms, and 48bp repeat (2x 4x or 7x) in third intracytoplasmic loop - D4 variants not linked to disease (except ADHD, 7x repeats) - D4 variants not associate ...
... thalamus (not cortex) D4 - despite high affinity for clozapine, & links to ADHD, receptor protein has very low density in human - many polymorphisms, and 48bp repeat (2x 4x or 7x) in third intracytoplasmic loop - D4 variants not linked to disease (except ADHD, 7x repeats) - D4 variants not associate ...
Chapter 2 - davis.k12.ut.us
... 5. Which of the following are located exclusively within the brain and spinal cord? A) sensory neurons B) motor neurons C) myelin sheath D) interneurons E) axons 6. In its resting state, the inside of a neuron carries a slight _____ charge with respect to the outside. A) positive B) negative C) act ...
... 5. Which of the following are located exclusively within the brain and spinal cord? A) sensory neurons B) motor neurons C) myelin sheath D) interneurons E) axons 6. In its resting state, the inside of a neuron carries a slight _____ charge with respect to the outside. A) positive B) negative C) act ...
A Novel Multigene Family May Encode Odorant
... •cilia is isolated from rat olfactory epithelium •response to odourous molecules leads to a rise in cyclic AMP Nakamura and Gold, 1987 • rise in cyclic AMP leads to depolarization of olfactory neurons ...
... •cilia is isolated from rat olfactory epithelium •response to odourous molecules leads to a rise in cyclic AMP Nakamura and Gold, 1987 • rise in cyclic AMP leads to depolarization of olfactory neurons ...
PowerPoint from lab
... antagonistic muscle at the same time. The sensory neuron also synapses with an inhibitory association neuron for the antagonistic muscle. This is called reciprocal innervation. • Axon collaterals from the sensory neuron also synapses with cells that carry information about the state of this muscle t ...
... antagonistic muscle at the same time. The sensory neuron also synapses with an inhibitory association neuron for the antagonistic muscle. This is called reciprocal innervation. • Axon collaterals from the sensory neuron also synapses with cells that carry information about the state of this muscle t ...
Dysregulated Postsynaptic Density and Endocytic Zone in the
... Taking the substance in larger amounts or for longer than the you meant to Wanting to cut down or stop using the substance but not managing to Spending a lot of time getting, using, or recovering from use of the substance Cravings and urges to use the substance Not managing to do what you ...
... Taking the substance in larger amounts or for longer than the you meant to Wanting to cut down or stop using the substance but not managing to Spending a lot of time getting, using, or recovering from use of the substance Cravings and urges to use the substance Not managing to do what you ...
1.Unwanted drug effects, allergy. 2. Effects of age and disease on
... 1.Unwanted drug effects, allergy. 2. Effects of age and disease on drug ...
... 1.Unwanted drug effects, allergy. 2. Effects of age and disease on drug ...
Endocrine System
... Main inhibitory neurotransmitter Benzodiazepines (which include tranquilizers such as Valium) and alcohol work on GABA receptor complexes ...
... Main inhibitory neurotransmitter Benzodiazepines (which include tranquilizers such as Valium) and alcohol work on GABA receptor complexes ...
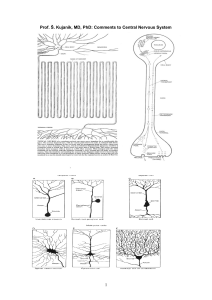
Study materials CNS
... a) SATIETY CENTRE is situated in the ventromedial HT nucleus dependent on the glucose blood level and percepted like a positive sensation after food b) HUNGER CENTRE is situated in the lateral HT nucleus, it has the permanent activity which is decreased for some time by stimulation of the satiety c ...
... a) SATIETY CENTRE is situated in the ventromedial HT nucleus dependent on the glucose blood level and percepted like a positive sensation after food b) HUNGER CENTRE is situated in the lateral HT nucleus, it has the permanent activity which is decreased for some time by stimulation of the satiety c ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.