background information - Teacher Enrichment Initiatives
... Nicotine and it’s Effect on the Body and Brain “The Effects of Extended Pre-Quit Varenicline Treatment on Smoking Behavior and Short-Term Abstinence: A Randomized Clinical Trial” The neurotransmitters in the brain are responsible for how we react to internal and external stimuli. They determine memo ...
... Nicotine and it’s Effect on the Body and Brain “The Effects of Extended Pre-Quit Varenicline Treatment on Smoking Behavior and Short-Term Abstinence: A Randomized Clinical Trial” The neurotransmitters in the brain are responsible for how we react to internal and external stimuli. They determine memo ...
Cranial Nerve I
... Input comes from exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors The three main levels of neural integration in the somatosensory system are: ...
... Input comes from exteroceptors, proprioceptors, and interoceptors The three main levels of neural integration in the somatosensory system are: ...
Hydrophobic signal molecules
... Cells do not work in isolation but continually ‘talk’ to each other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a tar ...
... Cells do not work in isolation but continually ‘talk’ to each other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a tar ...
Math Module II Review
... A physical disorder that is the result of stress rather than from illness or injury? ...
... A physical disorder that is the result of stress rather than from illness or injury? ...
Neurotransmitters:
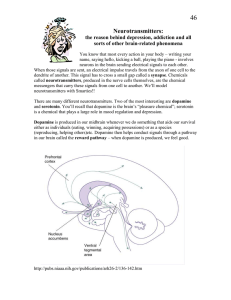
... dendrite of another. This signal has to cross a small gap called a synapse. Chemicals called neurotransmitters, produced in the nerve cells themselves, are the chemical messengers that carry these signals from one cell to another. We’ll model neurotransmitters with Smarties!! There are many differen ...
... dendrite of another. This signal has to cross a small gap called a synapse. Chemicals called neurotransmitters, produced in the nerve cells themselves, are the chemical messengers that carry these signals from one cell to another. We’ll model neurotransmitters with Smarties!! There are many differen ...
Can an Injured Spinal Cord Be Fixed?
... Paraplegia is paralysis of the lower half of the body Quadriplegia is paralysis from the neck down Research on nerve cells is leading to new therapies ...
... Paraplegia is paralysis of the lower half of the body Quadriplegia is paralysis from the neck down Research on nerve cells is leading to new therapies ...
Avello_1.4_The_Believer_s_Brain
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
... The Paradox of Nietzschean Atheism Jason Wakefield, University of Cambridge, England. Review: The Believer's Brain (2014) R.S Donda & K.M Heilman. Psychology Press. Heilman was raised in Brooklyn, New York. He graduated from the University of Virginia School of Medicine in 1963 before studying neuro ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... FIGURE 22.3 Example of labeled lines in the somatosensory system. Two dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells (blue) send peripheral axons to be part of a touch receptor, whereas a third cell (red) is a pain receptor. By activating the neurons of touch receptors, direct touching of the skin or electrical ...
... FIGURE 22.3 Example of labeled lines in the somatosensory system. Two dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells (blue) send peripheral axons to be part of a touch receptor, whereas a third cell (red) is a pain receptor. By activating the neurons of touch receptors, direct touching of the skin or electrical ...
lesson 6
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
... 1) synthesized and released by neurons 2) released at the nerve terminal in a 'chemically identifiable' form 3) the chemical should reproduce the activity of the presynaptic neuron 4) can be blocked by competitive antagonist based on concentration 5) active mechanisms to stop the function of the neu ...
Nerve cells - Spark (e
... synapses; the cell that sends the signal is the presynaptic cell while which receives it is the postsynaptic one. The space that separates the cells is said synaptic gap or synaptic cleft. ...
... synapses; the cell that sends the signal is the presynaptic cell while which receives it is the postsynaptic one. The space that separates the cells is said synaptic gap or synaptic cleft. ...
Nerve Cells
... • Below: 1 action potential every 4 msec • Invasion of the synapse results in release of neurotransmitter that bind to postsynaptic receptors and ...
... • Below: 1 action potential every 4 msec • Invasion of the synapse results in release of neurotransmitter that bind to postsynaptic receptors and ...
Selected topics in drug design
... The amide group is electronically more stable than ester group ...
... The amide group is electronically more stable than ester group ...
SompolinskyAug09
... basic cellular mechanism that enables networks of neurons to efficiently decode speech in changing conditions. The research may lead to the upgrading of computer algorithms for faster and more precise speech recognition as well as to the development of innovative treatments for auditory problems amo ...
... basic cellular mechanism that enables networks of neurons to efficiently decode speech in changing conditions. The research may lead to the upgrading of computer algorithms for faster and more precise speech recognition as well as to the development of innovative treatments for auditory problems amo ...
A Mindful Vixen: Degradation Due to Methamphetamine
... Life was good. I was the most popular neuron of the mesocorticolimbic-dopamine system in the small town of Ventral Tegmentum, Midbrain USA; home of the famous reward circuit of Stewart Evans. Stewart Evans exists because I allow him to think and function and he loves activating his reward circuit an ...
... Life was good. I was the most popular neuron of the mesocorticolimbic-dopamine system in the small town of Ventral Tegmentum, Midbrain USA; home of the famous reward circuit of Stewart Evans. Stewart Evans exists because I allow him to think and function and he loves activating his reward circuit an ...
The Brain - Central Connecticut State University
... except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
... except smell and routes it to the higher brain regions that deal with seeing, hearing, tasting, and touching. ...
TBI Abstract - Stacey Lee, PhD
... Department of Cellular and Structural Biology, UTHSCSA Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are the cause of over 30% of injury-related deaths in the United States. Both civilians and military personnel are at risk for TBIs from blunt force or blast trauma. Side effects of TBI can range from dizziness, n ...
... Department of Cellular and Structural Biology, UTHSCSA Traumatic brain injuries (TBIs) are the cause of over 30% of injury-related deaths in the United States. Both civilians and military personnel are at risk for TBIs from blunt force or blast trauma. Side effects of TBI can range from dizziness, n ...
PRACTICE QUIZ
... The loss of taste sensation is called _________________________________________________________. ...
... The loss of taste sensation is called _________________________________________________________. ...
12-nervoussystemintro - Alexmac
... There are two functioning parts of the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System – Brain and spinal cord – Processes information and creates response ...
... There are two functioning parts of the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System – Brain and spinal cord – Processes information and creates response ...
The Sensory System
... – Iris- Circular band of muscles that controls the size of the pupil. The pigmentation of the iris gives "color" to the eye. Blue eyes have the least amount of pigment; brown eyes have the most. – Lens- Transparent tissue that bends light passing through the eye. To focus light, the lens can change ...
... – Iris- Circular band of muscles that controls the size of the pupil. The pigmentation of the iris gives "color" to the eye. Blue eyes have the least amount of pigment; brown eyes have the most. – Lens- Transparent tissue that bends light passing through the eye. To focus light, the lens can change ...
Theories of Depression
... from the drugs that are used to treat it. The evolution of antidepressant drugs has, in some ways, been the systematic narrowing down of monoamines to Serotonin. MAO inhibitors are Dopamine-Epinephrine-Norephinephrine-Seratonin agonists. Tricyclic Antidepressants are Norepinephrine-Serotonin agonist ...
... from the drugs that are used to treat it. The evolution of antidepressant drugs has, in some ways, been the systematic narrowing down of monoamines to Serotonin. MAO inhibitors are Dopamine-Epinephrine-Norephinephrine-Seratonin agonists. Tricyclic Antidepressants are Norepinephrine-Serotonin agonist ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.