Chapter 28
... (b) different kind of neurotransmitter (i) excitatory – open Na+ channels (ii) inhibitory – open Cl- (flows in) or K+ (flows out) channels (3) rate of signaling is summation of all the signals (4) contrast excitatory and inhibitory synapses in how they change a receiving cell’s membrane potential re ...
... (b) different kind of neurotransmitter (i) excitatory – open Na+ channels (ii) inhibitory – open Cl- (flows in) or K+ (flows out) channels (3) rate of signaling is summation of all the signals (4) contrast excitatory and inhibitory synapses in how they change a receiving cell’s membrane potential re ...
Anatomy Notes on the Brain
... If we are lucky, we fall asleep within 10 to 20 minutes of going to bed. Our bodies begin a cycle of sleep. The first four stages are NREM. Stages one and two are light sleep where we can be awakened easily and contractions of our muscles can be seen. In stages three and four our brain waves slow an ...
... If we are lucky, we fall asleep within 10 to 20 minutes of going to bed. Our bodies begin a cycle of sleep. The first four stages are NREM. Stages one and two are light sleep where we can be awakened easily and contractions of our muscles can be seen. In stages three and four our brain waves slow an ...
Sense Organs - human anatomy
... Referred pain results from the convergence of neuronal pathways in the CNS o In the case of cardiac pain, spinal cord segments T1 to T5 receive input from the heat as well as the chest and arm o Pain fibers from the heart and skin converge on the same spinal interneurons, then follow the same pathwa ...
... Referred pain results from the convergence of neuronal pathways in the CNS o In the case of cardiac pain, spinal cord segments T1 to T5 receive input from the heat as well as the chest and arm o Pain fibers from the heart and skin converge on the same spinal interneurons, then follow the same pathwa ...
The Nervous System
... There are two types of photo receptors. Rods. Cones. Rods are extremely sensitive to light but they do not distinguish different colors. Cones are less sensitive then rods but they do respond to light of different colors producing color vision. ...
... There are two types of photo receptors. Rods. Cones. Rods are extremely sensitive to light but they do not distinguish different colors. Cones are less sensitive then rods but they do respond to light of different colors producing color vision. ...
Anatomical and physiological bases of consciousness and sleep
... • subject to damage in Alzheimer's disease (impaired attention & memory) • Acetylcholine (ACh) = excitatory GABA = inhibitiory • hypothalamus • arousal • antihistamine drugs may cause drowsiness • Histamine ...
... • subject to damage in Alzheimer's disease (impaired attention & memory) • Acetylcholine (ACh) = excitatory GABA = inhibitiory • hypothalamus • arousal • antihistamine drugs may cause drowsiness • Histamine ...
Chapter Outlines - Cengage Learning
... parasympathetic nervous system. In the brain, cholinergic neurons are involved in movement and memory. A loss of cholinergic neurons is linked to Alzheimer’s disease. b) Arousal is the main task of norepinephrine, which is also known as noradrenaline. Noradrenaline is used by neurons in the sympathe ...
... parasympathetic nervous system. In the brain, cholinergic neurons are involved in movement and memory. A loss of cholinergic neurons is linked to Alzheimer’s disease. b) Arousal is the main task of norepinephrine, which is also known as noradrenaline. Noradrenaline is used by neurons in the sympathe ...
Nervous System III – Senses
... i. Optic fibers radiate outward into the temporal lobe before reaching their destination in the visual cortex in the occipital lobe. ...
... i. Optic fibers radiate outward into the temporal lobe before reaching their destination in the visual cortex in the occipital lobe. ...
nervous system
... stalk of nerve cells and fibers that connect spinal cord to the rest of the brain. ...
... stalk of nerve cells and fibers that connect spinal cord to the rest of the brain. ...
Slide ()
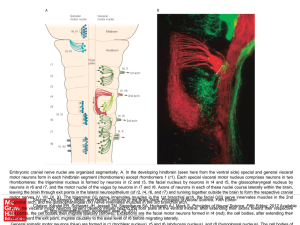
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
... Embryonic cranial nerve nuclei are organized segmentally. A. In the developing hindbrain (seen here from the ventral side) special and general visceral motor neurons form in each hindbrain segment (rhombomere) except rhombomere 1 (r1). Each special visceral motor nucleus comprises neurons in two rho ...
Document
... glucose, lipids and metabolism • The renin-angiotensin/aldosterone system controls blood pressure • Hormones control reproduction • And probably many other examples, which show the importance of hormones in normal life and development. ...
... glucose, lipids and metabolism • The renin-angiotensin/aldosterone system controls blood pressure • Hormones control reproduction • And probably many other examples, which show the importance of hormones in normal life and development. ...
Dr. Doug Leonard PowerPoint Presentation regarding the Teenage
... • Vital in helping us identify emotional tone of faces • Adolescents will misread faces due to their reliance on use of limbic structures (gut feel) preferentially over prefrontal cortex • As Prefrontal cortex develops identifying emotional tones of faces becomes more reliable • Teens will often see ...
... • Vital in helping us identify emotional tone of faces • Adolescents will misread faces due to their reliance on use of limbic structures (gut feel) preferentially over prefrontal cortex • As Prefrontal cortex develops identifying emotional tones of faces becomes more reliable • Teens will often see ...
Chapter 2
... • Excitatory Synapses – synapse at which a neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire. • Inhibitory Synapses – synapse at which neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to stop firing. Agonists – chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor si ...
... • Excitatory Synapses – synapse at which a neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to fire. • Inhibitory Synapses – synapse at which neurotransmitter causes the receiving cell to stop firing. Agonists – chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor si ...
04 Sensation and perception
... many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
... many were temporarily distorted, and their brain-wave patterns, which had slowed down during the experiment, took several hours to return to normal. ...
Addiction - Biological, Not Sociological
... system with dopamine. Drugs release 2-10 times more dopamine than natural rewards do and it can last longer. Such a powerful reward overrides the natural reward system and it motivates the user to take more. Drugs such as, heroin and marijuana, can activate neurons because their chemical structures ...
... system with dopamine. Drugs release 2-10 times more dopamine than natural rewards do and it can last longer. Such a powerful reward overrides the natural reward system and it motivates the user to take more. Drugs such as, heroin and marijuana, can activate neurons because their chemical structures ...
Sleep Physiology
... This is the initial stage of sleep. It is characterized by the appearance of theta waves of 3.5-7.5 Hz. Stage 1 of sleep is the border line between the wakefulness and sleep. Stage 2 The second stage of sleep generally occurs after 10 or 15 minutes if the person is in stage 1. Stage 2 is marked by t ...
... This is the initial stage of sleep. It is characterized by the appearance of theta waves of 3.5-7.5 Hz. Stage 1 of sleep is the border line between the wakefulness and sleep. Stage 2 The second stage of sleep generally occurs after 10 or 15 minutes if the person is in stage 1. Stage 2 is marked by t ...
Ch 5 lec 1
... Dilates blood vessels in brain Stimulates the changes in blood vessels that produce ...
... Dilates blood vessels in brain Stimulates the changes in blood vessels that produce ...
GROUP “A” L T P/S SW/FW TOTAL CREDIT UNITS 1 1 -
... associated with subcortical lesions of the brain. 12. List symptoms that are typical of focal and diffuse brain damage. 13. Enumerate the characteristics of clinical syndrome and the nature of neuropsychological deficits seen in various cortical and subcortical ...
... associated with subcortical lesions of the brain. 12. List symptoms that are typical of focal and diffuse brain damage. 13. Enumerate the characteristics of clinical syndrome and the nature of neuropsychological deficits seen in various cortical and subcortical ...
Dr. Coyle`s NIH Biosketch
... perikaryal specific brain lesions. This method permitted us to show that the nucleus basalis of Meynert was the source of cholinergic innervation to the cortex, leading to the identification of its degeneration in AD. The excitotoxin lesion method was been adopted widely in neuroscience. Subsequent ...
... perikaryal specific brain lesions. This method permitted us to show that the nucleus basalis of Meynert was the source of cholinergic innervation to the cortex, leading to the identification of its degeneration in AD. The excitotoxin lesion method was been adopted widely in neuroscience. Subsequent ...
Unit 1 Practice
... d. resting potential. 3. Communication between neurons is _________________. a. electrical b. chemical c. magical d. genetic 4. Dopamine, serotonin, and histamine are examples of a. neuropeptides. b. nerves. c. neurotransmitters. d. neural pathways. 5. Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When ...
... d. resting potential. 3. Communication between neurons is _________________. a. electrical b. chemical c. magical d. genetic 4. Dopamine, serotonin, and histamine are examples of a. neuropeptides. b. nerves. c. neurotransmitters. d. neural pathways. 5. Ray is suffering from multiple sclerosis. When ...
Neuron Functioning
... • This is different than refractory period because when a neuron is at resting potential it is waiting to fire NOT unable to fire ...
... • This is different than refractory period because when a neuron is at resting potential it is waiting to fire NOT unable to fire ...
o Saul R. Korey, M.D. IN MEMORIAM 1918—1963
... extensively described, analyzed, and exquisitely illustrated in their reports. Distinctive biochemical findings were also reported—a deficiency in the degradation of gangliosides, and a lowered content of free amino acids in the brain. To the clinic he brought his active, analytic, inquiring, restle ...
... extensively described, analyzed, and exquisitely illustrated in their reports. Distinctive biochemical findings were also reported—a deficiency in the degradation of gangliosides, and a lowered content of free amino acids in the brain. To the clinic he brought his active, analytic, inquiring, restle ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.