Nerve activates contraction
... motor neurons (red), which excite extrafusal fibers by stretch, the associated sensory of the stretched muscle. Afferent fibers also neurons (blue) transmit afferent impulses synapse with interneurons (green) that inhibit motor at higher frequency to the spinal cord. neurons (purple) controlling ant ...
... motor neurons (red), which excite extrafusal fibers by stretch, the associated sensory of the stretched muscle. Afferent fibers also neurons (blue) transmit afferent impulses synapse with interneurons (green) that inhibit motor at higher frequency to the spinal cord. neurons (purple) controlling ant ...
The Nervous System
... if 7th. cranial nerve is affected, Bell’s palsy (facial paralysis) results if optic nerve is affected blindness will occur ...
... if 7th. cranial nerve is affected, Bell’s palsy (facial paralysis) results if optic nerve is affected blindness will occur ...
Autonomic Nervous System I and II
... An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sy ...
... An axon may synapse with postganglionic neurons in the ganglion it first reaches or Sympathetic chains or An axon may continue, without synapsing, through the sympathetic trunk ganglion to end at a prevertebral ganglion and synapse with postganglionic neurons there or An axon may pass through the sy ...
Sensory Pathways
... • Visceral Sensory Pathways • Cranial Nerves V, VII, IX, and X • Carry visceral sensory information from mouth, palate, pharynx, larynx, trachea, esophagus, and associated vessels and glands ...
... • Visceral Sensory Pathways • Cranial Nerves V, VII, IX, and X • Carry visceral sensory information from mouth, palate, pharynx, larynx, trachea, esophagus, and associated vessels and glands ...
Sensory Receptors, Neuronal Circuits for Processing Information
... Loëwenstein WR: Excitation and inactivation in a receptor membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci 94:510, 1961.) ...
... Loëwenstein WR: Excitation and inactivation in a receptor membrane. Ann N Y Acad Sci 94:510, 1961.) ...
Escape behavior and neuronal responses to looming stimuli in the
... consisted of a 5·cm black square, which approached over a distance of 70·cm at a constant speed of 20·cm·s–1 (Fig.·1B). Thus, for the crab’s eye the stimulus had an apparent size subtending an angle of 4° at its stationary initial position and expanded until covering the entire screen (77° width, 62 ...
... consisted of a 5·cm black square, which approached over a distance of 70·cm at a constant speed of 20·cm·s–1 (Fig.·1B). Thus, for the crab’s eye the stimulus had an apparent size subtending an angle of 4° at its stationary initial position and expanded until covering the entire screen (77° width, 62 ...
Signal Integration in Thalamus: Labeled Lines Go
... ments were incredibly informative. Rompani et al. (2017) knew that even RGCs of the same type can vary their dendritic arbor size according to location in the retina—a feature referred to as retinotopic-dependent dendritic scaling. While this feature is thought to be less prominent in non-foveated s ...
... ments were incredibly informative. Rompani et al. (2017) knew that even RGCs of the same type can vary their dendritic arbor size according to location in the retina—a feature referred to as retinotopic-dependent dendritic scaling. While this feature is thought to be less prominent in non-foveated s ...
Modelling the Grid-like Encoding of Visual Space
... The majority of conventional grid cell models rely on mechanisms that directly integrate information on the velocity and direction of an animal into a periodic representation of the animal’s location (Kerdels, 2016). As a consequence, the particular models do not generalize well, i.e., they can not ...
... The majority of conventional grid cell models rely on mechanisms that directly integrate information on the velocity and direction of an animal into a periodic representation of the animal’s location (Kerdels, 2016). As a consequence, the particular models do not generalize well, i.e., they can not ...
7. MODELING THE SOMATOTOPIC MAP 7.1 The Somatotopic Map
... image area in the somatosensory cortex. Interestingly, the neural projections giving rise to these images are not rigid. Instead, they can change under the influence of sensory experience or as the result of a loss of sensory input, e.g., after nerve damage. The necessary modifications of the connec ...
... image area in the somatosensory cortex. Interestingly, the neural projections giving rise to these images are not rigid. Instead, they can change under the influence of sensory experience or as the result of a loss of sensory input, e.g., after nerve damage. The necessary modifications of the connec ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... language area, etc. However, it must be fully appreciated that no single area of the brain has been successfully identified as the sole functional area of any psycho-physical phenomenon. Rather, the brain appears to have a highly distributed functionality with many different areas of the brain (both ...
... language area, etc. However, it must be fully appreciated that no single area of the brain has been successfully identified as the sole functional area of any psycho-physical phenomenon. Rather, the brain appears to have a highly distributed functionality with many different areas of the brain (both ...
Cortical Neurons and Circuits: A Tutorial
... language area, etc. However, it must be fully appreciated that no single area of the brain has been successfully identified as the sole functional area of any psycho-physical phenomenon. Rather, the brain appears to have a highly distributed functionality with many different areas of the brain (both ...
... language area, etc. However, it must be fully appreciated that no single area of the brain has been successfully identified as the sole functional area of any psycho-physical phenomenon. Rather, the brain appears to have a highly distributed functionality with many different areas of the brain (both ...
Top-down influence in early visual processing: a Bayesian perspective
... find the Si that maximises P(EjSi)P(SijH)P(H), i.e., explaining E as well as being predicted by H optimally. This scheme can be applied again to higher areas recursively to form the whole hierarchy of inference. In this framework, each cortical area is an expert for inferring certain aspects of the ...
... find the Si that maximises P(EjSi)P(SijH)P(H), i.e., explaining E as well as being predicted by H optimally. This scheme can be applied again to higher areas recursively to form the whole hierarchy of inference. In this framework, each cortical area is an expert for inferring certain aspects of the ...
NeuroMem Decision Space Mapping
... modeling the decision space. The outcome can have three possible classification status: Identified with certainty, Identified with uncertainty, Unknown. As a result, the RCE/RBF classifier is very powerful since it allows managing uncertainty for a better, more refined diagnostic. It is also especia ...
... modeling the decision space. The outcome can have three possible classification status: Identified with certainty, Identified with uncertainty, Unknown. As a result, the RCE/RBF classifier is very powerful since it allows managing uncertainty for a better, more refined diagnostic. It is also especia ...
SCandSN 08
... Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in PNS (mixed) Tract = bundle of nerve fibers in the CNS (mixed) Ganglion = cluster of neuronal cell bodies in PNS Nucleus = cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS ...
... Nerve = bundle of nerve fibers in PNS (mixed) Tract = bundle of nerve fibers in the CNS (mixed) Ganglion = cluster of neuronal cell bodies in PNS Nucleus = cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the CNS ...
Neuronal Processing of Chemical Information in Crustaceans Chapter 7
... Fig. 7.1 Overview of chemoreception in decapod crustaceans. Center: Artists’ drawing of spiny lobster showing the location of chemoreceptive sensilla (white dot: aesthetascs; black dots: bimodal sensilla) on different body parts (1: lateral flagellum of antennule; 2: medial flagellum of antennule; 3 ...
... Fig. 7.1 Overview of chemoreception in decapod crustaceans. Center: Artists’ drawing of spiny lobster showing the location of chemoreceptive sensilla (white dot: aesthetascs; black dots: bimodal sensilla) on different body parts (1: lateral flagellum of antennule; 2: medial flagellum of antennule; 3 ...
spinal cord and reflexes - Sinoe Medical Association
... § Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves § Fibers travel to the periphery via several different routes § Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve § Damage to one spinal segment cannot completely paralyze a muscle Spinal Nerve I ...
... § Each resulting branch of a plexus contains fibers from several spinal nerves § Fibers travel to the periphery via several different routes § Each muscle receives a nerve supply from more than one spinal nerve § Damage to one spinal segment cannot completely paralyze a muscle Spinal Nerve I ...
spiking neuron models - Assets - Cambridge
... The neuronal signals consist of short electrical pulses and can be observed by placing a fine electrode close to the soma or axon of a neuron; see Fig. 1.2. The pulses, so-called action potentials or spikes, have an amplitude of about 100 mV and typically a duration of 1–2 ms. The form of the pulse ...
... The neuronal signals consist of short electrical pulses and can be observed by placing a fine electrode close to the soma or axon of a neuron; see Fig. 1.2. The pulses, so-called action potentials or spikes, have an amplitude of about 100 mV and typically a duration of 1–2 ms. The form of the pulse ...
Lecture-20-2013-Bi
... Proust, Remembrance of Things Past “as soon as I had recognized the taste of the piece of madeleine soaked in her decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey h ...
... Proust, Remembrance of Things Past “as soon as I had recognized the taste of the piece of madeleine soaked in her decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey h ...
Frequency decoding of periodically timed action potentials through
... neurons that encompasses about an octave. Frequency discrimination by such a network is accordingly restricted to a spectral band of less than an octave, and many networks, each with a distinct range of temporal delays, are required to cover a broader frequency range. Where might such structures exi ...
... neurons that encompasses about an octave. Frequency discrimination by such a network is accordingly restricted to a spectral band of less than an octave, and many networks, each with a distinct range of temporal delays, are required to cover a broader frequency range. Where might such structures exi ...
powerpoint lecture
... • Inborn (intrinsic) reflex - rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to stimulus – maintain posture, control visceral activities – Can be modified by learning and conscious effort ...
... • Inborn (intrinsic) reflex - rapid, involuntary, predictable motor response to stimulus – maintain posture, control visceral activities – Can be modified by learning and conscious effort ...
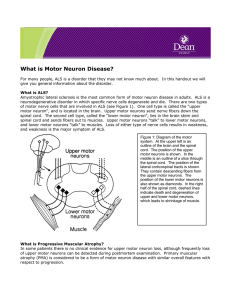
What is Motor Neuron
... occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is called familial ALS. People who have the hereditary form of ALS mostly have a clear family ...
... occupation and hobbies, etc. These studies have identified no clear factors associated with the development of ALS. A small percentage of patients, about 5%, have other members in the family with ALS. This is called familial ALS. People who have the hereditary form of ALS mostly have a clear family ...
What is the other 85% of V1 doing?
... Even when a neuron has been successfully isolated, detailed investigation of the neuron may be bypassed if the neuron does not respond “rationally” to the investigators stimuli or fit the stereotype of what the experimenter believes the neuron should do. This is especially true for higher visual are ...
... Even when a neuron has been successfully isolated, detailed investigation of the neuron may be bypassed if the neuron does not respond “rationally” to the investigators stimuli or fit the stereotype of what the experimenter believes the neuron should do. This is especially true for higher visual are ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.