Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light
... segmented the brain into 11 regions (Fig. 3a) and derived average fluorescence time series across each of these regions (Fig. 3b). Average activity in most brain areas was characterized by large, temporally sparse increases in fluorescence. In many cases, these discharges occurred synchronously acro ...
... segmented the brain into 11 regions (Fig. 3a) and derived average fluorescence time series across each of these regions (Fig. 3b). Average activity in most brain areas was characterized by large, temporally sparse increases in fluorescence. In many cases, these discharges occurred synchronously acro ...
Cellular and network mechanisms of electrographic
... are similar to spindles, it could be supposed that the runs of fast paroxysmal spikes share mechanisms with spindles and thus originate in the thalamus. However, the experimental evidence demonstrated that (a) during fast runs TC neurons display EPSPs that only rarely lead to the generation of actio ...
... are similar to spindles, it could be supposed that the runs of fast paroxysmal spikes share mechanisms with spindles and thus originate in the thalamus. However, the experimental evidence demonstrated that (a) during fast runs TC neurons display EPSPs that only rarely lead to the generation of actio ...
The functional organization of the intraparietal sulcus in humans and
... Kanwisher, 2001). These data are supported by studies of patients presenting with lesions of the parietal cortex and neuropsychological deficits such as visuospatial neglect, different forms of apraxia and other visuomotor coordination problems (for reviews see, for example, Marshall & Fink, 2001, 2 ...
... Kanwisher, 2001). These data are supported by studies of patients presenting with lesions of the parietal cortex and neuropsychological deficits such as visuospatial neglect, different forms of apraxia and other visuomotor coordination problems (for reviews see, for example, Marshall & Fink, 2001, 2 ...
Isodirectional Tuning of Adjacent Interneurons and Pyramidal Cells
... (Armstrong-James and Millar 1979; Fox et al. 1980). Recordings were made through a custom low-noise amplifier and were band-pass filtered between ;150 Hz and 12 kHz (4-pole Tchebychev, KrohnHite). The six barrels of the microelectrode were normally filled with up to three different receptor-specific ...
... (Armstrong-James and Millar 1979; Fox et al. 1980). Recordings were made through a custom low-noise amplifier and were band-pass filtered between ;150 Hz and 12 kHz (4-pole Tchebychev, KrohnHite). The six barrels of the microelectrode were normally filled with up to three different receptor-specific ...
Does the End Justify the Means?
... The human homologue of F5 is believed to be Broca’s area (left inferior frontal and gyrus), which would have similar mirror properties (see Rizzolatti et al., 2001). Indeed, an fMRI performed by Iacoboni et al. (1999) found this area during single finger movement copying. However, because the nature ...
... The human homologue of F5 is believed to be Broca’s area (left inferior frontal and gyrus), which would have similar mirror properties (see Rizzolatti et al., 2001). Indeed, an fMRI performed by Iacoboni et al. (1999) found this area during single finger movement copying. However, because the nature ...
PDF
... expressed by KCs [Kim et al., 2007]). Dopamine’s role as a putative aversive reinforcer in fly olfactory learning mirrors, but with reversed polarity, its rewarding role in mammals (Wise and Rompre, 1989; Schultz et al., 1997). While the evidence implicating dopamine as an aversive reinforcement sig ...
... expressed by KCs [Kim et al., 2007]). Dopamine’s role as a putative aversive reinforcer in fly olfactory learning mirrors, but with reversed polarity, its rewarding role in mammals (Wise and Rompre, 1989; Schultz et al., 1997). While the evidence implicating dopamine as an aversive reinforcement sig ...
Chapter 12 *Lecture PowerPoint Nervous Tissue
... • Diverse functions – Form a supportive framework of nervous tissue – Have extensions (perivascular feet) that contact blood capillaries that stimulate them to form a tight seal called the blood–brain barrier – Convert blood glucose to lactate and supply this to the neurons for nourishment ...
... • Diverse functions – Form a supportive framework of nervous tissue – Have extensions (perivascular feet) that contact blood capillaries that stimulate them to form a tight seal called the blood–brain barrier – Convert blood glucose to lactate and supply this to the neurons for nourishment ...
Neuron Production, Neuron Number, and Structure Size Are
... bird. An estimate of measurement reliability was made by remeasuring the hippocampus of the first brain traced, 2 months after the first tracing was made. Pearson correlations were calculated for the areas of both hemispheres (n ⫽ 12). The correlation coefficients were .981 and .899. The volumes of ...
... bird. An estimate of measurement reliability was made by remeasuring the hippocampus of the first brain traced, 2 months after the first tracing was made. Pearson correlations were calculated for the areas of both hemispheres (n ⫽ 12). The correlation coefficients were .981 and .899. The volumes of ...
Spike-Timing Theory of Working Memory
... In the model presented here, PNGs get spontaneously reactivated due to stochastic synaptic noise. Short-term strengthening of the synapses of selected PNGs can bias these reactivations, i.e., increase the reactivation rate of the selected PNGs, which results in activity patterns similar to those obs ...
... In the model presented here, PNGs get spontaneously reactivated due to stochastic synaptic noise. Short-term strengthening of the synapses of selected PNGs can bias these reactivations, i.e., increase the reactivation rate of the selected PNGs, which results in activity patterns similar to those obs ...
PDF file
... intermediate areas and motor output area. These later areas are more “abstract“ than the pixel level, and thus should be more useful as temporal context. However, how to use such information is a great challenge. Physiological studies (e.g. [3] and [8]) have shown that the primary visual cortex in m ...
... intermediate areas and motor output area. These later areas are more “abstract“ than the pixel level, and thus should be more useful as temporal context. However, how to use such information is a great challenge. Physiological studies (e.g. [3] and [8]) have shown that the primary visual cortex in m ...
Harris KD. Neural signatures of cell assembly organization. Nat Rev
... to two animals, and a sensory responsive neuron was recorded from each animal. Because there is no causal influence from one brain to the other, the response of two neurons recorded in the two brains will be independent, for any given stimulus presentation (conditional independence). Nevertheless, b ...
... to two animals, and a sensory responsive neuron was recorded from each animal. Because there is no causal influence from one brain to the other, the response of two neurons recorded in the two brains will be independent, for any given stimulus presentation (conditional independence). Nevertheless, b ...
Preparation for action: one of the key functions of motor cortex.
... In a series of experiments10-12,22, we compared neuronal activity recorded in four cortical areas (hand area of primary motor cortex - MI, dorsal premotor cortex - PM, area 5 of the posterior parietal cortex - PA, and area 1 and 2 of the somatosensory cortex - SI) during the execution of wrist exten ...
... In a series of experiments10-12,22, we compared neuronal activity recorded in four cortical areas (hand area of primary motor cortex - MI, dorsal premotor cortex - PM, area 5 of the posterior parietal cortex - PA, and area 1 and 2 of the somatosensory cortex - SI) during the execution of wrist exten ...
Chapter 20
... 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2. The ANS includes: i. autonomic sensory neurons ii. integrating centers in the CNS iii. autonomic motor neurons 3. The ANS is regulated by centers in the brain, primarily the hypothal ...
... 1. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. 2. The ANS includes: i. autonomic sensory neurons ii. integrating centers in the CNS iii. autonomic motor neurons 3. The ANS is regulated by centers in the brain, primarily the hypothal ...
Distinct or Gradually Changing Spatial and Nonspatial
... without continuous theta oscillation argues against the interpretation that continuous theta oscillation is an obligatory requirement for place cell spatial tuning. Third, Royer et al. (2010) suggested that nonspatial factors such as reward, fear, and stress robustly affect the firing of ventral, bu ...
... without continuous theta oscillation argues against the interpretation that continuous theta oscillation is an obligatory requirement for place cell spatial tuning. Third, Royer et al. (2010) suggested that nonspatial factors such as reward, fear, and stress robustly affect the firing of ventral, bu ...
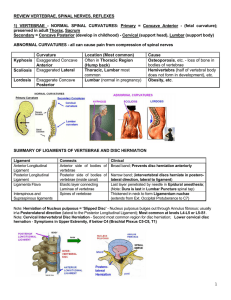
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... and is jittery, with a temperature of 38°C. A clinical diagnosis of early sepsis is made and a lumbar puncture to sample cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is suggested on the ward round as a part of sepsis evaluation. To perform the procedure of lumbar puncture (spinal tap) safely in a newborn, the needle m ...
... and is jittery, with a temperature of 38°C. A clinical diagnosis of early sepsis is made and a lumbar puncture to sample cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is suggested on the ward round as a part of sepsis evaluation. To perform the procedure of lumbar puncture (spinal tap) safely in a newborn, the needle m ...
Variance and invariance of neuronal long
... turn over on the scale of hours to days [2]. Individual synapses continuously change their size and strength both in vitro and in vivo [3–5]. Most notably, however, the mature brain appears to continuously rewire itself, even without experimental intervention [6,7]. This is evident from the perpetua ...
... turn over on the scale of hours to days [2]. Individual synapses continuously change their size and strength both in vitro and in vivo [3–5]. Most notably, however, the mature brain appears to continuously rewire itself, even without experimental intervention [6,7]. This is evident from the perpetua ...
morphometric parameters of the structures of the medulla oblongata
... during the ontogenetic development from the early stages of the prenatal ontogenesis to the definitive age is accompanied by an increase in their size, formation of axon and mediators, development of interneuron communications and other structural and functional changes [1, 5]. Studies by L.D. Starl ...
... during the ontogenetic development from the early stages of the prenatal ontogenesis to the definitive age is accompanied by an increase in their size, formation of axon and mediators, development of interneuron communications and other structural and functional changes [1, 5]. Studies by L.D. Starl ...
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development
... (ventral) ongoing developmental gradient of the PCP formation while the neocortex distal (dorsal) region still is at the PP developmental stage. Also illustrated are the ongoing and simultaneous establishments of the first lamina and subplate (SP) zone as the PCP is being formed, above and below it, ...
... (ventral) ongoing developmental gradient of the PCP formation while the neocortex distal (dorsal) region still is at the PP developmental stage. Also illustrated are the ongoing and simultaneous establishments of the first lamina and subplate (SP) zone as the PCP is being formed, above and below it, ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... • Adrenal medulla, arrector pili muscle, sweat glands, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic innervation. – Nonshivering thermogenesis. ...
... • Adrenal medulla, arrector pili muscle, sweat glands, and most blood vessels receive only sympathetic innervation. – Nonshivering thermogenesis. ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 40.1 Periodic activation in sleep cycles
... REM sleep (indicated by red bars) is brief or nonexistent. During the last two cycles of the night, NREM sleep is lighter (stage 2), and REM episodes are longer, sometimes more than an hour. (B) Fifteen nights of sleep. Each line represents one night of sleep, with REM periods shown as solid bars an ...
... REM sleep (indicated by red bars) is brief or nonexistent. During the last two cycles of the night, NREM sleep is lighter (stage 2), and REM episodes are longer, sometimes more than an hour. (B) Fifteen nights of sleep. Each line represents one night of sleep, with REM periods shown as solid bars an ...
NEURAL NETWORK DYNAMICS
... selectivity, and other features of neuronal responses to sensory input (reviewed, for example, in Dayan & Abbott 2001). In the absence of that input, neurons in these models are typically silent. Although this approach has had considerable success in accounting for response properties in primary sen ...
... selectivity, and other features of neuronal responses to sensory input (reviewed, for example, in Dayan & Abbott 2001). In the absence of that input, neurons in these models are typically silent. Although this approach has had considerable success in accounting for response properties in primary sen ...
Vestibular Signals of Posterior Parietal Cortex Neurons during
... sensory and motor cortices and thus could be involved in the formation of motor plans as well as abstract representations of space. We have recorded from neurons in the intraparietal sulcus, namely, the ventral and medial intraparietal areas (VIP and MIP, respectively), and analyzed their head-movem ...
... sensory and motor cortices and thus could be involved in the formation of motor plans as well as abstract representations of space. We have recorded from neurons in the intraparietal sulcus, namely, the ventral and medial intraparietal areas (VIP and MIP, respectively), and analyzed their head-movem ...
hanPNAS11
... In the postnatal day (P) 0 Tbr1−/− neocortex, the number of neurons highly expressing Fezf2-Gfp, which did not migrate normally (18), increased significantly from 21.8% in Tbr1+/+ to 33.3% in Tbr1−/− (P = 0.0058) (Fig. 2C). This significant increase in the total number of Fezf2-Gfp–expressing neurons ...
... In the postnatal day (P) 0 Tbr1−/− neocortex, the number of neurons highly expressing Fezf2-Gfp, which did not migrate normally (18), increased significantly from 21.8% in Tbr1+/+ to 33.3% in Tbr1−/− (P = 0.0058) (Fig. 2C). This significant increase in the total number of Fezf2-Gfp–expressing neurons ...