Chapter 3
... • Oxygen-rich air is delivered to alveoli with inspiration. • Oxygen diffuses into the blood. • The body does not use all the inhaled oxygen. ...
... • Oxygen-rich air is delivered to alveoli with inspiration. • Oxygen diffuses into the blood. • The body does not use all the inhaled oxygen. ...
Anatomy Info Pack. - Keswick School PE Department.
... There are three different types of muscle within the human body, skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Skeletal or voluntary muscles – these are striated in appearance in other words striped. The skeletal muscles are voluntary and are under our control. We use these muscles when we carry out daily tasks and ...
... There are three different types of muscle within the human body, skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Skeletal or voluntary muscles – these are striated in appearance in other words striped. The skeletal muscles are voluntary and are under our control. We use these muscles when we carry out daily tasks and ...
Bioenergetics and Cardiorespiratory Unit Test Review Chapter 3
... Summarize the interaction of the Energy systems to include: at rest, at the beginning of exercise, during steady-state exercise, during strenuous exercise, and during recovery (pp. ...
... Summarize the interaction of the Energy systems to include: at rest, at the beginning of exercise, during steady-state exercise, during strenuous exercise, and during recovery (pp. ...
6 - SP Moodle
... with the air through diffusion alone. A central ventilation system allows gases to be exchanged with the blood and carried around the body to the cells that require it. ...
... with the air through diffusion alone. A central ventilation system allows gases to be exchanged with the blood and carried around the body to the cells that require it. ...
Answer section - Stu..
... • Waste water released from the body as sweat on surface of the skin. • Release of energy - glycogen is stored in muscles and the liver and is released as glucose to allow the muscles to work. 9. Breathing becomes shallow resulting in gasping for breath - a result of oxygen debt 10. The ability to b ...
... • Waste water released from the body as sweat on surface of the skin. • Release of energy - glycogen is stored in muscles and the liver and is released as glucose to allow the muscles to work. 9. Breathing becomes shallow resulting in gasping for breath - a result of oxygen debt 10. The ability to b ...
Anatomy Workbook - Wright Wonders
... Muscular contraction involves the interaction of muscles with the nervous system. An electrical impulse is sent from the brain to the muscles via the spinal cord and nerve cells (motor neurons). Muscle fibres within the muscle contract according to the ‘all or nothing’ principle. That is, when they ...
... Muscular contraction involves the interaction of muscles with the nervous system. An electrical impulse is sent from the brain to the muscles via the spinal cord and nerve cells (motor neurons). Muscle fibres within the muscle contract according to the ‘all or nothing’ principle. That is, when they ...
the cardiovascular system - Teachnet UK-home
... • Describe and explain the events of the cardiac cycle and how it is linked to the conduction system • Know definitions and resting values for stroke volume, heart rate & cardiac output. • Describe and explain changes in heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output during sub–maximal and maximal wor ...
... • Describe and explain the events of the cardiac cycle and how it is linked to the conduction system • Know definitions and resting values for stroke volume, heart rate & cardiac output. • Describe and explain changes in heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output during sub–maximal and maximal wor ...
Control of blood tissue blood flow
... physical activity as vasodilation occurs Low levels of epinephrine bind to receptors Cholinergic receptors are occupied Intense exercise or sympathetic nervous system activation result in high levels of epinephrine High levels of epinephrine bind to receptors and cause vasoconstriction T ...
... physical activity as vasodilation occurs Low levels of epinephrine bind to receptors Cholinergic receptors are occupied Intense exercise or sympathetic nervous system activation result in high levels of epinephrine High levels of epinephrine bind to receptors and cause vasoconstriction T ...
Homeostasis Answers
... less blood flows through skin (capillaries) or nearer the surface of the skin; so more / less heat is lost (from the skin by radiation) 4. Suggest why an athlete overheats in humid conditions when the temperature is above 18oC. The sweat released cannot evaporate in humid conditions so less heat is ...
... less blood flows through skin (capillaries) or nearer the surface of the skin; so more / less heat is lost (from the skin by radiation) 4. Suggest why an athlete overheats in humid conditions when the temperature is above 18oC. The sweat released cannot evaporate in humid conditions so less heat is ...
What does it do?
... the right side of the heart, it is sent to the _______________ lungs oxygen red blood is then sent to get __________________. The _______ back to the left side of the heart to be circulated back body through the _______________. ...
... the right side of the heart, it is sent to the _______________ lungs oxygen red blood is then sent to get __________________. The _______ back to the left side of the heart to be circulated back body through the _______________. ...
M2 L7 - Energy Systems
... The generation of energy can continue for as long as there is glucose to fuel the system and as long as lactic acid is being removed quickly enough ...
... The generation of energy can continue for as long as there is glucose to fuel the system and as long as lactic acid is being removed quickly enough ...
1.2.2 - The cardiovascular system during exercise
... The resting heart rate gives an indication of fitness. This is because the heart is a muscle. As you train it the heart becomes bigger and stronger. This means it can push more blood out per beat and doesn't have to beat as many times to deliver the same amount as it used to. ...
... The resting heart rate gives an indication of fitness. This is because the heart is a muscle. As you train it the heart becomes bigger and stronger. This means it can push more blood out per beat and doesn't have to beat as many times to deliver the same amount as it used to. ...
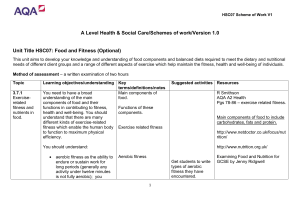
Scheme of work
... You will be assessed on your knowledge, understanding and skills relating to food and fitness through a written examination of two hours. There will be four compulsory structured questions which will include short-answer and free response items. These will require you to demonstrate and apply your k ...
... You will be assessed on your knowledge, understanding and skills relating to food and fitness through a written examination of two hours. There will be four compulsory structured questions which will include short-answer and free response items. These will require you to demonstrate and apply your k ...
6CO2 + 6H2O sunlight C 6H12O6 + 6O2 Name
... 2. What process is the equation above showing? Cellular respiration 3. Where does the process you answered in #2 occur (what organelle in the cell?) mitochondria ...
... 2. What process is the equation above showing? Cellular respiration 3. Where does the process you answered in #2 occur (what organelle in the cell?) mitochondria ...
Insulin-Dependent Diabetes - Wk 1-2
... Progressive abnormalities in β-cell function yield an apparent abrupt onset. This is due to the fact that clinically diagnosed hyperglycaemia is only present when 70-90% of β-cells have been damaged. Type I diabetes is often termed juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus as it commonly occurs during childh ...
... Progressive abnormalities in β-cell function yield an apparent abrupt onset. This is due to the fact that clinically diagnosed hyperglycaemia is only present when 70-90% of β-cells have been damaged. Type I diabetes is often termed juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus as it commonly occurs during childh ...
Energy Systems Live Show
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
1.5 Powerpoint - WordPress.com
... The carbon dioxide is breathed out via the lungs, while the water is lost as sweat, urine or in the air we breathe out as water vapour. As long as the muscles are supplied with enough oxygen, exercising aerobically can be carried out for a long period of time. ...
... The carbon dioxide is breathed out via the lungs, while the water is lost as sweat, urine or in the air we breathe out as water vapour. As long as the muscles are supplied with enough oxygen, exercising aerobically can be carried out for a long period of time. ...
File
... Interacting Body Systems Target: Provide evidence for how the body is a system of interacting subsystems ...
... Interacting Body Systems Target: Provide evidence for how the body is a system of interacting subsystems ...
Dietary Manipulation
... 8–9% Dizziness, laboured breathing, mental confusion, further weakness. 10% Muscle spasms, loss of balance, swelling of tongue. 11% Heat exhaustion, delirium, stroke, difficulty swallowing; death can occur. ...
... 8–9% Dizziness, laboured breathing, mental confusion, further weakness. 10% Muscle spasms, loss of balance, swelling of tongue. 11% Heat exhaustion, delirium, stroke, difficulty swallowing; death can occur. ...
Assignment 15
... Foods can boost energy in three ways: by providing sufficient calories, by delivering stimulants like caffeine, and by pushing the metabolism to burn fuel more efficiently. As for mood, the best foods are those that stabilize blood sugar and trigger feel-good brain chemicals, such as serotonin ...
... Foods can boost energy in three ways: by providing sufficient calories, by delivering stimulants like caffeine, and by pushing the metabolism to burn fuel more efficiently. As for mood, the best foods are those that stabilize blood sugar and trigger feel-good brain chemicals, such as serotonin ...
2. The Respiratory System
... 1. Describe the passage of oxygen from the nasal passages to the bloodstream. 2. David goes jogging once a week for 45 minutes. a) List two differences between the air that David inhales and the air that he exhales while jogging. b) What two substances are used by David’s body cells to produce energ ...
... 1. Describe the passage of oxygen from the nasal passages to the bloodstream. 2. David goes jogging once a week for 45 minutes. a) List two differences between the air that David inhales and the air that he exhales while jogging. b) What two substances are used by David’s body cells to produce energ ...
Energy Production
... The NADH and FADH2 produced during the Krebs cycle pass their electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC), the final stage of respiration (Figure 7). The electron transport chain consists of various proteins embedded in the mitochondrial membrane (complexes I –IV), as well as some mobile electro ...
... The NADH and FADH2 produced during the Krebs cycle pass their electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC), the final stage of respiration (Figure 7). The electron transport chain consists of various proteins embedded in the mitochondrial membrane (complexes I –IV), as well as some mobile electro ...
File
... Air sacs (alveoli) found at ends of tine branches. In air sacs, oxygen in air passes to blood inside capillaries. Blood carries oxygen to heart, which pumps blood with oxygen throughout body. Diaphragm (thick sheet of muscle located at bottom of chest cavity) moves down during inhaling. Moves up whe ...
... Air sacs (alveoli) found at ends of tine branches. In air sacs, oxygen in air passes to blood inside capillaries. Blood carries oxygen to heart, which pumps blood with oxygen throughout body. Diaphragm (thick sheet of muscle located at bottom of chest cavity) moves down during inhaling. Moves up whe ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.