Levels of Organisation
... 1. The diffusing capacity for oxygen increases almost three folds during exercise, this results mainly from increasing numbers of capillaries participating in the diffusion and a more V/Q ratio all over the lung. (It is the ratio of alveolar ventilation to pulmonary blood flow (cardiac output) per m ...
... 1. The diffusing capacity for oxygen increases almost three folds during exercise, this results mainly from increasing numbers of capillaries participating in the diffusion and a more V/Q ratio all over the lung. (It is the ratio of alveolar ventilation to pulmonary blood flow (cardiac output) per m ...
The Effects of Exercise on Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
... ❏ Overproduction of insulin leads to desensitization of the cells. ❏ 200 or more units of insulin per day to attain glycemic control and to prevent ketosis. ❏ Giving more insulin to increase cellular response only increasing insulin resistance. ❏ Increased risk of Postprandial Hypoglycemia ...
... ❏ Overproduction of insulin leads to desensitization of the cells. ❏ 200 or more units of insulin per day to attain glycemic control and to prevent ketosis. ❏ Giving more insulin to increase cellular response only increasing insulin resistance. ❏ Increased risk of Postprandial Hypoglycemia ...
Cardio-Weights-Stretch
... Cardiovascular conditioning strengthens the heart and lungs. Raising one’s heart rate will improve their heart capability. One form of cardiovascular conditioning is aerobic exercise. Aerobic exercise is typically running over a long distance at a paced rate. The opposite is anaerobic exercise, whic ...
... Cardiovascular conditioning strengthens the heart and lungs. Raising one’s heart rate will improve their heart capability. One form of cardiovascular conditioning is aerobic exercise. Aerobic exercise is typically running over a long distance at a paced rate. The opposite is anaerobic exercise, whic ...
Final Exam Review Sheet
... a) uremic toxicity b) metabolic acidosis c) glomerulonephritis d) renal tumors e) atherosclerosis 19. Eating a meal packed with refined carbohydrates can have what deleterious effect on your body? a) destroys cells of pancreas b) causes glucose levels to drop c) causes insulin levels to ‘spike’ d) ...
... a) uremic toxicity b) metabolic acidosis c) glomerulonephritis d) renal tumors e) atherosclerosis 19. Eating a meal packed with refined carbohydrates can have what deleterious effect on your body? a) destroys cells of pancreas b) causes glucose levels to drop c) causes insulin levels to ‘spike’ d) ...
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
... - WHAT WE BREATHE As well as breathing in oxygen, we also breathe out a lot of oxygen. This is most important when we give mouth to mouth resuscitation. AIR COMPOSITION ...
... - WHAT WE BREATHE As well as breathing in oxygen, we also breathe out a lot of oxygen. This is most important when we give mouth to mouth resuscitation. AIR COMPOSITION ...
A. Cellular Physiology a. Describe the cell membrane and its
... Anaerobic metabolism relies on the Embden-Meyerhof pathway only, yielding 4 ATP per glucose molecule less one for the phosphorylation of fructose 6-PO4 and one more if glucose 6-PO4 is generated from circulating glucose. The generation of NAD+ required is via the conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic ...
... Anaerobic metabolism relies on the Embden-Meyerhof pathway only, yielding 4 ATP per glucose molecule less one for the phosphorylation of fructose 6-PO4 and one more if glucose 6-PO4 is generated from circulating glucose. The generation of NAD+ required is via the conversion of pyruvic acid to lactic ...
Exercise-Antioxidants-and-Nutrition
... To be truly fit and healthy, daily exercise must be coupled with supporting the inside of the body. Intense training can actually deplete the body of vital substances. Many athletes main concerns are muscle mass and increased performance, the primary focus can be on ...
... To be truly fit and healthy, daily exercise must be coupled with supporting the inside of the body. Intense training can actually deplete the body of vital substances. Many athletes main concerns are muscle mass and increased performance, the primary focus can be on ...
The Digestive System
... Filtration and urine output • Removes wastes (other than carbon dioxide) from the blood. • Controls the amount of water in the body. ...
... Filtration and urine output • Removes wastes (other than carbon dioxide) from the blood. • Controls the amount of water in the body. ...
File
... Antarctic fishes, where temperatures can drop below the freezing point of unprotected body fluids (about -0.7oC). ...
... Antarctic fishes, where temperatures can drop below the freezing point of unprotected body fluids (about -0.7oC). ...
Athletes who eat well, play well
... 3 Supplement. Exercise is good, but athletes often exercise to the extreme, and this has an effect on their nutritional needs. An adequate discussion of sports-nutrition micronutrient supplementation would require several articles. However, several cutting edge supplements are worth noting briefly: ...
... 3 Supplement. Exercise is good, but athletes often exercise to the extreme, and this has an effect on their nutritional needs. An adequate discussion of sports-nutrition micronutrient supplementation would require several articles. However, several cutting edge supplements are worth noting briefly: ...
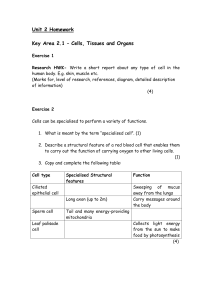
Unit 2 Homework
... why this is the case. (1) 4. Construct a table to compare the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries. (6) 5. What is the name given to the red blood pigment haemoglobin when it combines with oxygen? (1) Total 13 marks ...
... why this is the case. (1) 4. Construct a table to compare the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries. (6) 5. What is the name given to the red blood pigment haemoglobin when it combines with oxygen? (1) Total 13 marks ...
File
... Produce the most force and fatigue quickly…it does not take long to get tired! Use anaerobic respiration Sprinters, shot putters, and 1 repetition maximum weight ...
... Produce the most force and fatigue quickly…it does not take long to get tired! Use anaerobic respiration Sprinters, shot putters, and 1 repetition maximum weight ...
Introduction to A & P
... The process in which cells and organisms are able to maintain a stable balance of internal and external substances and forces is called… a) b) c) d) ...
... The process in which cells and organisms are able to maintain a stable balance of internal and external substances and forces is called… a) b) c) d) ...
02.422-03.2 Functional Anatomy
... is accomplished through the circulation of blood through the body; also cleanses the body by carrying toxic materials to the kidneys and sweat glands for excretion. Digestive system – takes the food ingested and converts it into a form that can be used. Nervous system – essential for all of the ...
... is accomplished through the circulation of blood through the body; also cleanses the body by carrying toxic materials to the kidneys and sweat glands for excretion. Digestive system – takes the food ingested and converts it into a form that can be used. Nervous system – essential for all of the ...
Lesson 1 Respiratory
... • Waste carbon dioxide is transferred from the blood back into the air. ...
... • Waste carbon dioxide is transferred from the blood back into the air. ...
The Oxygen Transport System
... •Ventilation will INCREASE out of proportion to workload so that Ventilation becomes greater than NecessaryHYPERVENTILATION •excessive movement of air in & out caused by increased depth and frequency of breathing and resulting in elimination of CO2 ...
... •Ventilation will INCREASE out of proportion to workload so that Ventilation becomes greater than NecessaryHYPERVENTILATION •excessive movement of air in & out caused by increased depth and frequency of breathing and resulting in elimination of CO2 ...
here - Philippine Heart Association
... - this should be increased first prior to increasing intensity - 30 minutes per day Frequency - most or all days of the week - if vigorous exercise is done, should be done only 3x a week. ...
... - this should be increased first prior to increasing intensity - 30 minutes per day Frequency - most or all days of the week - if vigorous exercise is done, should be done only 3x a week. ...
Chapter_25_Metabolism
... possible without food. • During fasting and starvation, nervous tissue and red blood cells continue to use glucose for ATP production. ...
... possible without food. • During fasting and starvation, nervous tissue and red blood cells continue to use glucose for ATP production. ...
Respiration
... Rate of respiration • Breathing rate/ pulse rate increases during exercise because muscle tissues require more energy and rate of respiration increases. Hence, the heart beats faster to increase the rate of transport of oxygen to muscle tissues and increase rate of transport of waste products away ...
... Rate of respiration • Breathing rate/ pulse rate increases during exercise because muscle tissues require more energy and rate of respiration increases. Hence, the heart beats faster to increase the rate of transport of oxygen to muscle tissues and increase rate of transport of waste products away ...
Record of Assessment
... • Young people in the 14 -16 age range and its implications for special • Antenatal and postnatal women populations exercise • Older people (50 plus) To include relevant tendon, ligament, muscle, joint and bone mineral density changes and their implications for exercise 7.1 Describe how carbohydrate ...
... • Young people in the 14 -16 age range and its implications for special • Antenatal and postnatal women populations exercise • Older people (50 plus) To include relevant tendon, ligament, muscle, joint and bone mineral density changes and their implications for exercise 7.1 Describe how carbohydrate ...
Body Systems Jeopardy
... Name the 4 main parts of the digestive system and the function of the system. ...
... Name the 4 main parts of the digestive system and the function of the system. ...
File - Northwoods 5th Grade
... 51. Cardiac muscle – type of muscle in the heart 52.Contract – to draw together (opposite of extend) 53.Endurance – the ability to do something difficult for a long time (like exercising) 54.Extend – to increase in length (opposite of contract) 55.Flex – to bend 56.Involuntary muscle – muscle contro ...
... 51. Cardiac muscle – type of muscle in the heart 52.Contract – to draw together (opposite of extend) 53.Endurance – the ability to do something difficult for a long time (like exercising) 54.Extend – to increase in length (opposite of contract) 55.Flex – to bend 56.Involuntary muscle – muscle contro ...
Energy 2
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
... Anaerobic Respiration is how sprinters produce the energy that is used in short periods of ‘all out effort’ - high intensity. Oxygen cannot reach the muscles fast enough, so anaerobic respiration is used. Glucose Produces… ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.