10th grade physical education level two certification name
... anaerobic means without oxygen; more specifically, aerobic activities are those that enable the cells in your body to utilize oxygen during extended periods of energy expenditure; anaerobic activities are those activities that are done at such a fast rate of speed (or heart rate) that your cells do ...
... anaerobic means without oxygen; more specifically, aerobic activities are those that enable the cells in your body to utilize oxygen during extended periods of energy expenditure; anaerobic activities are those activities that are done at such a fast rate of speed (or heart rate) that your cells do ...
Document
... The whole point of Inhaling is to get air into the Alveoli so that the surrounding blood capillaries can pick up some Oxygen on the Red cells and carry it to every living cell in the body along with Glucose. The cells can then use the Oxygen and Glucose to release energy. When the cells release Ener ...
... The whole point of Inhaling is to get air into the Alveoli so that the surrounding blood capillaries can pick up some Oxygen on the Red cells and carry it to every living cell in the body along with Glucose. The cells can then use the Oxygen and Glucose to release energy. When the cells release Ener ...
Doping in Sports
... Appetite suppressant Insomnia (affects GH) Tachycardia, arrhythmias and heart disease Mental status changes Fatigue depression and lethargy ...
... Appetite suppressant Insomnia (affects GH) Tachycardia, arrhythmias and heart disease Mental status changes Fatigue depression and lethargy ...
LEARNING OBJECTIVES Muscle Metabolism At the end of this
... The available oxygen is sufficient to meet the energy needs of the contracting muscles up to a point, when muscular exertion is very great oxygen can not be supplied to muscles fast enough & cellular respiration can not produce enough ATP ...
... The available oxygen is sufficient to meet the energy needs of the contracting muscles up to a point, when muscular exertion is very great oxygen can not be supplied to muscles fast enough & cellular respiration can not produce enough ATP ...
Skeletal System Body Systems Revision Guide Long Term Effects
... The key principles when planning a programme are: Specificity – training must be matched to the needs of the sporting activity to improve fitness in the body parts the sport uses. Overload - fitness can only be improved by training more than you normally do. You must work hard. Progression – start s ...
... The key principles when planning a programme are: Specificity – training must be matched to the needs of the sporting activity to improve fitness in the body parts the sport uses. Overload - fitness can only be improved by training more than you normally do. You must work hard. Progression – start s ...
The Five Components of Fitness
... Cardiovascular fitness (also known as cardiorespiratory fitness) is the ability of the heart, lungs and vascular system to deliver oxygen-rich blood to working muscles during sustained physical activity. A. Your body develops cardiorespiratory endurance when you participate in activities for about 2 ...
... Cardiovascular fitness (also known as cardiorespiratory fitness) is the ability of the heart, lungs and vascular system to deliver oxygen-rich blood to working muscles during sustained physical activity. A. Your body develops cardiorespiratory endurance when you participate in activities for about 2 ...
physiology9
... 1. Might be occurring coz of genetic but that would be very rare and does not represent the general case of this type. 2. There is insulin ( and some times high level of it in blood) but there is some abnormality in the insulin receptors (either these receptors are structurally abnormal or decreased ...
... 1. Might be occurring coz of genetic but that would be very rare and does not represent the general case of this type. 2. There is insulin ( and some times high level of it in blood) but there is some abnormality in the insulin receptors (either these receptors are structurally abnormal or decreased ...
The Human Body Systems
... around the body providing oxygen to the other cells. Red blood cells also pick up and remove carbon dioxide and water that cells create as waste. ...
... around the body providing oxygen to the other cells. Red blood cells also pick up and remove carbon dioxide and water that cells create as waste. ...
7.b. Insect Tracheoles
... hollow tubes (trachea) to the tissues where oxygen is required and where carbon dioxide is produced. The fine tubules that deliver oxygen to the tissues themselves are called tracheoles and often have a film of moisture in their extremities. This system has its limitations because it is essentially ...
... hollow tubes (trachea) to the tissues where oxygen is required and where carbon dioxide is produced. The fine tubules that deliver oxygen to the tissues themselves are called tracheoles and often have a film of moisture in their extremities. This system has its limitations because it is essentially ...
Using energy Exercise
... which needs oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. During exercise, the breathing rate and heart rate increase. During hard exercise an oxygen debt may build up. ...
... which needs oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. During exercise, the breathing rate and heart rate increase. During hard exercise an oxygen debt may build up. ...
BIO_MODULE_02_RESPIRATION_AND _GAS EXCHANGE
... Effects of exercise The body needs much more Oxygen. The breathing becomes faster and deeper and produces a large vol. of Oxygen. More Carbon Dioxide is produced which is the waste product, which blood carries back to the lungs to be exhaled Because the body needs more blood to carry more Oxygen an ...
... Effects of exercise The body needs much more Oxygen. The breathing becomes faster and deeper and produces a large vol. of Oxygen. More Carbon Dioxide is produced which is the waste product, which blood carries back to the lungs to be exhaled Because the body needs more blood to carry more Oxygen an ...
Here
... Before each sport activity, the user sends an SMS providing data which are specific to that day (measured glycemia, expected time, duration, and intensity of the sport activity…), and the system replies with an estimate of the extra carbohydrates the patient is suggested to eat in order to prevent h ...
... Before each sport activity, the user sends an SMS providing data which are specific to that day (measured glycemia, expected time, duration, and intensity of the sport activity…), and the system replies with an estimate of the extra carbohydrates the patient is suggested to eat in order to prevent h ...
How Can I Train Effectively
... ▪ Specific activity to the sport you play. (skills/grids etc) Flexibility exercises ▪ Putting your joints through a wide range of motion. (Stretching!!) ...
... ▪ Specific activity to the sport you play. (skills/grids etc) Flexibility exercises ▪ Putting your joints through a wide range of motion. (Stretching!!) ...
i. cardiovascular system
... b. ventricles: two lower chambers c. aorta: main artery in the body d. heart-rate: number of times heart contracts each minute ...
... b. ventricles: two lower chambers c. aorta: main artery in the body d. heart-rate: number of times heart contracts each minute ...
Overall Function of Respiratory System
... • 3) diffusion (how gas gets across the air blood barrier) – rate of diffusion • pressure gradient • diffusability of the gas – CO2 very soluble, in and out of solution easily – O2 low solubility, transported by hemoglobin • thickness of membrane ...
... • 3) diffusion (how gas gets across the air blood barrier) – rate of diffusion • pressure gradient • diffusability of the gas – CO2 very soluble, in and out of solution easily – O2 low solubility, transported by hemoglobin • thickness of membrane ...
Introduction to homeostasis
... Feed forward mechanisms anticipate changes in a variable, improving the speed of homeostatic response. For example, presence of food in the intestine stimulates secretion of hormones that promote cellular uptake and storage of the food which is about to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Examples of ...
... Feed forward mechanisms anticipate changes in a variable, improving the speed of homeostatic response. For example, presence of food in the intestine stimulates secretion of hormones that promote cellular uptake and storage of the food which is about to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Examples of ...
Chapter_07_4E - Ironbark (xtelco)
... at a running velocity of 14.4 km/h (8.9 mph) is evident only in the ...
... at a running velocity of 14.4 km/h (8.9 mph) is evident only in the ...
What are the parts and functions of the Muscular System?
... 1. Identify the 3 types of muscles. 2. Describe where each type of muscle is ...
... 1. Identify the 3 types of muscles. 2. Describe where each type of muscle is ...
2. The Respiratory System
... below the lungs contracts and flattens, increasing the size of the chest the lungs increase in size, so the pressure inside them falls. This causes air to rush in through the nose or mouth. ...
... below the lungs contracts and flattens, increasing the size of the chest the lungs increase in size, so the pressure inside them falls. This causes air to rush in through the nose or mouth. ...
TOPIC: Locomotion AIM: What are the parts and functions of the
... HW: Ditto – Skeletal System Matching Column ...
... HW: Ditto – Skeletal System Matching Column ...
Respiration Aerobic and Anaerobic PPT
... Short, intense activities like sprinting, weightlifting, jumping and throwing use anaerobic respiration. ...
... Short, intense activities like sprinting, weightlifting, jumping and throwing use anaerobic respiration. ...
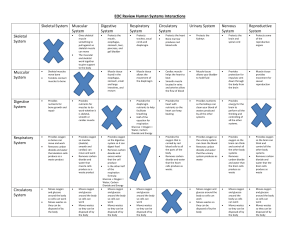
Body Systems Work Together
... oxygen into cell and carbon dioxide out of cells. 2. Digestive and Circulatory work together to break down foods and bring nutrients to all cell. 3. Nervous and Muscle work together by sending signals based on the senses to contract muscles and move. 4. Nervous and Endocrine work together by reactin ...
... oxygen into cell and carbon dioxide out of cells. 2. Digestive and Circulatory work together to break down foods and bring nutrients to all cell. 3. Nervous and Muscle work together by sending signals based on the senses to contract muscles and move. 4. Nervous and Endocrine work together by reactin ...
Body in Action summary notes
... Place where exchange of substances between body cells and capillaries occurs Oxygen and glucose move into body cells by diffusion Carbon dioxide moves into blood by diffusion Capillaries have very thin walls to allow easy exchange of substances Capillary networks are dense (lots of) to increase exch ...
... Place where exchange of substances between body cells and capillaries occurs Oxygen and glucose move into body cells by diffusion Carbon dioxide moves into blood by diffusion Capillaries have very thin walls to allow easy exchange of substances Capillary networks are dense (lots of) to increase exch ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.