* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Using energy Exercise
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Animal nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Fluorescent glucose biosensor wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Carbohydrate wikipedia , lookup
Primary production wikipedia , lookup
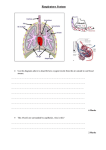
Aerobic and anaerobic respiration (B2 REVISION) Respiration releases energy for cells from glucose. This can be aerobic respiration, which needs oxygen, or anaerobic respiration, which does not. During exercise, the breathing rate and heart rate increase. During hard exercise an oxygen debt may build up. What is aerobic respiration? Respiration is a series of reactions in which energy is released from glucose.Aerobic respiration is the form of respiration which uses oxygen. It can be summarised by this equation: glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water (+ energy) Energy is shown in brackets because it is not a substance. Notice that: Glucose and oxygen are used up Carbon dioxide and water are produced as waste products Aerobic respiration happens all the time in the cells of animals and plants. Most of the reactions involved happen inside mitochondria, tiny objects inside the cytoplasm of the cell. The reactions are controlled by enzymes. Using energy Energy released during respiration is used by the organism in several ways. It may be used to build up larger molecules from smaller ones. For example: Plants make amino acids from sugars, nitrates and other nutrients These amino acids are then built up into larger molecules - proteins Energy is used by animals to enable the muscles to contract so that the animals can move. Mammals and birds keep their body temperature steady. Energy from respiration is used to do this when their surroundings are colder than they are. Exercise During exercise, the muscle cells respire more than they do at rest. This means that: Oxygen and glucose must be delivered to them more quickly Waste carbon dioxide must be removed more quickly This is achieved by increasing the heart rate, rate of breathing and the depth of breathing. The increased heart rate increases the rate of blood flow around the body. The increased rate and depth of breathing increases the rate of gaseous exchange in the lungs. The muscles store glucose as glycogen. This can then be converted back to glucose for use during exercise. Take care not to get confused: plants store glucose as starch and animals store it as glycogen. In addition, respiration and breathing are not the same thing: respiration releases energy, while breathing lets air into and out of our lungs. Anaerobic respiration Not enough oxygen may reach the muscles during exercise. When this happens, they use anaerobic respiration to obtain energy. Anaerobic respiration involves the incomplete breakdown of glucose. It releases around 5% of the energy released by aerobic respiration, per molecule ofglucose. The waste product is lactic acid rather than carbon dioxide and water: glucose → lactic acid (+ little energy) Muscle fatigue Muscles become fatigued (tired) during long periods of vigorous activity. This means that they stop contracting efficiently. One cause of this is the build-up of lactic acid in the muscles from anaerobic respiration. The lactic acid is removed from the muscles by blood flowing through them. Fitness versus health Fit people are able to carry out physical activities more effectively than unfit people. Their pulse rate is likely to return to normal more quickly after exercise. But being fit is not the same as being healthy. Healthy people are free from disease and infection - they may or may not be fit as well. It is possible to be fit but unhealthy, or healthy but unfit. Now try a Test Bite. Oxygen debt - Higher tier Much less energy is released during anaerobic respiration than during aerobic respiration. This is because the breakdown of glucose is incomplete. Anaerobic respiration produces an oxygen debt. This is the amount of oxygen needed to oxidise lactic acid to carbon dioxide and water. The existence of an oxygen debt explains why we continue to breathe deeply and quickly for a while after exercise. 1. Paula is training for a marathon. When she runs, her heart beats faster than it does when she is resting. Complete the sentences, using words from the box. blood breathe heat nitrogen carbon dioxide oxygen glucose respire When she is running, Paula‘s muscle activity increases. To do this, her muscle cells ................................................. at a faster rate to give her more energy. Her muscles need to be supplied with ........................................... and .......................................................... more quickly. Her heart beats faster to increase the flow of.................................................. which carries the products ........................................................................................... and ............................................................ away from her muscles. (Total 6 marks) 2. The diagram shows part of the breathing system in a human. (a) Use words from the list to label the parts on the drawing. alveoli (b) bronchiole bronchus diaphragm trachea (windpipe) Where in the lungs does oxygen enter the blood? ..................................................................................................................................... (c) (4) (1) Which process in cells produces carbon dioxide? .................................................................................................................................. (1) (Total 6 marks) 3. (a) Explain, as fully as you can, why respiration has to take place more rapidly during exercise. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. (b) (2) During exercise the process of respiration produces excess heat. Explain how the body prevents this heat from causing a rise in the core (deep) body temperature. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................. (4) (Total 6 marks) 4. (a) (i) Complete the word equation for the process of aerobic respiration. Glucose + ........................... → carbon dioxide + water (1) (ii) Which organ removes carbon dioxide from your body? ................................................................................................................. (1) (b) Use names from the box to complete the two spaces in the passage. carbon dioxide lactic acid nitrogen oxygen water Anaerobic respiration can occur when an athlete does vigorous exercise. This is because there is not enough ....................................................... in the body. The product of anaerobic respiration is .................................................................. (2) (Total 4 marks) 5. Oxygen from our lungs is carried, by our blood, to cells in our body where aerobic respiration takes place. (a) (i) Complete the two spaces to balance the chemical reaction for aerobic respiration. C6H12O6 + 6O2 → ....... CO2 + ...... H2O (ii) (1) Name the substance with the formula C6H12O6. ................................................................................................................................. (iii) (1) Name the structures in the cytoplasm of our cells where aerobic respiration takes place. .................................................................................................................................. (b) (1) Oxygen is absorbed through the alveoli in the lungs. (i) How are the alveoli adapted for this function? .......................................................................................................................... .......................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ (ii) Name the gas which is excreted through the alveoli. .......................................................................................................................... (c) (i) (2) (1) What is the name of the process of respiration when oxygen is not available? .......................................................................................................................... (1) (7 marks) 1 (a) respire 1 2 blood 1 2 [6] 2 (a) trachea / windpipe bronchus alveoli diaphragm for 1 mark each 4 (b) alveoli / air sacs (reject capillaries) for one mark 1 (c) respiration for one mark 1 [6] 3 (a) more energy needed, for increased muscular activity for 1 mark each 2 (b) increased sweat production, evaporation of sweat cools body, vasodilation OWTTE, more heat loss (by radiation) for 1 mark each 4 [6] 4 (a) (i) oxygen do not credit air 1 (ii) lung(s) do not credit blood or nose or windpipe alone but accept as a neutral answer if included with lungs 1 (b) oxygen 1 lactic acid both words required 1 [4] 5 (i) 6 in both spaces do not credit if any formula has been altered 1 (ii) glucose allow fructose or dextrose 1 (iii) mitochondria accept organelles 1 [3] (b) (i) any two from large surface thin (surface) moist (surface) (with a good) blood supply 2 (ii) carbon dioxide accept water vapour do not credit just water 1 (c) (i) anaerobic (respiration) 1