Neuromuscular Adaptations to Resistance Training
... Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy resulting from resistive training can be accompanied by strengthened myocardium and increased stroke volume at rest and during exercise. Stroke volume is not significantly increased when it is related to body surface area or lean body mass. ...
... Left ventricular concentric hypertrophy resulting from resistive training can be accompanied by strengthened myocardium and increased stroke volume at rest and during exercise. Stroke volume is not significantly increased when it is related to body surface area or lean body mass. ...
Muscles - The Science Queen
... http://www.calhoun.edu/distance/Internet/Natural/Healthlinks/ems/paramedic %20student%20page/Vol.%201%20Ch.%208a_files/slide0018.htm ...
... http://www.calhoun.edu/distance/Internet/Natural/Healthlinks/ems/paramedic %20student%20page/Vol.%201%20Ch.%208a_files/slide0018.htm ...
Organ Integration and Control
... Once the fats reserves are used up the only readily available resource left is the protein found in muscle. Muscle protein is degraded and concerted to amino acids, which the liver converts to glucose. Finally once muscle protein is exhausted all that is left is essential protein, which is then brok ...
... Once the fats reserves are used up the only readily available resource left is the protein found in muscle. Muscle protein is degraded and concerted to amino acids, which the liver converts to glucose. Finally once muscle protein is exhausted all that is left is essential protein, which is then brok ...
EXERCISE PHYSIOLOGY
... however, refers to the ability to make large quantities of ATP. Power and capacity are inversely related. Metabolic pathways that are the most powerful also have the least capacity, and vice versa. The anaerobic pathways are far more powerful than the aerobic pathways, but have a very limited capac ...
... however, refers to the ability to make large quantities of ATP. Power and capacity are inversely related. Metabolic pathways that are the most powerful also have the least capacity, and vice versa. The anaerobic pathways are far more powerful than the aerobic pathways, but have a very limited capac ...
RevisionResource
... Respiration is the release of energy from glucose in the muscles. When the body is at rest this is aerobic respiration. As you exercise you breathe harder and deeper and the heart beats faster to get oxygen to the muscles. Glucose + oxygen → energy + water + carbon dioxide ...
... Respiration is the release of energy from glucose in the muscles. When the body is at rest this is aerobic respiration. As you exercise you breathe harder and deeper and the heart beats faster to get oxygen to the muscles. Glucose + oxygen → energy + water + carbon dioxide ...
Basic Energy Systems
... Exercising • Oxygen enters the lungs and passes into your arteries • Oxygen rich blood travels to the heart where it is pumped to the rest of your body • Lactic Acid an Carbon Dioxide are waste products of exercising and are carried away from your cells through the veins • These waste products can ...
... Exercising • Oxygen enters the lungs and passes into your arteries • Oxygen rich blood travels to the heart where it is pumped to the rest of your body • Lactic Acid an Carbon Dioxide are waste products of exercising and are carried away from your cells through the veins • These waste products can ...
Acute responses of the respiratory system
... centre in the brain to increase the respiratory rate (RR) and tidal volume (TV) ...
... centre in the brain to increase the respiratory rate (RR) and tidal volume (TV) ...
Components of a Balanced Diet File
... Proteins provide the ‘fabric’ for all the soft tissues of the body; skin, muscles and organs. They are therefore vital for growth and repair. ...
... Proteins provide the ‘fabric’ for all the soft tissues of the body; skin, muscles and organs. They are therefore vital for growth and repair. ...
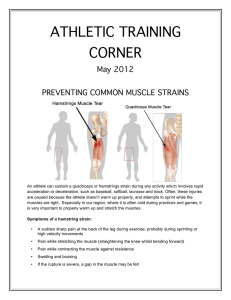
athletic training corner
... When dealing with muscle strains. it is important to first address swelling and pain. Once these are improving, then it is important to restore normal range of motion. Finally, strengthening exercises need to be done to return the muscle to prior function. In sports, the athlete will be put through ...
... When dealing with muscle strains. it is important to first address swelling and pain. Once these are improving, then it is important to restore normal range of motion. Finally, strengthening exercises need to be done to return the muscle to prior function. In sports, the athlete will be put through ...
Homeostasis Tree Map
... which might need 15 to 25 times more oxygen than when they are resting, according to Williams Sport Training. Consequently, you breathe faster during exercise. The harder you exercise, the more rapid your breathing rate becomes. This also helps release carbon dioxide, a by-product of energy metaboli ...
... which might need 15 to 25 times more oxygen than when they are resting, according to Williams Sport Training. Consequently, you breathe faster during exercise. The harder you exercise, the more rapid your breathing rate becomes. This also helps release carbon dioxide, a by-product of energy metaboli ...
Physical Fitness
... Relates to the ability of the heart, blood, blood vessels, and respiratory system to supply oxygen and fuel to muscles during exercise Example: Aerobic exercise (body uses a large amount of oxygen for a sustained period of time) ...
... Relates to the ability of the heart, blood, blood vessels, and respiratory system to supply oxygen and fuel to muscles during exercise Example: Aerobic exercise (body uses a large amount of oxygen for a sustained period of time) ...
RESPIRATION IN LIVING THINGS GRADE:07 NOTES Respiration is
... We need to get oxygen from the air into the blood, and we need to remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood into the air. Moving gases like this is called gas exchange. The alveoli are adapted to make gas exchange in lungs happen easily and efficiently. Here are some features of the alveoli that al ...
... We need to get oxygen from the air into the blood, and we need to remove waste carbon dioxide from the blood into the air. Moving gases like this is called gas exchange. The alveoli are adapted to make gas exchange in lungs happen easily and efficiently. Here are some features of the alveoli that al ...
Rectus Femoris Injuries - The London Sports Injury Clinic
... program altered to aid the recovery process. ...
... program altered to aid the recovery process. ...
Fitness Concepts
... Body Composition- The ratio of lean body mass to body fat. Lean body mass refers to muscle, bone, nerve tissue, skin and organs. Lean tissue is metabolically active which means it needs more fuel to maintain its activity than fat. Because muscle weighs more than fat it is important to measure body c ...
... Body Composition- The ratio of lean body mass to body fat. Lean body mass refers to muscle, bone, nerve tissue, skin and organs. Lean tissue is metabolically active which means it needs more fuel to maintain its activity than fat. Because muscle weighs more than fat it is important to measure body c ...
Revision Questions What is the definition of energy and what are the
... It also affects lipoprotein kinase, which is the enzyme that helps to breakdown fats. These conditions reduce the ability of enzymes to function optimally and therefore the body’s ability to synthesize ATP is temporarily reduced which causes fatigue. ...
... It also affects lipoprotein kinase, which is the enzyme that helps to breakdown fats. These conditions reduce the ability of enzymes to function optimally and therefore the body’s ability to synthesize ATP is temporarily reduced which causes fatigue. ...
Exercise Physiology
... • Amount of air taken in each a greater volume of air, and with breath increases it oxygen ...
... • Amount of air taken in each a greater volume of air, and with breath increases it oxygen ...
Components of Fitness
... to be able to finish physical jobs; to not be too tired by the end of the day. is the ability of the heart, lungs and blood vessels to deliver oxygen to working muscles and tissues ...
... to be able to finish physical jobs; to not be too tired by the end of the day. is the ability of the heart, lungs and blood vessels to deliver oxygen to working muscles and tissues ...
Midterm 3 - Creighton Biology
... Individuals with Type I diabetes can no longer produce insulin and (without treatment) will have very high blood glucose levels after a meal. Based on what you know about the effects of insulin, the reason for the high blood sugar levels is most likely that oo. the small intestine absorbs glucose mo ...
... Individuals with Type I diabetes can no longer produce insulin and (without treatment) will have very high blood glucose levels after a meal. Based on what you know about the effects of insulin, the reason for the high blood sugar levels is most likely that oo. the small intestine absorbs glucose mo ...
Functions - kcpe-kcse
... Basal Metabolic Rate • The amount of energy needed to carry on vital life processes of the body when it is at complete rest. • e.g heartbeat, circulation, breathing, brain functions and other essential reactions in the organs. ...
... Basal Metabolic Rate • The amount of energy needed to carry on vital life processes of the body when it is at complete rest. • e.g heartbeat, circulation, breathing, brain functions and other essential reactions in the organs. ...
Glossary pe - Perth Grammar
... When a muscle shortens and gets fatter as it contracts A head injury which may cause a person to become unconscious, dizzy or disorientated Where the rules or the way a game is played is changed during a practice session to work on a particular aspect Being able to perform a skill properly, the same ...
... When a muscle shortens and gets fatter as it contracts A head injury which may cause a person to become unconscious, dizzy or disorientated Where the rules or the way a game is played is changed during a practice session to work on a particular aspect Being able to perform a skill properly, the same ...
File
... • Because the respiratory system only has one entrance and exit point, anything blocking the pathway will interrupt gas exchange (choke). • Since oxygen cannot reach the alveoli, no oxygen can go into the blood. • If no oxygen gets into the blood, the body cell will not be able to perform cellular r ...
... • Because the respiratory system only has one entrance and exit point, anything blocking the pathway will interrupt gas exchange (choke). • Since oxygen cannot reach the alveoli, no oxygen can go into the blood. • If no oxygen gets into the blood, the body cell will not be able to perform cellular r ...
The Sea Floor
... Heat loss or gain due to water or _____ currents The still layer of air or water around any object is called the ____________ Evaporation: The most effective mode of heat loss for ...
... Heat loss or gain due to water or _____ currents The still layer of air or water around any object is called the ____________ Evaporation: The most effective mode of heat loss for ...
Animal Form and Function – Intro Integumentary System
... • digestion breaks down food into nutrient molecules + some energy returns to environment as feces – elimination of waste • nutrient molecules travel to body cells via circulatory system + convert to useful form (ATP) in cells - water and CO2 are excreted from the body • cells use ATP for cellular w ...
... • digestion breaks down food into nutrient molecules + some energy returns to environment as feces – elimination of waste • nutrient molecules travel to body cells via circulatory system + convert to useful form (ATP) in cells - water and CO2 are excreted from the body • cells use ATP for cellular w ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.