* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
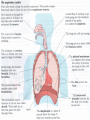
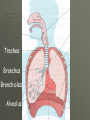
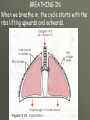
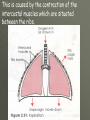
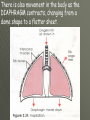
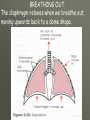
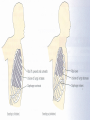
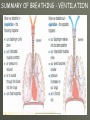
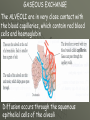
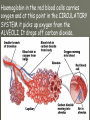
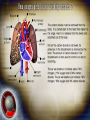
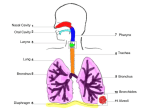
THE GAS EXCHANGE SYSTEM THE VARIOUS PARTS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM ARE:•TRACHEA •EPIGLOTTIS •LARYNX •BRONCHUS •BRONCHIOLES •ALVEOLI •DIAPHRAGM Occasionally this doesn’t happen and we have all experienced feeling “choking” when food goes down the wrong way. At the bottom of the TRACHEA are 2 branches called the BRONCHI, through which air passes into either lung. Smaller and smaller branches, called BRONCHIOLES, extend out from the BRONCHI and at the very ends of these they form tiny sacs called ALVEOLI. Trachea Bronchus Bronchioles Alveolus ALVEOLI It is these that give the lungs their spongy texture. The linings of the ALVEOLI are very thin and only work well when they are moist and clean. When air is breathed in through the nose, it is: 1. FILTERED by the hairs at the entrance to the nose and by mucus. 2.WARMED by blood vessels passing close to the lining of the nose. 3.MOISTENED by water vapour. BREATHING IN When we breathe in, the cycle starts with the ribs lifting upwards and outwards. This is caused by the contraction of the intercostal muscles which are situated between the ribs. There is also movement in the body as the DIAPHRAGM contracts, changing from a dome shape to a flatter sheet. BREATHING OUT The diaphragm relaxes when we breathe out, moving upwards back to a dome shape. SUMMARY OF BREATHING - VENTILATION GASEOUS EXCHANGE The ALVEOLI are in very close contact with the blood capillaries, which contain red blood cells and haemoglobin Diffusion occurs through the squamous epithelial cells of the alveoli Haemoglobin in the red blood cells carries oxygen and at this point in the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM it picks up oxygen from the ALVEOLI. It drops off carbon dioxide. So the RESPIRATORY SYSTEM has 2 main jobs: 1. To get oxygen into the body 2.To get carbon dioxide out of the body. AIR COMPOSITION - WHAT WE BREATHE As well as breathing in oxygen, we also breathe out a lot of oxygen. This is most important when we give mouth to mouth resuscitation. AIR COMPOSITION This is why we can give the “kiss of life” OXYGEN DEBT- You will develop oxygen debt after intense physical exercise. This is the point when the exercise becomes ANAEROBIC (without the use of oxygen) and which has to be paid back later- OXYGEN DEBT. The oxygen debt is the volume of oxygen needed to completely oxidise (break down) the lactic acid that builds up in the body during anaerobic respiration. If the exercise is just AEROBIC (with oxygen) there will be no oxygen debt.