File - Ms. Francis` Anatomy & Physiology Class
... 28. The location where a nerve connects with a muscle is called a a. Joint b. Sliding filament junction c. Neurotransmitter d. Neuromuscular junction 29. Structurally, neurons are unique because they are the only cells in the body that have a. Lacunae and canaliculi b. Axons and dendrites c. Satelli ...
... 28. The location where a nerve connects with a muscle is called a a. Joint b. Sliding filament junction c. Neurotransmitter d. Neuromuscular junction 29. Structurally, neurons are unique because they are the only cells in the body that have a. Lacunae and canaliculi b. Axons and dendrites c. Satelli ...
Nutrition Now J. Brown
... Fat Use during Exercise • When you exercise, the fat your muscles burn comes from the fatty deposits all over the body. • A person who is of desirable body weight may store 25 to 30 pounds of body fat but only about 1 pound of carbohydrate. • Although your supply of fat is almost unlimited, the abil ...
... Fat Use during Exercise • When you exercise, the fat your muscles burn comes from the fatty deposits all over the body. • A person who is of desirable body weight may store 25 to 30 pounds of body fat but only about 1 pound of carbohydrate. • Although your supply of fat is almost unlimited, the abil ...
The Levator Scapulae: A common cause of neck
... What is it? The Levator Scapulae muscle or Levator is a small muscle either side of the neck. It originates from the first four vertebrae of the neck ( C1 to C4) and inserts into the top of the shoulder blade (medial border and superior angle of the scapula) What does it do? Levator is the muscle th ...
... What is it? The Levator Scapulae muscle or Levator is a small muscle either side of the neck. It originates from the first four vertebrae of the neck ( C1 to C4) and inserts into the top of the shoulder blade (medial border and superior angle of the scapula) What does it do? Levator is the muscle th ...
HYPERMOBILITY SYNDROME
... What is joint hypermobility syndrome? Pereception of JHS as a mild or trivial condition with lax joints, pain, joint dislocation/subluxation, possible OA in later life. This has changed….. Now considered an inherited, genetically determined multisystemic disorder of connective tissues rendering the ...
... What is joint hypermobility syndrome? Pereception of JHS as a mild or trivial condition with lax joints, pain, joint dislocation/subluxation, possible OA in later life. This has changed….. Now considered an inherited, genetically determined multisystemic disorder of connective tissues rendering the ...
Eating for Cycling Being properly nourished and hydrated is
... Fluid: Adequate hydration is important when cycling. Cyclists may be unaware of the fluid they are losing due to various factors that cause sweat to evaporate easily. Professionals recommend four to five ounces of fluid every 15 to 20 minutes, or a minimum of a 16 ounce bottle every hour to avoid de ...
... Fluid: Adequate hydration is important when cycling. Cyclists may be unaware of the fluid they are losing due to various factors that cause sweat to evaporate easily. Professionals recommend four to five ounces of fluid every 15 to 20 minutes, or a minimum of a 16 ounce bottle every hour to avoid de ...
Human Body Systems
... germs, bugs, and poisons out the body. • The skin is the immune system’s first line of defense. • There are germ-killing chemicals in saliva, tears, ear wax, and mucus. • White blood cells destroy germs that enter through cuts. • Sticky yellow pus is made of bodies of white blood cells that die in t ...
... germs, bugs, and poisons out the body. • The skin is the immune system’s first line of defense. • There are germ-killing chemicals in saliva, tears, ear wax, and mucus. • White blood cells destroy germs that enter through cuts. • Sticky yellow pus is made of bodies of white blood cells that die in t ...
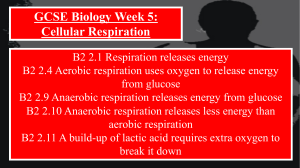
respiration - Learn Biology
... This is what’s is going on… Glucose (C6H12O6) is delivered to the cells (muscles) via the blood stream. Lactic acid is a waste product (that builds up in the muscles – and leads to “cramp”) Energy (ATP) only a small amount is produced – but is enough for short term / explosive activity. ...
... This is what’s is going on… Glucose (C6H12O6) is delivered to the cells (muscles) via the blood stream. Lactic acid is a waste product (that builds up in the muscles – and leads to “cramp”) Energy (ATP) only a small amount is produced – but is enough for short term / explosive activity. ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology I
... Physiology is the study of how the body Functions. The “how” is often on a chemical level. Anatomy and Physiology are closely integrated, both theoretically and practically All specific functions are performed by specific structures. ...
... Physiology is the study of how the body Functions. The “how” is often on a chemical level. Anatomy and Physiology are closely integrated, both theoretically and practically All specific functions are performed by specific structures. ...
Revision Booklet Mark Scheme
... Must state the receptor and the role Baroreceptors – detect decrease in blood pressure Must state the receptor and the role Impulses sent to cardiac control centre / medulla (oblongata) Do not accept CCC Increase in impulses to the SA node via the sympathetic nervous system / cardiac accelerator ner ...
... Must state the receptor and the role Baroreceptors – detect decrease in blood pressure Must state the receptor and the role Impulses sent to cardiac control centre / medulla (oblongata) Do not accept CCC Increase in impulses to the SA node via the sympathetic nervous system / cardiac accelerator ner ...
Breathing
... There are more than 640 skeletal muscles in the body, making up half of the bodies weight. This particular muscle is red in couler because of all the blood in the muscle fibres. There are different layers to these muscles, under the skin is the Superficial layer, the second layer is called the Deepe ...
... There are more than 640 skeletal muscles in the body, making up half of the bodies weight. This particular muscle is red in couler because of all the blood in the muscle fibres. There are different layers to these muscles, under the skin is the Superficial layer, the second layer is called the Deepe ...
The Endocrine Pancreas
... themselves (autophosphorylation), thus activating the catalytic activity of the receptor. • The activated receptor then phosphorylates a number of intracellular proteins, which is insulin receptor substrate 1 or IRS-1, which in turn generate a biological response that ultimately mediate insulin's ef ...
... themselves (autophosphorylation), thus activating the catalytic activity of the receptor. • The activated receptor then phosphorylates a number of intracellular proteins, which is insulin receptor substrate 1 or IRS-1, which in turn generate a biological response that ultimately mediate insulin's ef ...
PLCs 1.2.x Booklet - Carshalton Boys Sports College
... form on the inside walls of your blood vessels. This reduces blood flow and increases blood pressure. This can lead to coronary heart disease, strokes, heart attacks and even death. Eating a healthy diet which contains high density lipoproteins and fruit and vegetables will reduce cholesterol levels ...
... form on the inside walls of your blood vessels. This reduces blood flow and increases blood pressure. This can lead to coronary heart disease, strokes, heart attacks and even death. Eating a healthy diet which contains high density lipoproteins and fruit and vegetables will reduce cholesterol levels ...
File - Berwick PDHPE Stage 6
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
File
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
... The parts of the respiratory system and their functions 1) Oxygen enters the body through the mouth or nose. Through the nasal cavities the air is warmed, moistened and filtered for any foreign material 2) The pharynx serves as a common passage for air to the trachea. It leads from the nasal cavit ...
Exercise Modalities - Lemon Bay High School
... – Manipulates acceleration, creating an environment in which the body is stimulated to increase strength as a result of higher g-forces ...
... – Manipulates acceleration, creating an environment in which the body is stimulated to increase strength as a result of higher g-forces ...
Lecture Notes - Pitt Honors Human Physiology
... Probably the most common stomach disorder is peptic ulcer, which was discussed previously. Ulcers often occur in the duodenum of patients with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, in which a tumor begins to excrete gastrin. The end result is that stomach acid secretion becomes so high that the small intestin ...
... Probably the most common stomach disorder is peptic ulcer, which was discussed previously. Ulcers often occur in the duodenum of patients with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome, in which a tumor begins to excrete gastrin. The end result is that stomach acid secretion becomes so high that the small intestin ...
CHAPTER 2: The respiratory system
... • a-v-O2diff describes the difference in oxygen content between arterial and mixed-venous blood. • During exercise tissue pO2 decreases. • This forces Hb to release greater quantities of oxygen to meet metabolic needs. • This expands the tissue a-v-O2diff difference. • And so more oxygen is rel ...
... • a-v-O2diff describes the difference in oxygen content between arterial and mixed-venous blood. • During exercise tissue pO2 decreases. • This forces Hb to release greater quantities of oxygen to meet metabolic needs. • This expands the tissue a-v-O2diff difference. • And so more oxygen is rel ...
Why Do We Breath?
... Cells need more energy during exercise so need more oxygen (input) Evidence: Doodle sheet part H The heart and cardiovascular system provide a path for the inputs and outputs needed by cells for cellular respiration Evidence: cardiovascular notes There is a complex system of feedback loops that allo ...
... Cells need more energy during exercise so need more oxygen (input) Evidence: Doodle sheet part H The heart and cardiovascular system provide a path for the inputs and outputs needed by cells for cellular respiration Evidence: cardiovascular notes There is a complex system of feedback loops that allo ...
The aerobic capacity and fitness of Hungarian soldiers
... decreases the emergence and progression of hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes, stroke, some tumors, osteoporosis and depression. According to exercise physiology studies, regular exercise at the anaerobic threshold increases performance and improves aerobic output. Aerobic capacity refle ...
... decreases the emergence and progression of hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes, stroke, some tumors, osteoporosis and depression. According to exercise physiology studies, regular exercise at the anaerobic threshold increases performance and improves aerobic output. Aerobic capacity refle ...
File - margolis sport exercise
... The entire respiratory system would be useless unless the alveolar air were regularly changed. Since humans do not possess a one-way system for air circulation through the lungs, inhaled an exhaled air must be mixed to some degree. This does not normally produce any difficulty, since the respiratory ...
... The entire respiratory system would be useless unless the alveolar air were regularly changed. Since humans do not possess a one-way system for air circulation through the lungs, inhaled an exhaled air must be mixed to some degree. This does not normally produce any difficulty, since the respiratory ...
The Liver Although skin is considered to be the largest organ of the
... Liver converts stored glycogen to glucose and releases them into the blood when needed in order to maintain a stable blood glucose level during fasting state and between meals. Liver can also convert non-carbohydrate compounds such as lactic acid, amino acid to glucose. Inappropriately high output o ...
... Liver converts stored glycogen to glucose and releases them into the blood when needed in order to maintain a stable blood glucose level during fasting state and between meals. Liver can also convert non-carbohydrate compounds such as lactic acid, amino acid to glucose. Inappropriately high output o ...
暨 南 大 学 考 试 试 卷
... potential or a pressure gradient, and the energy is derived directly from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or some other high-energy phosphate compound. ...
... potential or a pressure gradient, and the energy is derived directly from the breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or some other high-energy phosphate compound. ...
Today`s Objective: SOL 3.d
... Happens in low/no oxygen conditions 1 Glucose only partially broken down to form waste products and 2 ATP ...
... Happens in low/no oxygen conditions 1 Glucose only partially broken down to form waste products and 2 ATP ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.