systems
... through our veins lacks oxygen, so it is dark red in color. This blood runs under a layer of subcutaneous fat which allows blue light to penetrate skin all the way to veins, so this is the color that is reflected back. ...
... through our veins lacks oxygen, so it is dark red in color. This blood runs under a layer of subcutaneous fat which allows blue light to penetrate skin all the way to veins, so this is the color that is reflected back. ...
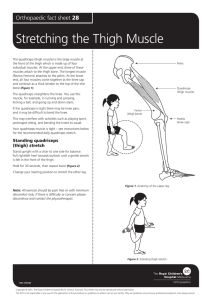
Stretching the Thigh Muscle
... (Rectus Femoris) attaches to the pelvis. At the lower end, all four muscles come together at the knee cap and continue as a thick tendon to the top of the shin bone (Figure 1). ...
... (Rectus Femoris) attaches to the pelvis. At the lower end, all four muscles come together at the knee cap and continue as a thick tendon to the top of the shin bone (Figure 1). ...
When we exercise we use several systems the main 3 systems are
... spiral pattern. That helps to squeeze the blood through . the cardiac muscle has no tendons as its constantly moving. ...
... spiral pattern. That helps to squeeze the blood through . the cardiac muscle has no tendons as its constantly moving. ...
CYCLING PERFORMANCE TIPS -- Compiled from Various Sources
... the amount being extracted by the working skeletal muscles) and the maximal cardiac output (the maximal heart rate times the volume of blood pumped per beat). This is called the Fick equation. Ranges of VO2max by age/sex Calculating %VO2max based on your % of your MHR (Maximum Heart Rate). Anaerobic ...
... the amount being extracted by the working skeletal muscles) and the maximal cardiac output (the maximal heart rate times the volume of blood pumped per beat). This is called the Fick equation. Ranges of VO2max by age/sex Calculating %VO2max based on your % of your MHR (Maximum Heart Rate). Anaerobic ...
Station 2: Circulatory system
... Include: 1: The functions and structures of the respiratory system. 2: Why the human body needs oxygen. 3: The difference between respiration and breathing. 4: Describe the effects of smoking on respiration. 5: The function of the excretory system. 6: The structure and function of the kidney. 7: How ...
... Include: 1: The functions and structures of the respiratory system. 2: Why the human body needs oxygen. 3: The difference between respiration and breathing. 4: Describe the effects of smoking on respiration. 5: The function of the excretory system. 6: The structure and function of the kidney. 7: How ...
NiaTopics - Request a Spot account
... There are four muscle groups that make up the walls of our abdominal area power house, from the outside in: The Rectus Abdominis – The rectus abdominis runs vertically along the front of our torso from the pubic bone to the sternum (inserting in the cartilage of the fifth, sixth, and seventh ribs). ...
... There are four muscle groups that make up the walls of our abdominal area power house, from the outside in: The Rectus Abdominis – The rectus abdominis runs vertically along the front of our torso from the pubic bone to the sternum (inserting in the cartilage of the fifth, sixth, and seventh ribs). ...
Nutrition - Northmont City Schools
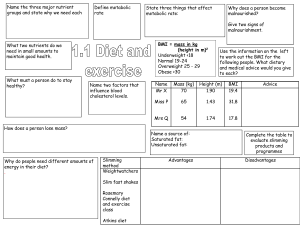
... Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body They include sugars, starches, and fiber The following is additional information on ...
... Carbohydrates are the main source of energy for the body They include sugars, starches, and fiber The following is additional information on ...
Structure and Function of the Muscular, Neuromuscular
... • Older Muscle – Muscle function is reduced in older adults. – Reductions in muscle size and strength are amplified in weight-bearing extensor muscles. – Muscle atrophy with aging results from losses in both number and size of muscle fibers, especially Type II muscle fibers. – Inactivity plays a maj ...
... • Older Muscle – Muscle function is reduced in older adults. – Reductions in muscle size and strength are amplified in weight-bearing extensor muscles. – Muscle atrophy with aging results from losses in both number and size of muscle fibers, especially Type II muscle fibers. – Inactivity plays a maj ...
types of muscle tissue
... each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are also called red muscles. They are dense in capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscle its red colour. It can carry more ...
... each fiber is uniform throughout its length and they do not branch out. Skeletal/ voluntary muscle is divided into two; a) Slow twitch These muscles are also called red muscles. They are dense in capillaries and rich in mitochondria and myoglobin, giving the muscle its red colour. It can carry more ...
Peak Performance
... • Skeletal, cardiac and smooth • Skeletal muscle tissue can be sub divided into 2 different types, each with a different function ...
... • Skeletal, cardiac and smooth • Skeletal muscle tissue can be sub divided into 2 different types, each with a different function ...
Cardiovascular System
... The muscular systems is responsible for making the body move. The muscular system works very closely with the other systems. The muscular system relies on the digestive for energy. It relies on the respiratory to help provide it with the oxygen the muscles need. The cardiovascular and circulatory sy ...
... The muscular systems is responsible for making the body move. The muscular system works very closely with the other systems. The muscular system relies on the digestive for energy. It relies on the respiratory to help provide it with the oxygen the muscles need. The cardiovascular and circulatory sy ...
Cardiopulmonary
... increase in stroke volume from 70ml/beat up to 140ml/beat represents a two-fold increase in stroke volume (usually only well trained or large subjects can increase stroke volume two-fold above resting values). Thus, in college age students heart rate can increase about three-fold and stroke volume ...
... increase in stroke volume from 70ml/beat up to 140ml/beat represents a two-fold increase in stroke volume (usually only well trained or large subjects can increase stroke volume two-fold above resting values). Thus, in college age students heart rate can increase about three-fold and stroke volume ...
Muscle Spasms and Cramps - Midlands Family Medicine
... Muscle spasms, especially in the neck, also may occur when you are under lots of stress. Cramps in the calf of the leg often occur at night during sleep. What are the symptoms? A spasm feels like tightness or a knot in a muscle. It may hurt when you use the muscle. It may be hard to use the muscle. ...
... Muscle spasms, especially in the neck, also may occur when you are under lots of stress. Cramps in the calf of the leg often occur at night during sleep. What are the symptoms? A spasm feels like tightness or a knot in a muscle. It may hurt when you use the muscle. It may be hard to use the muscle. ...
Muscle and jointpain
... As is often the case, prevention is better than a cure, in that it takes little effort to implement some relatively straightforward measures and reduces the chance of the individual experiencing pain as a result of an injury. Warming up properly before exercise can seem like a waste of time, but it ...
... As is often the case, prevention is better than a cure, in that it takes little effort to implement some relatively straightforward measures and reduces the chance of the individual experiencing pain as a result of an injury. Warming up properly before exercise can seem like a waste of time, but it ...
m5zn_dc4109a43372373
... Balance in the Homeostasis of Chemical Substances in the Body • Many homeostatic systems regulate the balance between addition and removal of a chemical substance from the body. • Two important generalizations concerning the balance concept: (1) During any period of time, total-body balance depends ...
... Balance in the Homeostasis of Chemical Substances in the Body • Many homeostatic systems regulate the balance between addition and removal of a chemical substance from the body. • Two important generalizations concerning the balance concept: (1) During any period of time, total-body balance depends ...
Appreciating Proprioception
... concentrated effort to touch their nose (the most common expression is of surprise as they feel like they are putting their finger into their skull). Lastly the standing balance activity, while slightly risky since some students react strongly and would fall to the ground if not caught by the spotte ...
... concentrated effort to touch their nose (the most common expression is of surprise as they feel like they are putting their finger into their skull). Lastly the standing balance activity, while slightly risky since some students react strongly and would fall to the ground if not caught by the spotte ...
B1Mind Maps have a go then check answers
... • causes the body to go into a state of ketosis, which means it burns its own fat for fuel. • When the body is in ketosis, you tend to feel less hungry, and thus you're likely to eat less than you might otherwise. • However, ketosis can also cause a variety of unpleasant effects (such as unusual bre ...
... • causes the body to go into a state of ketosis, which means it burns its own fat for fuel. • When the body is in ketosis, you tend to feel less hungry, and thus you're likely to eat less than you might otherwise. • However, ketosis can also cause a variety of unpleasant effects (such as unusual bre ...
Resistance Training
... certain exercise, weight should be added to that exercise for the next training session. Quantity of load increases: Variations in training status, volume loads, and exercises influence the appropriate load increases; to contend with this variability, relative load increases of 2.5-10% can be ...
... certain exercise, weight should be added to that exercise for the next training session. Quantity of load increases: Variations in training status, volume loads, and exercises influence the appropriate load increases; to contend with this variability, relative load increases of 2.5-10% can be ...
Physiology with elements of clinical physiology
... Physiology with elements of clinical physiology course is designed to provide students with understanding of physiological mechanisms of human body functions, at the cellular and organ level as well as integrative functioning of the human body. Course content will include neural and hormonal homeos ...
... Physiology with elements of clinical physiology course is designed to provide students with understanding of physiological mechanisms of human body functions, at the cellular and organ level as well as integrative functioning of the human body. Course content will include neural and hormonal homeos ...
effects of exercise on heart and respiratory rates lab.pub
... When you exercise, your heart rate and breathing rate increase to provide your cells with more oxygen and nutrients and rid your body of excess carbon dioxide. Heart rate is a measure of the number of times that the heart beats in a minute. As the heart pumps blood into arteries, vibrations result f ...
... When you exercise, your heart rate and breathing rate increase to provide your cells with more oxygen and nutrients and rid your body of excess carbon dioxide. Heart rate is a measure of the number of times that the heart beats in a minute. As the heart pumps blood into arteries, vibrations result f ...
how is injury rehabilitation managed? - Sports-Nerd
... area and surrounding body parts must be developed to reduce muscle atrophy and for support and performance reasons. Isometric exercises are used when there is no movement at the joint. As movement at the joint increases isotonic and isokinetic exercises using further resistance can be introduced ...
... area and surrounding body parts must be developed to reduce muscle atrophy and for support and performance reasons. Isometric exercises are used when there is no movement at the joint. As movement at the joint increases isotonic and isokinetic exercises using further resistance can be introduced ...
08. Invol.muscle
... (autostimulation) results from less negative resting potential (-50 to -60 mv.) and permeability of sarcolemma; sufficient numbers of sodium-calcium (slow) channels are open at resting potential to provoke depolarization; in some cases, rhythmical 'slow waves' occur (graded potentials); in many case ...
... (autostimulation) results from less negative resting potential (-50 to -60 mv.) and permeability of sarcolemma; sufficient numbers of sodium-calcium (slow) channels are open at resting potential to provoke depolarization; in some cases, rhythmical 'slow waves' occur (graded potentials); in many case ...
Supplementary Appendixes
... enlargement. The major goal of exercise restrictions is to reduce the amount of chronic hemodynamic stress imposed upon the aorta. This can be achieved, at least in part, by avoiding exercise regimens that cause a sustained elevation of either heart rate or blood pressure. We therefore recommend tha ...
... enlargement. The major goal of exercise restrictions is to reduce the amount of chronic hemodynamic stress imposed upon the aorta. This can be achieved, at least in part, by avoiding exercise regimens that cause a sustained elevation of either heart rate or blood pressure. We therefore recommend tha ...
Respiratory system 1
... Gaseous Exchange • In the lungs, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the blood passes into the alveoli through the respiratory membrane, a thin barrier that has several layers. • Oxygen (O2) crosses the membrane in the opposite direction, from the alveoli to the blood capillaries. • The fitter we become the ...
... Gaseous Exchange • In the lungs, carbon dioxide (CO2) from the blood passes into the alveoli through the respiratory membrane, a thin barrier that has several layers. • Oxygen (O2) crosses the membrane in the opposite direction, from the alveoli to the blood capillaries. • The fitter we become the ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.