Unit 1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... VOCABULARY (Additional vocabulary will be outlined with each individual unit) Abrasion – minor wound in which the skin’s surface is rubbed or scraped away. Acclimatization – the process of the body physiologically adapting to an unfamiliar environment (altitude or temperature). Acute – sudden onset, ...
... VOCABULARY (Additional vocabulary will be outlined with each individual unit) Abrasion – minor wound in which the skin’s surface is rubbed or scraped away. Acclimatization – the process of the body physiologically adapting to an unfamiliar environment (altitude or temperature). Acute – sudden onset, ...
Hemoglobin and O2 transport - SHMD 339: Exercise Physiology 3
... - Found in large quantities in slow-twitch fibers (high aerobic capacity) - Smaller amounts in intermediate fibers - Limited quantity in fast twitch fibers ...
... - Found in large quantities in slow-twitch fibers (high aerobic capacity) - Smaller amounts in intermediate fibers - Limited quantity in fast twitch fibers ...
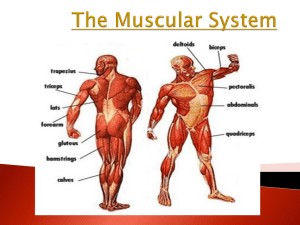
The Muscular System
... Questions coming about this so read carefully! In order to contract (move), your muscles require energy in the form of ATP. (Adenosine Triphosphate) Muscles can produce ATP in two different ways. We have discussed aerobic respiration where oxygen is required. The second way is called anaerobic respi ...
... Questions coming about this so read carefully! In order to contract (move), your muscles require energy in the form of ATP. (Adenosine Triphosphate) Muscles can produce ATP in two different ways. We have discussed aerobic respiration where oxygen is required. The second way is called anaerobic respi ...
Flight Physiology
... The Lung • Within the red blood cell, there is Hemoglobin, which function as specialized oxygen transport system that allows far more oxygen to be carried by blood • At high altitude, we need to increase rate and depth of breathing in order to get enough oxygen into our lung. ...
... The Lung • Within the red blood cell, there is Hemoglobin, which function as specialized oxygen transport system that allows far more oxygen to be carried by blood • At high altitude, we need to increase rate and depth of breathing in order to get enough oxygen into our lung. ...
Energy Sources for Physical Performance
... stored as glycogen. With the aid of enzymes (proteins which initiate specific chemical reactions), the glycogen is converted into a substance called Lactic Acid. During this reaction, energy is released, and this energy is used to recombine the ADP and Phosphate to ATP. Only 2 ATP molecules are prod ...
... stored as glycogen. With the aid of enzymes (proteins which initiate specific chemical reactions), the glycogen is converted into a substance called Lactic Acid. During this reaction, energy is released, and this energy is used to recombine the ADP and Phosphate to ATP. Only 2 ATP molecules are prod ...
Section 13.1
... of fat tissue in your body compared to the amount of lean tissue, such as muscles and ...
... of fat tissue in your body compared to the amount of lean tissue, such as muscles and ...
Respiration (physiology) - Frank`s Hospital Workshop
... biochemical definition of respiration, which refers to cellular respiration: the metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy by reacting oxygen with glucose to give water, carbon dioxide and ATP (energy). Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thu ...
... biochemical definition of respiration, which refers to cellular respiration: the metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy by reacting oxygen with glucose to give water, carbon dioxide and ATP (energy). Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thu ...
How are humans like other life? 11/16/2015
... Smooth muscle forms the walls of the stomach, intestines, blood vessels, and other internal organs. Individual smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped, have a single nucleus, and interlace to form sheets. Notice that smooth muscles lacks the striations found in skeletal muscles, and are surrounded by ...
... Smooth muscle forms the walls of the stomach, intestines, blood vessels, and other internal organs. Individual smooth muscle cells are spindle-shaped, have a single nucleus, and interlace to form sheets. Notice that smooth muscles lacks the striations found in skeletal muscles, and are surrounded by ...
Respiration - segaran1996
... of glucose cannot produce all the ATP required for further muscle contraction. • During such periods, additional ATP is generated by anaerobic breakdown of glucose. In the process, a lot of lactic acid is produced. ...
... of glucose cannot produce all the ATP required for further muscle contraction. • During such periods, additional ATP is generated by anaerobic breakdown of glucose. In the process, a lot of lactic acid is produced. ...
Respiratory System
... – Arrival of the action potential at the nerve terminal causes the release of acetylcholine. Once a sufficient amount of acetylcholine is released, an action potential is generated across the sarcolemma, and the fiber contracts. ...
... – Arrival of the action potential at the nerve terminal causes the release of acetylcholine. Once a sufficient amount of acetylcholine is released, an action potential is generated across the sarcolemma, and the fiber contracts. ...
Pulmonary Functions Pulmonary Ventilation Conducting Airways
... • Partial pressure of a gas (mm Hg) = total pressure (mm Hg) X fraction of the gas • PG = PB X FG • Note that as air enters the nasal cavities it completely saturates with water vapor, diluting the ...
... • Partial pressure of a gas (mm Hg) = total pressure (mm Hg) X fraction of the gas • PG = PB X FG • Note that as air enters the nasal cavities it completely saturates with water vapor, diluting the ...
Words - American Society of Exercise Physiologists
... supervision, safety, and care of clients and patients are increasingly evident throughout the public sector” (16). In closing, it has been know for many years that chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, different respiratory diseases, and osteoarthritis represent t ...
... supervision, safety, and care of clients and patients are increasingly evident throughout the public sector” (16). In closing, it has been know for many years that chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease, cancer, type 2 diabetes, different respiratory diseases, and osteoarthritis represent t ...
The Muscular System
... These muscles push food and blood through our body but do not move the skeleton. There is a third kind of muscle found only in the heart which is called Cardiac Muscle. ...
... These muscles push food and blood through our body but do not move the skeleton. There is a third kind of muscle found only in the heart which is called Cardiac Muscle. ...
feedback loop
... Feedback Loops • If the hypothalamus registers that the concentration of solutes in the blood is high, it will trigger a sense of thirst, as well as triggering the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the pituitary, which travels through the bloodstream and acts on the kidneys. • The kidneys a ...
... Feedback Loops • If the hypothalamus registers that the concentration of solutes in the blood is high, it will trigger a sense of thirst, as well as triggering the release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) from the pituitary, which travels through the bloodstream and acts on the kidneys. • The kidneys a ...
pituitary gland
... The conditions which must be controlled include water content, ion content, body temperature and __________ glucose concentration. The_________ ________ is the part of the brain that monitors and controls body temperature. The _______________ monitors and controls blood glucose concentration. It pro ...
... The conditions which must be controlled include water content, ion content, body temperature and __________ glucose concentration. The_________ ________ is the part of the brain that monitors and controls body temperature. The _______________ monitors and controls blood glucose concentration. It pro ...
Sports Nutrition:
... Fluid lost is 1.2-1.5 times the actual fluid lost because of continued sweating and urine production Hydration Schedule 2 hours before exercise Every 15 minutes during exercise After exercise ...
... Fluid lost is 1.2-1.5 times the actual fluid lost because of continued sweating and urine production Hydration Schedule 2 hours before exercise Every 15 minutes during exercise After exercise ...
Motor Unit and All or None principle
... Each fibre is activated through impulses delivered via motor end plate Motor unit: a group of fibres activated via the same nerve All muscle fibres of one particular motor unit are always of the same fibre type Muscles needed to perform precise movements generally consist of a large number of motor ...
... Each fibre is activated through impulses delivered via motor end plate Motor unit: a group of fibres activated via the same nerve All muscle fibres of one particular motor unit are always of the same fibre type Muscles needed to perform precise movements generally consist of a large number of motor ...
ANATOMY HANDOUT 2011
... Two phases of Pulmonary Ventilation – involves diaphragm, Intercostal muscles, Pectoralis minor muscle and the gas laws. Physiology of Pulmonary Ventilation & the Gas Laws Airflow is governed by basic pressure, flow, and resistance principles Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air is the forc ...
... Two phases of Pulmonary Ventilation – involves diaphragm, Intercostal muscles, Pectoralis minor muscle and the gas laws. Physiology of Pulmonary Ventilation & the Gas Laws Airflow is governed by basic pressure, flow, and resistance principles Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air is the forc ...
L.I.F.E. HEALTH HISTORY QUESTIONNAIRE
... The participant has been informed that there will not be a physician present during any of the exercise. The participant will have to be taken to a hospital if they develop the need for any emergency care, with the understanding that it will take time to travel from exercise site to the hospital. Th ...
... The participant has been informed that there will not be a physician present during any of the exercise. The participant will have to be taken to a hospital if they develop the need for any emergency care, with the understanding that it will take time to travel from exercise site to the hospital. Th ...
Human Physiology
... • Most common form • 4 subunits – 2 a peptides – 2 b peptides – each contain a _________________ group which has an iron atom. – The iron atom interacts with two oxygen atoms (one oxygen molecule). Sherwood’s Human Physiology 11-3 ...
... • Most common form • 4 subunits – 2 a peptides – 2 b peptides – each contain a _________________ group which has an iron atom. – The iron atom interacts with two oxygen atoms (one oxygen molecule). Sherwood’s Human Physiology 11-3 ...
Intro. to Weights Presentation
... thighs, hips, lower back, neck and shoulders. Also stretch muscles and joints that you routinely use at work or play. Warm up first. Stretching muscles when they're cold increases your risk of injury, including pulled muscles. Warm up by walking while gently pumping your arms, or do a favorite exerc ...
... thighs, hips, lower back, neck and shoulders. Also stretch muscles and joints that you routinely use at work or play. Warm up first. Stretching muscles when they're cold increases your risk of injury, including pulled muscles. Warm up by walking while gently pumping your arms, or do a favorite exerc ...
Tips To Prevent Baseball Injuries
... • Rest: Resting is important immediately after injury for two reasons. First, rest is vital to protect the injured muscle, tendon, ligament or other tissue from further injury. Second, your body needs to rest so it has the energy it needs to heal itself most effectively. • Ice: Use ice bags, cold pa ...
... • Rest: Resting is important immediately after injury for two reasons. First, rest is vital to protect the injured muscle, tendon, ligament or other tissue from further injury. Second, your body needs to rest so it has the energy it needs to heal itself most effectively. • Ice: Use ice bags, cold pa ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.