GCSE_revision_booklet
... What component of fitness is aimed at being improved? Cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength or flexibility perhaps? Skill focus – this could be done through a circuit ...
... What component of fitness is aimed at being improved? Cardiovascular fitness, muscular strength or flexibility perhaps? Skill focus – this could be done through a circuit ...
MORE IS BETTER STRENGTH TRAINING REDUCES FLEXIBILITY
... performed for low repetitions are most effective for bulking up while lighter weights performed for higher repetitions will aid in gaining definition. • This misconception is disproved by understanding the specific physiological responses to training with various loads. • Heavy weights <6RM – are ...
... performed for low repetitions are most effective for bulking up while lighter weights performed for higher repetitions will aid in gaining definition. • This misconception is disproved by understanding the specific physiological responses to training with various loads. • Heavy weights <6RM – are ...
HEAT ACCLIMATIZATION
... • Strength can decrease by approximately 1.8% per year from 35 years. • Maximal and dynamic strength is reduced. • Active people experience a shift towards slow twitch muscle fibres. • The total number of muscle fibres and fibre cross sectional areas decrease with age. ...
... • Strength can decrease by approximately 1.8% per year from 35 years. • Maximal and dynamic strength is reduced. • Active people experience a shift towards slow twitch muscle fibres. • The total number of muscle fibres and fibre cross sectional areas decrease with age. ...
Cardiac Muscle
... Cerebral Palsy impacts your posture, it takes away your balance and motor functions. Your muscles no longer function. Cerebral Palsy also breaks down your nervous system. This disease cannot be cured , variety of treatment can only help with symptoms and improve quality of life, physical treatment i ...
... Cerebral Palsy impacts your posture, it takes away your balance and motor functions. Your muscles no longer function. Cerebral Palsy also breaks down your nervous system. This disease cannot be cured , variety of treatment can only help with symptoms and improve quality of life, physical treatment i ...
HAZARDS OF IMMOBILITY MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM
... *** if 8 stress is placed on bone as in athletic activity, more bone is deposited *** if 9 stress or no stress as in prolonged bedrest, bone is reabsorbed *** Encourage clients to stand and walk as the body functions best in the vertical position *** Physical activity forces muscles to move and incr ...
... *** if 8 stress is placed on bone as in athletic activity, more bone is deposited *** if 9 stress or no stress as in prolonged bedrest, bone is reabsorbed *** Encourage clients to stand and walk as the body functions best in the vertical position *** Physical activity forces muscles to move and incr ...
Ergogenic_Aids
... • L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid which stimulates the breakdown of fat • It transports fatty acids into the mitochondria • Studies examining L-carnitine’s role as an ergogenic aid for increasing fat oxidation have not shown clear efficacy • Studies show L-carnitine may enhance recov ...
... • L-Carnitine is a naturally occurring amino acid which stimulates the breakdown of fat • It transports fatty acids into the mitochondria • Studies examining L-carnitine’s role as an ergogenic aid for increasing fat oxidation have not shown clear efficacy • Studies show L-carnitine may enhance recov ...
Positive feedback system
... control center (integrating center) to increase breathing. The effectors in this example are the respiratory muscles. This increase in breathing will reduce extracellular CO 2 concentrations back to normal, thus reestablishing homeostasis. The reason that this type of feedback is termed negative ...
... control center (integrating center) to increase breathing. The effectors in this example are the respiratory muscles. This increase in breathing will reduce extracellular CO 2 concentrations back to normal, thus reestablishing homeostasis. The reason that this type of feedback is termed negative ...
Chapter Four
... Ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to process and transport oxygen over a period of time Continuous, repetitive movements Aerobic energy production (using oxygen) Structural and functional benefits Examples: brisk walking, jogging, cycling ...
... Ability of the heart, lungs, and blood vessels to process and transport oxygen over a period of time Continuous, repetitive movements Aerobic energy production (using oxygen) Structural and functional benefits Examples: brisk walking, jogging, cycling ...
the nervous system
... A hormone is a chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland and released into the blood stream to alter the activity of one or more target organs; e.g. insulin is released by the pancreas to cause the liver to absorb sugar from the blood and convert it to glycogen. When released by the gland, h ...
... A hormone is a chemical substance produced by an endocrine gland and released into the blood stream to alter the activity of one or more target organs; e.g. insulin is released by the pancreas to cause the liver to absorb sugar from the blood and convert it to glycogen. When released by the gland, h ...
2. The Respiratory System
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
Aerobic respiration
... don’t contract as strongly as they normally do, and cannot do as much work. You feel an increasing weakness and pain or cramps in the muscles. The cause of fatigue is not well understood because there are many changes happening in muscle during activity. In prolonged activity some chemicals needed f ...
... don’t contract as strongly as they normally do, and cannot do as much work. You feel an increasing weakness and pain or cramps in the muscles. The cause of fatigue is not well understood because there are many changes happening in muscle during activity. In prolonged activity some chemicals needed f ...
The 2015 Meeting of the American College of Sports
... outlined experimental evidence via single isolated muscle fiber models indicating low pH is not important and that impaired contractility is the primary mechanism of muscular fatigue. He concluded that lactate and H+ are good markers but not the makers of fatigue. In contrast, Fitts contended that m ...
... outlined experimental evidence via single isolated muscle fiber models indicating low pH is not important and that impaired contractility is the primary mechanism of muscular fatigue. He concluded that lactate and H+ are good markers but not the makers of fatigue. In contrast, Fitts contended that m ...
Introduction to FireFit
... Cardiovascular Fitness is the backbone of a general fitness program. The primary purpose of aerobic conditioning is to make the heart stronger and work more efficiently, while improving one’s health and enhancing the quality of life. Cardiovascular fitness includes both aerobic (moderate intensity) ...
... Cardiovascular Fitness is the backbone of a general fitness program. The primary purpose of aerobic conditioning is to make the heart stronger and work more efficiently, while improving one’s health and enhancing the quality of life. Cardiovascular fitness includes both aerobic (moderate intensity) ...
Gas Exchange
... glucose to your cells. However during intense exercise your heat cannot supply your cells quickly enough to release all the energy they need. During intense exercise, your cells start to do a different type of respiration, anaerobic respiration (respiration without oxygen). Anaerobic respiration rel ...
... glucose to your cells. However during intense exercise your heat cannot supply your cells quickly enough to release all the energy they need. During intense exercise, your cells start to do a different type of respiration, anaerobic respiration (respiration without oxygen). Anaerobic respiration rel ...
Conditioning Muscle Soreness And Massage
... In the fit horse, it is internal resistance that limits performance. In the horse being conditioned, resistance limits the potential for strength as well as increases the possibility of muscle injury. Muscle tightening is the natural physiological response to trauma, be it from a blow or some form o ...
... In the fit horse, it is internal resistance that limits performance. In the horse being conditioned, resistance limits the potential for strength as well as increases the possibility of muscle injury. Muscle tightening is the natural physiological response to trauma, be it from a blow or some form o ...
ENERGY SYSTEMS
... The carbon dioxide is breathed out through the process of respiration and the water is available to the cells. These by-products are not harmful to performance. ...
... The carbon dioxide is breathed out through the process of respiration and the water is available to the cells. These by-products are not harmful to performance. ...
Option A3 Non-Nutritional Ergogenic Aids Answers
... Researchers use placebos during studies to help them understand what effect a new drug or some other treatment might have on a particular condition. For instance, some people in a study might be given a new drug to lower cholesterol. Others would get a placebo. None of the people in the study will k ...
... Researchers use placebos during studies to help them understand what effect a new drug or some other treatment might have on a particular condition. For instance, some people in a study might be given a new drug to lower cholesterol. Others would get a placebo. None of the people in the study will k ...
Columbia College
... 9. Graph relationships among pulmonary ventilation, blood lactate concentrations, and oxygen uptake during incremental exercise. Indicate the demarcation points for the lactate threshold and onset of blood lactate ...
... 9. Graph relationships among pulmonary ventilation, blood lactate concentrations, and oxygen uptake during incremental exercise. Indicate the demarcation points for the lactate threshold and onset of blood lactate ...
8167 Muscular CE 8x11
... isometric: A minimal shortening of the muscle; tension on the muscle increases greatly, where muscles are pitted against an immovable object. isotonic: When the muscle shortens and pulls on another structure, such as a bone, to produce movement. lactic acid: Byproduct produced when muscles use sugar ...
... isometric: A minimal shortening of the muscle; tension on the muscle increases greatly, where muscles are pitted against an immovable object. isotonic: When the muscle shortens and pulls on another structure, such as a bone, to produce movement. lactic acid: Byproduct produced when muscles use sugar ...
Muscles Part 1 Powerpoint
... • When a neurotransmitter is released onto a muscle fiber, the electrochemical signal is transmitted through the T tubules through the entire fiber • As the signal moves through the T tubules, it stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium – Modified version of the ...
... • When a neurotransmitter is released onto a muscle fiber, the electrochemical signal is transmitted through the T tubules through the entire fiber • As the signal moves through the T tubules, it stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium – Modified version of the ...
The Human body
... Muscles are bundles of cells and fibers. Muscles work in a very simple way. All they do is tighten up--that is, contract--and relax. You have two sets of muscles attached to many of your bones which allow them to move. There are 630 active muscles in your body and they act in groups. Muscles can onl ...
... Muscles are bundles of cells and fibers. Muscles work in a very simple way. All they do is tighten up--that is, contract--and relax. You have two sets of muscles attached to many of your bones which allow them to move. There are 630 active muscles in your body and they act in groups. Muscles can onl ...
The Human body
... Muscles are bundles of cells and fibers. Muscles work in a very simple way. All they do is tighten up--that is, contract--and relax. You have two sets of muscles attached to many of your bones which allow them to move. There are 630 active muscles in your body and they act in groups. Muscles can onl ...
... Muscles are bundles of cells and fibers. Muscles work in a very simple way. All they do is tighten up--that is, contract--and relax. You have two sets of muscles attached to many of your bones which allow them to move. There are 630 active muscles in your body and they act in groups. Muscles can onl ...
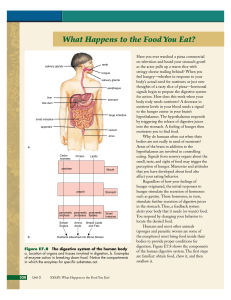
What Happens to the Food You Eat?
... Substances present in excess amounts are removed and stored. Substances that are lacking are increased. The liver accomplishes that by releasing stored forms or by stimulating synthesis processes. For example, when you exercise heavily and glucose levels drop in your bloodstream, sensors trigger the ...
... Substances present in excess amounts are removed and stored. Substances that are lacking are increased. The liver accomplishes that by releasing stored forms or by stimulating synthesis processes. For example, when you exercise heavily and glucose levels drop in your bloodstream, sensors trigger the ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.