Nervous tissue
... Describe the relationship between surface area and volume for a small cell compared to a large cell. Which is more efficient at exchange with the environment? ...
... Describe the relationship between surface area and volume for a small cell compared to a large cell. Which is more efficient at exchange with the environment? ...
Bio211 Lecture 11
... Smooth muscle • walls of organs and blood vessels • skin • involuntary • not striated (it’s smooth!) • single, centrally located nucleus • unbranched ...
... Smooth muscle • walls of organs and blood vessels • skin • involuntary • not striated (it’s smooth!) • single, centrally located nucleus • unbranched ...
Slide 1
... It has also proven to increase muscle mass therefore having an anabolic like reaction, similar to steroids. ...
... It has also proven to increase muscle mass therefore having an anabolic like reaction, similar to steroids. ...
New at OSPTI
... P- Protect the injured site. The injured muscle, joint, or structure should be protected from further injuries for a minimum of 24 hours. Example: wearing a brace to prevent movement. R- Rest. Rest may include a decrease in activity or a complete cessation of activity. Many medical/orthopedic profes ...
... P- Protect the injured site. The injured muscle, joint, or structure should be protected from further injuries for a minimum of 24 hours. Example: wearing a brace to prevent movement. R- Rest. Rest may include a decrease in activity or a complete cessation of activity. Many medical/orthopedic profes ...
Cellular Respiration
... Human muscle cells can make ATP with and without oxygen They have enough ATP to support activities such as quick sprinting for about 5 seconds A secondary supply of energy (creatine phosphate) can keep muscle cells going for another 10 seconds To keep running, your muscles must generate ATP by the a ...
... Human muscle cells can make ATP with and without oxygen They have enough ATP to support activities such as quick sprinting for about 5 seconds A secondary supply of energy (creatine phosphate) can keep muscle cells going for another 10 seconds To keep running, your muscles must generate ATP by the a ...
The respiratory system
... Diffusion capacity for oxygen (from lungs to blood) is determined by: 1. Gas exchange area (surface area) between the alveoli and capillaries 2. Thickness of the alveolocapillary membrane 3. Pressure difference (alveoli – blood) 4. Available amount of hemoglobin ...
... Diffusion capacity for oxygen (from lungs to blood) is determined by: 1. Gas exchange area (surface area) between the alveoli and capillaries 2. Thickness of the alveolocapillary membrane 3. Pressure difference (alveoli – blood) 4. Available amount of hemoglobin ...
Topic 11: Human health and physiology (17 hours)
... including the acrosome reaction, penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
... including the acrosome reaction, penetration of the egg membrane by a sperm and the cortical reaction. ...
Body Systems - Duplin County Schools
... ◦ Alveoli-thin microscopic sacs located at the terminal end to respiratory system. Location of actual carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange. ◦ Lungs- large lobed organs that contain parts essential for oxygen exchange. Spongy, pinkish colored organ located between the front legs of the animal and exten ...
... ◦ Alveoli-thin microscopic sacs located at the terminal end to respiratory system. Location of actual carbon dioxide and oxygen exchange. ◦ Lungs- large lobed organs that contain parts essential for oxygen exchange. Spongy, pinkish colored organ located between the front legs of the animal and exten ...
Chapter 9 A and B Questions
... What is the source of ATP for the first 5-10 minutes of exercise? for the next 30 minutes? for longer than 30 minutes? What is oxygen debt and how is it repaid? How would one know it is being repaid? Is ATP depletion responsible for muscle fatigue? If not, what is? What determines whether a myofiber ...
... What is the source of ATP for the first 5-10 minutes of exercise? for the next 30 minutes? for longer than 30 minutes? What is oxygen debt and how is it repaid? How would one know it is being repaid? Is ATP depletion responsible for muscle fatigue? If not, what is? What determines whether a myofiber ...
Hydration Final with Logo.indd - Beacon Orthopaedics and Sports
... and environmental conditions. Athletes with respiratory, gastrointestinal or other illness should be evaluated before exercise, as these conditions increase the risk of heat illness. When should an athelete hydrate? ...
... and environmental conditions. Athletes with respiratory, gastrointestinal or other illness should be evaluated before exercise, as these conditions increase the risk of heat illness. When should an athelete hydrate? ...
Fitness Weight Training Centennial Physical Education
... Burn Calories: Adding 3 pounds of muscle increases metabolic rate by 7%, which causes the daily caloric requirements to increase by 15% at rest. In addition, base metabolic rates can stay elevated up to 24 hours after a strength training workout; therefore the body burns calories at a faster rate ...
... Burn Calories: Adding 3 pounds of muscle increases metabolic rate by 7%, which causes the daily caloric requirements to increase by 15% at rest. In addition, base metabolic rates can stay elevated up to 24 hours after a strength training workout; therefore the body burns calories at a faster rate ...
Energy Systems
... The central and peripheral nervous systems – fatigue usually results from maximal intensity arousing the feeling of exhaustion before exhaustion has taken place in the muscles. This targets the ATP/PC system as muscles are not given time to react to exhaustion. The Energy Systems – Fatigue resul ...
... The central and peripheral nervous systems – fatigue usually results from maximal intensity arousing the feeling of exhaustion before exhaustion has taken place in the muscles. This targets the ATP/PC system as muscles are not given time to react to exhaustion. The Energy Systems – Fatigue resul ...
Chapter 25
... Capacity of cardiovascular and respiratory systems to deliver required fuel and oxygen to muscles and carry away waste products ...
... Capacity of cardiovascular and respiratory systems to deliver required fuel and oxygen to muscles and carry away waste products ...
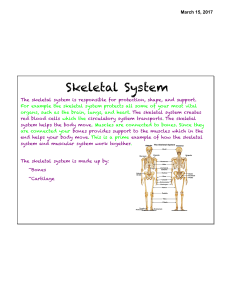
Skeletal System
... The digestive systems function is to break down food into nutrients. The digestive system also helps move the nutrients into the blood stream. The nutrients that are made by the digestive system become energy that the body needs to function. There are two systems that the digestive system works with ...
... The digestive systems function is to break down food into nutrients. The digestive system also helps move the nutrients into the blood stream. The nutrients that are made by the digestive system become energy that the body needs to function. There are two systems that the digestive system works with ...
Fitness Components
... Being fit is not just about how fast you can run or for how long or how much weight you can lift or how many times you can lift it. Fitness is actually all of these things, and more. To be truly fit and able to live healthily and deal with the rigors of an active life, you need to be fit in several ...
... Being fit is not just about how fast you can run or for how long or how much weight you can lift or how many times you can lift it. Fitness is actually all of these things, and more. To be truly fit and able to live healthily and deal with the rigors of an active life, you need to be fit in several ...
Homeostasis
... • Homeostasis or regulation therefore involves fluctuations around a set-point. • The size of the fluctuations depends on the sensitivity and location of the sensory receptors, the tolerance of the control centre to variation from the set-point, and efficiency of the response mechanism. • Most biolo ...
... • Homeostasis or regulation therefore involves fluctuations around a set-point. • The size of the fluctuations depends on the sensitivity and location of the sensory receptors, the tolerance of the control centre to variation from the set-point, and efficiency of the response mechanism. • Most biolo ...
Body Systems Overview
... tubes, pharynx, larynx, nasal region, alveoli), Diaphragm • Tissues: Connective Tissues, Epithelial lining of respiratory tract, muscle • How’s it work? Diaphragm inflates lungs, air moves in and oxygen/carbon dioxide diffuse into blood at capillaries in alveoli; tightly allied with circulatory syst ...
... tubes, pharynx, larynx, nasal region, alveoli), Diaphragm • Tissues: Connective Tissues, Epithelial lining of respiratory tract, muscle • How’s it work? Diaphragm inflates lungs, air moves in and oxygen/carbon dioxide diffuse into blood at capillaries in alveoli; tightly allied with circulatory syst ...
+ Energy - WordPress.com
... The effect of exercise on heart rate and breathing (copy) During exercise, the heart pumps faster and breathing rate increases to ensure the muscles are being provided with enough glucose and oxygen to produce energy to power the muscles. ...
... The effect of exercise on heart rate and breathing (copy) During exercise, the heart pumps faster and breathing rate increases to ensure the muscles are being provided with enough glucose and oxygen to produce energy to power the muscles. ...
An Introduction to Animal Structure and Function Key Concepts of
... – the overall flow and transformation of energy in an animal ...
... – the overall flow and transformation of energy in an animal ...
Topic 6.4 Notes
... Exchange occurs over the body surface or respiratory surface. Diffusion requirements: • Large SA:V in-foldings (lungs or gills) • Permeable • Thin efficient up to 1mm thickness • Moist O2 and CO2 diffuse in solution ...
... Exchange occurs over the body surface or respiratory surface. Diffusion requirements: • Large SA:V in-foldings (lungs or gills) • Permeable • Thin efficient up to 1mm thickness • Moist O2 and CO2 diffuse in solution ...
Class Notes
... Our voice box (larynx), is made of two sheets of muscle that vibrate as the air passes between them and so we can produce sounds and speech, in co-operation with our tongue, mouth and teeth. ...
... Our voice box (larynx), is made of two sheets of muscle that vibrate as the air passes between them and so we can produce sounds and speech, in co-operation with our tongue, mouth and teeth. ...
3.4.4 Lungs Breathing - Spanish Point Biology
... Our voice box (larynx), is made of two sheets of muscle that vibrate as the air passes between them and so we can produce sounds and speech, in co-operation with our tongue, mouth and teeth. ...
... Our voice box (larynx), is made of two sheets of muscle that vibrate as the air passes between them and so we can produce sounds and speech, in co-operation with our tongue, mouth and teeth. ...
skeletal ms
... It produces great amount of ATP (38 ATP). It is economic but slow. 4) In exhausted ms: There is an emergency mechanism for the supply of ATP ADP + ADP ATP + AMP ...
... It produces great amount of ATP (38 ATP). It is economic but slow. 4) In exhausted ms: There is an emergency mechanism for the supply of ATP ADP + ADP ATP + AMP ...
Homeostasis - Cloudfront.net
... point, the alpha cells secrete glucagons • glucagon activates phosphorylase (enzyme in liver) which catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis) • also increases the conversion of amino acids and glycerol into glucose 6-phosphate (to enter cellular respiration pathways) • READ ABO ...
... point, the alpha cells secrete glucagons • glucagon activates phosphorylase (enzyme in liver) which catalyzes the breakdown of glycogen to glucose (glycogenolysis) • also increases the conversion of amino acids and glycerol into glucose 6-phosphate (to enter cellular respiration pathways) • READ ABO ...
Living High and Training Low? By: Kellie Hays Running a marathon
... carbohydrates per hour. Though carbohydrates are not considered an electrolyte, they are an important component in sports nutrition. Furthermore, the most important minerals lost in sweat are sodium and potassium and must be replaced immediately. The replacement of these minerals is important for op ...
... carbohydrates per hour. Though carbohydrates are not considered an electrolyte, they are an important component in sports nutrition. Furthermore, the most important minerals lost in sweat are sodium and potassium and must be replaced immediately. The replacement of these minerals is important for op ...
Exercise physiology

Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise, that is, study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to a wide range of exercise conditions. In addition, many exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. Accreditation programs exist with professional bodies in most developed countries, ensuring the quality and consistency of education. In Canada, one may obtain the professional certification title – Certified Exercise Physiologist for those working with clients (both clinical and non clinical) in the health and fitness industry.An exercise physiologist's area of study may include but is not limited to biochemistry, bioenergetics, cardiopulmonary function, hematology, biomechanics, skeletal muscle physiology, neuroendocrine function, and central and peripheral nervous system function. Furthermore, exercise physiologists range from basic scientists, to clinical researchers, to clinicians, to sports trainers.