* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 6.4 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
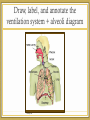
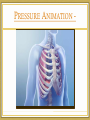
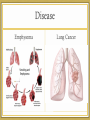
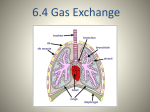
Topic 6 & 11: Human Physiology 6.4 Gas exchange Draw, label, and annotate the ventilation system + alveoli diagram Teachpe.com 1 - Ventilation Read & Consider 6.4.1, 6.4.4 - 6.4.6 • What do you know? • What questions do you have? Ventilation System In larger organisms not every cell has access to oxygen sources so a ventilation system is needed to maintain a concentration gradient in alveoli. RESPIRATION Muscles Ventilation Inspiration – • The diaphragm contracts and flattens downwards • External intercostal muscles contract, pulling ribs up and out this increases the volume of the thorax • Increased volume decreases the pressure of alveoli and air flow in to equalize pressure • Forced inspiration: accessory neck muscles contract to increase volume Expiration Passive • Diaphragm relaxes and curves upward. • External intercostal muscles relax, allowing ribs to fall and decreasing the volume of the thorax • This increases the pressure in the alveoli pushing air out of the lungs. • During forced expiration (exercise) internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles contract for force exhalation. PRESSURE ANIMATION - 2 - Exchange Read & Consider 6.4.2 – 6.4.3 • What do you know? • What questions do you have? Gas Exchange Diffusion of gases; process of swapping one gas for another. O2 & CO2 1. Alveoli – O2 diffuses into the blood from the alveoli and CO2 diffuses from the blood to the alveoli 2. Tissues – O2 diffuses from blood into the cells and CO2 diffuses from cells to the blood. Pneumocytes Type I • Extremely attenuated (25nm) • Cover 97% of alveolar surface • Organelles gathered near the nucleus • Vesicles to clear contaminates Type II • Cuboidal in shape • 60% of total cells, but <5% of surface area • Production and secretion of surfactant • Act as alveolar stem cells Increasing Diffusion Exchange occurs over the body surface or respiratory surface. Diffusion requirements: • Large SA:V in-foldings (lungs or gills) • Permeable • Thin efficient up to 1mm thickness • Moist O2 and CO2 diffuse in solution • Transport system maintain a concentration gradient art..com Alveoli Disease Emphysema Lung Cancer Practical How does vigorous exercise affect ventilation rate and tidal volume in humans? • "Advanced Practice Providers." SIU School of Medicine. SIU School of Medicine, n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2014. • Bishop, Adrian. "Lung Cancer Tumours in Smokers Have 10-times More Genetic Mutations." Earth Times. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2014. • "Laboratory Manual for Exercise Physiology: Pulmonary Function Testing a Valuable Diagnostic Tool." Human-kinetics. N.p., n.d. Web. 24 Oct. 2014. • "Stock Photo - Human Alveoli, Computer Artwork." Human Alveoli, Computer Artwork. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 Oct. 2014. • Zyga, Lisa. "Scientists Discover First Multicellular Life That Doesn't Need Oxygen." Phys.Org. N.p., 7 Apr. 2010. Web. 10 Oct. 2014. Works Cited