isomorphic tessellations for musical keyboards
... For our layout to work, any closed circuit must bring us back to the original layout. If we consider the triangle of interest shown in Fig. 4, there are two triangles which include the still unknown interval A (assuming we have defined V and H). These triangular circuits are: U +A+x = U + V and U + ...
... For our layout to work, any closed circuit must bring us back to the original layout. If we consider the triangle of interest shown in Fig. 4, there are two triangles which include the still unknown interval A (assuming we have defined V and H). These triangular circuits are: U +A+x = U + V and U + ...
Daniel Liles
... sanctioned by Nature herself.” (Nouvelles Suites de Pièces de Clavecin, Preface. See Lehman, Bradley) The reference to “Nature” can hardly be overlooked. This piece was composed during the French enlightenment, an age when nature was thought of as being rationally ordered and reducible to basic mech ...
... sanctioned by Nature herself.” (Nouvelles Suites de Pièces de Clavecin, Preface. See Lehman, Bradley) The reference to “Nature” can hardly be overlooked. This piece was composed during the French enlightenment, an age when nature was thought of as being rationally ordered and reducible to basic mech ...
12 Scale- A scale is a series of pitches in ascending order, such as
... Diatonic scale- A diatonic scale uses all 7 pitch names once each until the octave is reached. Major Scale- Major scale is a diatonic scale with the following pattern of steps: 1, 1, 1/2, 1, 1, 1, 1/2. Major scales are named both by the starting letter and the step pattern. For example, a D Major sc ...
... Diatonic scale- A diatonic scale uses all 7 pitch names once each until the octave is reached. Major Scale- Major scale is a diatonic scale with the following pattern of steps: 1, 1, 1/2, 1, 1, 1, 1/2. Major scales are named both by the starting letter and the step pattern. For example, a D Major sc ...
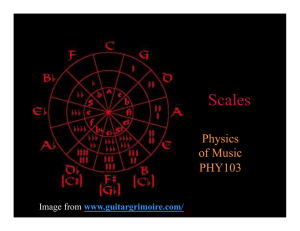
Scales - University of Rochester
... musical compositions on a musical scale tuned in just intonation and based on the 11-limit tonality diamond, played on instruments he designed and built himself to be played in that tuning. The number of notes varied for a time from about 29 to 55, until he finally settled on a scale of 43 tones to ...
... musical compositions on a musical scale tuned in just intonation and based on the 11-limit tonality diamond, played on instruments he designed and built himself to be played in that tuning. The number of notes varied for a time from about 29 to 55, until he finally settled on a scale of 43 tones to ...
Harmonics - Homework References
... produced by it Pythagoras exposed the first four overtones which create consonant intervals in music harmony: the octave, perfect fifth, perfect fourth, and major third ...
... produced by it Pythagoras exposed the first four overtones which create consonant intervals in music harmony: the octave, perfect fifth, perfect fourth, and major third ...
Musical Intervals and Scales
... • Step 4 - create the fourth by descending a fifth and then moving up an octave ...
... • Step 4 - create the fourth by descending a fifth and then moving up an octave ...
Partita no. 4 in D: Sarabande and Gigue JS Bach
... not typical of the Classical period (and have only rarely been revived since then). Moreover Suites of several dance movements are also characteristic of the Baroque rather than of other periods Composition for harpsichord (or perhaps clavichord – see ‘Instrumentation’ below) rather than for piano – ...
... not typical of the Classical period (and have only rarely been revived since then). Moreover Suites of several dance movements are also characteristic of the Baroque rather than of other periods Composition for harpsichord (or perhaps clavichord – see ‘Instrumentation’ below) rather than for piano – ...
Neo-Riemannian Theory and the Analysis of Pop
... four of which are provided in Examples 2(b) through 2(e). Example 2(b) assumes a single key for the progression, D minor. As in much pop-rock music, repetition and metric strength are paramount in establishing the tonal center of this chord progression—the D- triad comes first and is metrically emph ...
... four of which are provided in Examples 2(b) through 2(e). Example 2(b) assumes a single key for the progression, D minor. As in much pop-rock music, repetition and metric strength are paramount in establishing the tonal center of this chord progression—the D- triad comes first and is metrically emph ...
The Guitar Chord – An analysis of Alberto Ginastera use of the guitar
... From this point the melodic phrases that occur after the succession of chords become more complex. In the case of the Semi-phase 2b it starts with an arpeggiated tetrachord (0167). This tetrachord, a member of OCT01, is composed of two augmented fourths separated by a perfect fifth; the 4th interval ...
... From this point the melodic phrases that occur after the succession of chords become more complex. In the case of the Semi-phase 2b it starts with an arpeggiated tetrachord (0167). This tetrachord, a member of OCT01, is composed of two augmented fourths separated by a perfect fifth; the 4th interval ...
Kamavardhini and the Blues scale – just one step and one note
... Since the ascend and descend notes are the same, we will examine just the ascend. ...
... Since the ascend and descend notes are the same, we will examine just the ascend. ...
national 5 concepts list az jyhs music department
... Alberti bass – A broken chord pattern played in the left hand. Classical composers such as Haydn and Mozart used this technique in their piano music. ...
... Alberti bass – A broken chord pattern played in the left hand. Classical composers such as Haydn and Mozart used this technique in their piano music. ...
Music Lettering Test
... a minor scale or a major scale. A few of the things that may help to determine whether the piece is in major or minor are the following: 1. What does the piece sound like? Is it major sounding or minor? 2. Are there a lot of accidentals in the piece? If there are this could be a good sign that it ma ...
... a minor scale or a major scale. A few of the things that may help to determine whether the piece is in major or minor are the following: 1. What does the piece sound like? Is it major sounding or minor? 2. Are there a lot of accidentals in the piece? If there are this could be a good sign that it ma ...
Vivaldi: Concerto in D minor, Op. 3 No. 11 (for component 3
... The music modulates briefly to closely related keys such as G minor (subdominant) and A minor (dominant). There are also occasional passages in more remote keys, such as F minor in the third movement. The music uses what is called functional tonality (where key relationships are built on a carefully ...
... The music modulates briefly to closely related keys such as G minor (subdominant) and A minor (dominant). There are also occasional passages in more remote keys, such as F minor in the third movement. The music uses what is called functional tonality (where key relationships are built on a carefully ...
1 Basic Tuning for the Autoharp Introduction Setting The Foundation
... Octave - multiples of a given frequency. An octave higher than a note is twice the frequency and an octave lower is one half the frequency. There are twelve half steps or chromatic semitones and seven diatonic steps in an octave interval. Chromatic - a scale having all twelve semitones in an octave, ...
... Octave - multiples of a given frequency. An octave higher than a note is twice the frequency and an octave lower is one half the frequency. There are twelve half steps or chromatic semitones and seven diatonic steps in an octave interval. Chromatic - a scale having all twelve semitones in an octave, ...
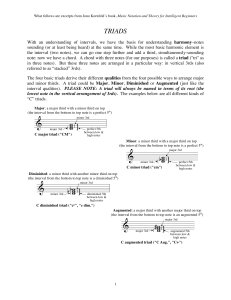
Triads, 7th chords, the roman numeral harmony system, inversions
... As a means of relating these different qualities to the different chords based on the seven scale degrees, a Roman numeral system is used. Upper case numbers represent major triads (I, IV, V), lower case numbers represent minor triads (ii, iii, vi), and a lower case number with the diminished symbol ...
... As a means of relating these different qualities to the different chords based on the seven scale degrees, a Roman numeral system is used. Upper case numbers represent major triads (I, IV, V), lower case numbers represent minor triads (ii, iii, vi), and a lower case number with the diminished symbol ...
Alois Hába`s Suite für vier Posaunen
... interval throughout the Suite is int 2.5, an interval that, according to Tam, appears frequently throughout Hába’s quarter-tone works, often as a component of interval cycles that can contain from 3 to 24 successive iterations.6 In Chapter 1, I show that int 2.5 can function as a passing tone that d ...
... interval throughout the Suite is int 2.5, an interval that, according to Tam, appears frequently throughout Hába’s quarter-tone works, often as a component of interval cycles that can contain from 3 to 24 successive iterations.6 In Chapter 1, I show that int 2.5 can function as a passing tone that d ...
Chords symbols and their chords
... Now 5 + 4 = 8 is bad arithmetic, but a perfect fifth plus a perfect fourth makes an octave. [The underlying reason for this seemingly strange result is that when we are figuring out the size of an interval by counting notes up a scale, we call the lower note note one instead of note zero.] More arit ...
... Now 5 + 4 = 8 is bad arithmetic, but a perfect fifth plus a perfect fourth makes an octave. [The underlying reason for this seemingly strange result is that when we are figuring out the size of an interval by counting notes up a scale, we call the lower note note one instead of note zero.] More arit ...
Composing In the Flesh: Perceptually
... minor second above the same note, on the other hand, contains a great deal of roughness, or sensory dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest freque ...
... minor second above the same note, on the other hand, contains a great deal of roughness, or sensory dissonance. The degree of roughness of an interval or chord depends on the extent to which it has spectral components within the same critical band. The critical band is related to the smallest freque ...
Good Melodic Writing
... of C-Major, C can be harmonized by C-Major, A-minor and F-Major triads. 3. Explore the possibilities of chromatic harmony: Make a list of different chords which share the same chord tone, e.g. C could also be harmonized by Ab-Major triad (bVI), D7 (V7/V), F# dim.7 (viio7/V) etc. 4. Choose one/a few ...
... of C-Major, C can be harmonized by C-Major, A-minor and F-Major triads. 3. Explore the possibilities of chromatic harmony: Make a list of different chords which share the same chord tone, e.g. C could also be harmonized by Ab-Major triad (bVI), D7 (V7/V), F# dim.7 (viio7/V) etc. 4. Choose one/a few ...
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (1756 – 1791)
... Wagner had achieved, either by using classical forms and key relationships in their own way or by abandoning them completely. Composers in the impressionist style such as Ravel and Debussy wrote music that used recognisable chords and harmonies, but combined them in original ways, using instrument ...
... Wagner had achieved, either by using classical forms and key relationships in their own way or by abandoning them completely. Composers in the impressionist style such as Ravel and Debussy wrote music that used recognisable chords and harmonies, but combined them in original ways, using instrument ...
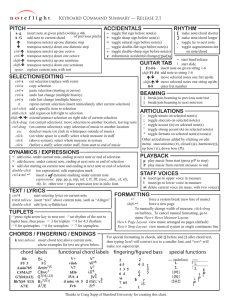
Keyboard Command Summary
... (on current selection): copy selection of music to another location deselect music (or click in whitespace outside of music) (on white space in a staff): select whole measure in staff (above system): select whole measure in system (before a staff): select entire staff, from start to end of music ...
... (on current selection): copy selection of music to another location deselect music (or click in whitespace outside of music) (on white space in a staff): select whole measure in staff (above system): select whole measure in system (before a staff): select entire staff, from start to end of music ...
Notes - Stanford University
... same pitch at the same volume level, or that an opera singer sings the same note on an “oo” and an “ee” vowel. It is easy to hear the differences between these sounds, but how are they manifested in the physical sound waves? The answer lies in that, even though our brain perceives the sinusoidal wav ...
... same pitch at the same volume level, or that an opera singer sings the same note on an “oo” and an “ee” vowel. It is easy to hear the differences between these sounds, but how are they manifested in the physical sound waves? The answer lies in that, even though our brain perceives the sinusoidal wav ...
Music for Small Ensemble
... Galliard is rhythmically more complex, especially in the opening section, with its syncopations (see line 4) Texture Contrapuntal – somewhat like a civilised conversation between the five players: each part has a melodic line of its own Imitation between the parts Lines cross over each other ...
... Galliard is rhythmically more complex, especially in the opening section, with its syncopations (see line 4) Texture Contrapuntal – somewhat like a civilised conversation between the five players: each part has a melodic line of its own Imitation between the parts Lines cross over each other ...
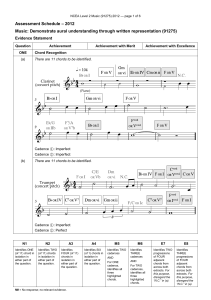
NCEA Level 2 Music (91275) 2012 Assessment Schedule
... Identifies ONE way that the use of TWO of the specified features contrasts with the previous extract, eg: ...
... Identifies ONE way that the use of TWO of the specified features contrasts with the previous extract, eg: ...
dotted eighth notes - Introduction to Music Theory
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
... Minor, augmented, and diminished intervals are always chromatic intervals in all major keys. ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.