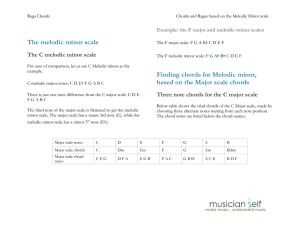
Chords and Ragas based on the Melodic minor scale
... This scale is similar to the Lydian mode (Raga Kalyani). The Lydian mode has a 5th note, while this mode has a #5th note – the minor 6th interval. This mode, the 3rd mode of the Melodic minor scale can be called the Lydian augmented scale because it has the notes of the Lydian scale, with the 5th no ...
... This scale is similar to the Lydian mode (Raga Kalyani). The Lydian mode has a 5th note, while this mode has a #5th note – the minor 6th interval. This mode, the 3rd mode of the Melodic minor scale can be called the Lydian augmented scale because it has the notes of the Lydian scale, with the 5th no ...
Automatic Chord Detection in Polyphonic Audio Data
... Automatic analysis of digital audio data has a long tradition. Many tasks that humans solve easily, like distinguishing the constituting instrument in polyphonic audio or the recognition of rhythm or harmonies are still not solved for computers. Especially the development of an ...
... Automatic analysis of digital audio data has a long tradition. Many tasks that humans solve easily, like distinguishing the constituting instrument in polyphonic audio or the recognition of rhythm or harmonies are still not solved for computers. Especially the development of an ...
simpler list of musical terminology
... of music its tune. The melody line is the most prominent line of the music. It is the line you hum or remember most vividly. A hymn gets its identity from its melody. Although a hymn’s chords and harmonic movement may be similar to other hymns, its melody will be unique. The hymn melody is usually i ...
... of music its tune. The melody line is the most prominent line of the music. It is the line you hum or remember most vividly. A hymn gets its identity from its melody. Although a hymn’s chords and harmonic movement may be similar to other hymns, its melody will be unique. The hymn melody is usually i ...
POTTER VOICE STUDIO INTERVALS , SCALES , KE Y
... An interval is the distance between two notes. Intervals are always counted from the lower note to the higher one, with the lower note being counted as one. Intervals come in different qualities and size. If the notes are sounded successively, it is a melodic interval. If sounded simultaneously, the ...
... An interval is the distance between two notes. Intervals are always counted from the lower note to the higher one, with the lower note being counted as one. Intervals come in different qualities and size. If the notes are sounded successively, it is a melodic interval. If sounded simultaneously, the ...
Assessment Schedule – 2011
... (a) Intervals Perfect 4th Major 2nd Minor 6th Minor 2nd (b) Keys and scales (i) One-octave descending scale of G major in semibreves, including key signature: ...
... (a) Intervals Perfect 4th Major 2nd Minor 6th Minor 2nd (b) Keys and scales (i) One-octave descending scale of G major in semibreves, including key signature: ...
EKU Music Theory Study Guide with PAGE NUMBERS
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
Chapter Seven: Melody, Harmony, and Form
... Scales - Major and Minor - Melodies are made up of the tones in a scale. Most children's melodies are major scales, but some are minor scales. Major and minor scales include 8 notes moving step by step from one pitch to the same pitch an octave higher (8 notes above). The scale is named by the first ...
... Scales - Major and Minor - Melodies are made up of the tones in a scale. Most children's melodies are major scales, but some are minor scales. Major and minor scales include 8 notes moving step by step from one pitch to the same pitch an octave higher (8 notes above). The scale is named by the first ...
EKU Music Theory Study Guide - Music Theory And Composition
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
Music Theory And Composition - Eastern Kentucky University
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
Unit 10. Music theory
... conduct to. First find the beat that seems the strongest, then try tapping along to it. Eventually you should be able to tap along with the music, and you will have found the pulse. Listen to the bass line and the rhythm section, as often they play with the pulse. ...
... conduct to. First find the beat that seems the strongest, then try tapping along to it. Eventually you should be able to tap along with the music, and you will have found the pulse. Listen to the bass line and the rhythm section, as often they play with the pulse. ...
Modern harmony, its explanation and application - DMU
... away the whole of the theories of the past. The earnest student may well be excused if he is bewildered completely on rising up fresh from his theoretical treatises to plunge into the music of actual life of the twentieth-century operahousesj concert-halls, and music-rooms. The sincere mind can hard ...
... away the whole of the theories of the past. The earnest student may well be excused if he is bewildered completely on rising up fresh from his theoretical treatises to plunge into the music of actual life of the twentieth-century operahousesj concert-halls, and music-rooms. The sincere mind can hard ...
Scales, Voice
... Notes on lines are letters between. Short lines indicate where sharp/flat would be , graphically. ...
... Notes on lines are letters between. Short lines indicate where sharp/flat would be , graphically. ...
Sample Responses Q7 - AP Central
... 5. Unresolved sevenths or incorrectly resolved sevenths. 6. Other note-against-note dissonances (including fourths) that are not treated correctly, including Roman numerals that do not match with the given melody note and nonsensical ornamental tones. 7. Poor chord succession (e.g., V–IV or ii–iii) ...
... 5. Unresolved sevenths or incorrectly resolved sevenths. 6. Other note-against-note dissonances (including fourths) that are not treated correctly, including Roman numerals that do not match with the given melody note and nonsensical ornamental tones. 7. Poor chord succession (e.g., V–IV or ii–iii) ...
A Rule-based System for Tuning Chord Progressions
... pure interval 3:2; conversely, any attempt at using the perfect fifth to fit some other relationship will sound too dissonant to be included in tonal harmony. The following list of propositions can be used to ensure that the principles of just intonation are maintained for most simple chord progress ...
... pure interval 3:2; conversely, any attempt at using the perfect fifth to fit some other relationship will sound too dissonant to be included in tonal harmony. The following list of propositions can be used to ensure that the principles of just intonation are maintained for most simple chord progress ...
General Principles of Harmony by Alan Belkin
... human brain's highly evolved capacities for making sense of auditory experience have surely not changed over the past few centuries. Another, related method, consists of intensive drill with harmonic formulas. Based on the notion that harmony, like language, uses many idioms, the goal here is to lea ...
... human brain's highly evolved capacities for making sense of auditory experience have surely not changed over the past few centuries. Another, related method, consists of intensive drill with harmonic formulas. Based on the notion that harmony, like language, uses many idioms, the goal here is to lea ...
Tonal Harmony Introduction
... consists of two pitches whose frequencies are in the ratio of 1:2, separated by 12 half steps ...
... consists of two pitches whose frequencies are in the ratio of 1:2, separated by 12 half steps ...
Music Theory Review Guide - Guitar
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
... Melodic minor scale—a natural minor scale with the sixth and seventh scale degrees raised one half step in the ascending part of the scale, and a return (or re-lowering of the sixth and seventh scale degrees one half step) of the natural minor scale in the descending part of the scale. ...
Spectral analysis of different harmonies Implemented by Equal
... noticeable differences in the specific range, and the red-lettered frequencies exist only in the equal tempered tuning. Although the Just tuned major and minor triads have significantly clearer frequency ratio relationships than the Equal tempered major and minor triads, many newly arisen integer re ...
... noticeable differences in the specific range, and the red-lettered frequencies exist only in the equal tempered tuning. Although the Just tuned major and minor triads have significantly clearer frequency ratio relationships than the Equal tempered major and minor triads, many newly arisen integer re ...
Theory 9-26 - Introduction to Music Theory
... you are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. ...
... you are in. When a melody is rewritten into another key with the exact same sequence of notes and intervals, it is called TRANSPOSITION. This raises or lowers the notes to make a melody easier to sing or play, or so it can be played by an instrument in a different key. ...
Dictionary of Musical Terms
... apppearing at the start of a piece....... ________ ________ (Eng.) KEE sihg-nuh-chur ...
... apppearing at the start of a piece....... ________ ________ (Eng.) KEE sihg-nuh-chur ...
This Worldes Joie Part 3 analysis
... (see previous notes). Bars 38-40 are octatonic (Collection I – B tone-semitone ordering - with two chromatic decorations – C (tenor, 384) and Eb (strings, 40)). Once again the celesta interjects its more sinister-sounding 12-note figure (at the original pitch) in bar 39. The tenor’s next phrase (41- ...
... (see previous notes). Bars 38-40 are octatonic (Collection I – B tone-semitone ordering - with two chromatic decorations – C (tenor, 384) and Eb (strings, 40)). Once again the celesta interjects its more sinister-sounding 12-note figure (at the original pitch) in bar 39. The tenor’s next phrase (41- ...
NCEA Level 1 Music (91094) 2011 Assessment Schedule
... short and detached / given less than its full duration. ...
... short and detached / given less than its full duration. ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 11 Non Chord Tones 1
... 9-8 suspension is a special kind of suspension because the note of resolution should NOT be present anywhere in the texture when a suspension occurs 11-10 suspensions is actually a 4-3 suspension 9-8 suspension is NOT labeled as a 2-1 suspension because 2-1suspension if found much less frequen ...
... 9-8 suspension is a special kind of suspension because the note of resolution should NOT be present anywhere in the texture when a suspension occurs 11-10 suspensions is actually a 4-3 suspension 9-8 suspension is NOT labeled as a 2-1 suspension because 2-1suspension if found much less frequen ...
Write like Mozart – lecture notes Table of Contents
... Voice Leading with the Common Tone Approach..............................................................................10 I-V-I................................................................................................................................................10 I-IV-I.................. ...
... Voice Leading with the Common Tone Approach..............................................................................10 I-V-I................................................................................................................................................10 I-IV-I.................. ...
Phrase Painting and Goal Orientation In Two Late Gesualdo Madrigals
... the progressions that are regarded as compatible with Baroque harmonic practice involve the presence of secondary dominants or the Neapolitan triad. An example of the former is I-V/ii-ii, in which the progression from I to Viii is a chromatic-third relationship. The only other types of chromatic pro ...
... the progressions that are regarded as compatible with Baroque harmonic practice involve the presence of secondary dominants or the Neapolitan triad. An example of the former is I-V/ii-ii, in which the progression from I to Viii is a chromatic-third relationship. The only other types of chromatic pro ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.