Assessment Schedule – 2011
... the beats are clearly grouped as 3+2 in many parts, shown by the dotted minim + minim rest (eg Bass Clarinet) In Percussion I, the ride cymbal has hits on the strong beats in bars 10 and 11, so the hits on beats 1 and 4 of bar 9 must indicate they are strong beats too. Other responses possible. ...
... the beats are clearly grouped as 3+2 in many parts, shown by the dotted minim + minim rest (eg Bass Clarinet) In Percussion I, the ride cymbal has hits on the strong beats in bars 10 and 11, so the hits on beats 1 and 4 of bar 9 must indicate they are strong beats too. Other responses possible. ...
A Field Guide to Chromaticism
... protracted, as though all of Act II, for instance, were a succession of diatonic and chromatic deceptive cadences. But as a rule Wagner's deceptive cadences, no less than Chopin's, are between triads, whether closely related or remotely related; the context is diatonic, and the chromatic details are ...
... protracted, as though all of Act II, for instance, were a succession of diatonic and chromatic deceptive cadences. But as a rule Wagner's deceptive cadences, no less than Chopin's, are between triads, whether closely related or remotely related; the context is diatonic, and the chromatic details are ...
Year-9-Music
... Minimalism is a style of music using short musical ideas known as motifs or cells. These musical ideas are repeated many times creating ostinatos (repeating patterns). These patterns can be layered, to create contrapuntal (layered) textures. In minimalist pieces, complex, syncopated rhythms are comm ...
... Minimalism is a style of music using short musical ideas known as motifs or cells. These musical ideas are repeated many times creating ostinatos (repeating patterns). These patterns can be layered, to create contrapuntal (layered) textures. In minimalist pieces, complex, syncopated rhythms are comm ...
Music Theory ==> Basic Level
... The first note of a scale is called the tonic, and gives its name to the scale - so this is a C scale. If the first 3rd of the scale (with respect to the tonic) is a major third (3), the scale will be "major"; if it is a minor third (m3), the scale will correspondingly be "minor". So the scale above ...
... The first note of a scale is called the tonic, and gives its name to the scale - so this is a C scale. If the first 3rd of the scale (with respect to the tonic) is a major third (3), the scale will be "major"; if it is a minor third (m3), the scale will correspondingly be "minor". So the scale above ...
The Craft of Singing
... extending down to C, an octave below middle c'. Since one of the primary characteristics of barbershop music is its cone-shaped sound, the bass must sing with a heavier production than that used by the upper voices, and she will actually sing with more volume than used by any part above her. The har ...
... extending down to C, an octave below middle c'. Since one of the primary characteristics of barbershop music is its cone-shaped sound, the bass must sing with a heavier production than that used by the upper voices, and she will actually sing with more volume than used by any part above her. The har ...
Lesson_LLL_-_Mixture..
... Secondary mixture, double mixture, and other chromatic chords: All of the examples of mixture presented so far have been relatively straightforward. In each case, one or two tones are borrowed from the parallel key to emphasize or intensify certain harmonies. Occasionally, however, you will encounte ...
... Secondary mixture, double mixture, and other chromatic chords: All of the examples of mixture presented so far have been relatively straightforward. In each case, one or two tones are borrowed from the parallel key to emphasize or intensify certain harmonies. Occasionally, however, you will encounte ...
AP Music Syllabus
... Finish modes: use the acronym, etc. Test review TEST DAY Sing from packet, including some canons and two-part things. Triads: major, minor, diminished, and augmented, root position. Seventh chords: M7, Mm7, m7, dim7, half-dim ...
... Finish modes: use the acronym, etc. Test review TEST DAY Sing from packet, including some canons and two-part things. Triads: major, minor, diminished, and augmented, root position. Seventh chords: M7, Mm7, m7, dim7, half-dim ...
here
... - Individual playing the melody, or a group? How does this affect the timbre? - Articulation – does the way in which it is articulated affect its timbre? Harsh, scratchy, bouncy, airy, thin, sparse ...
... - Individual playing the melody, or a group? How does this affect the timbre? - Articulation – does the way in which it is articulated affect its timbre? Harsh, scratchy, bouncy, airy, thin, sparse ...
How Music Works
... Music theory originates after composition. Composers have rarely “painted by numbers,” using music theory to create their works. Instead, music theorists throughout history researched finished compositions for recognizable patterns to document. This text book is not a manual for music composition. M ...
... Music theory originates after composition. Composers have rarely “painted by numbers,” using music theory to create their works. Instead, music theorists throughout history researched finished compositions for recognizable patterns to document. This text book is not a manual for music composition. M ...
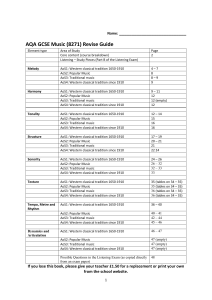
GCSE Music Revision Guide
... Understanding music (40%). This component focuses on listening and contextual understanding. It is assessed through a written exam lasting 1 hour and 30 minutes. In Section A (worth 68 marks) students answer questions on excerpts of music that are played; in Section B (worth 28 marks) students a ...
... Understanding music (40%). This component focuses on listening and contextual understanding. It is assessed through a written exam lasting 1 hour and 30 minutes. In Section A (worth 68 marks) students answer questions on excerpts of music that are played; in Section B (worth 28 marks) students a ...
Concepts of music overview
... Harmony: the ‘vertical’ relationship of pitches (intervals, chords, ‘harmony vocals’, chord progressions etc) ...
... Harmony: the ‘vertical’ relationship of pitches (intervals, chords, ‘harmony vocals’, chord progressions etc) ...
Basic Music Theory
... The music commonly played in our part of the world has twelve different notes: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G with a sharp (#) or flat (b) note between all the notes except B and C and E and F. The notes between the letters can be called either sharp or flat. A sharp (#) note is one fret higher than the le ...
... The music commonly played in our part of the world has twelve different notes: A, B, C, D, E, F, and G with a sharp (#) or flat (b) note between all the notes except B and C and E and F. The notes between the letters can be called either sharp or flat. A sharp (#) note is one fret higher than the le ...
NGFL_Shost_movt_4_analysis
... TEXTURE: Apart from the A# pedal note held low in violin 1 which lasts here for 21 bars, the chords are a key feature –but also significant is the unison playing by the lower three parts of the triadic motif from the cello concerto. THEMES: Theme a is heard in the lower 3 parts. In bar 10, this moti ...
... TEXTURE: Apart from the A# pedal note held low in violin 1 which lasts here for 21 bars, the chords are a key feature –but also significant is the unison playing by the lower three parts of the triadic motif from the cello concerto. THEMES: Theme a is heard in the lower 3 parts. In bar 10, this moti ...
Expanded Tonality in Quartal Space: Back to Debussy`s
... collection forms a perfect fourths' scale (A-D-G-C-F) (fig. 1, left). Therefore, the F triad in measure 18 can be described as a subset of the perfect fourth, while the final chord, its plain expression. Another analogy is thus possible with traditional tonal harmonic structures that usually utilize ...
... collection forms a perfect fourths' scale (A-D-G-C-F) (fig. 1, left). Therefore, the F triad in measure 18 can be described as a subset of the perfect fourth, while the final chord, its plain expression. Another analogy is thus possible with traditional tonal harmonic structures that usually utilize ...
How to Dissect Modes to Create New Melodic Material
... introduce jumps and leaps into our playing which help to break up the monotony of long step-wise lines. Another important advantage of this is that we can ‘cherry pick’ the colourful notes of a scale and imply its unique colour by only playing a limited number of notes. Each scale can be broken down ...
... introduce jumps and leaps into our playing which help to break up the monotony of long step-wise lines. Another important advantage of this is that we can ‘cherry pick’ the colourful notes of a scale and imply its unique colour by only playing a limited number of notes. Each scale can be broken down ...
A - The sixth note of the diatonic major scale of C
... Augmented - The term for a major or perfect interval which has been enlarged by one half-step, e.g. c-g , (an augmented fifth,) or c-d , (an augmented second). Also used for a triad with an augmented fifth, e.g. the augmented tonic triad in C major, C+, c-e-g . Balance - The harmonious adjustment of ...
... Augmented - The term for a major or perfect interval which has been enlarged by one half-step, e.g. c-g , (an augmented fifth,) or c-d , (an augmented second). Also used for a triad with an augmented fifth, e.g. the augmented tonic triad in C major, C+, c-e-g . Balance - The harmonious adjustment of ...
Blues and Other Popular Styles
... each built above middle C. A major-major seventh chord (MM7) is a major triad plus a M7; a minor-minor seventh chord (mm7) is a minor triad plus a m7. A MM7 is often called a major seventh for short, a mm7 is a minor seventh, and a major-minor seventh chord (Mm7) is a dominant seventh. A seventh cho ...
... each built above middle C. A major-major seventh chord (MM7) is a major triad plus a M7; a minor-minor seventh chord (mm7) is a minor triad plus a m7. A MM7 is often called a major seventh for short, a mm7 is a minor seventh, and a major-minor seventh chord (Mm7) is a dominant seventh. A seventh cho ...
Powerpoint
... music. This resulted in ska, named after the lively ‘skank’ dance, followed by rock steady, which had a slower tempo and was an early form of reggae. The word ‘reggae’ is probably derived from patois for a ‘regular’ beat. The three styles share some principal characteristics: Heavy, repetitive cho ...
... music. This resulted in ska, named after the lively ‘skank’ dance, followed by rock steady, which had a slower tempo and was an early form of reggae. The word ‘reggae’ is probably derived from patois for a ‘regular’ beat. The three styles share some principal characteristics: Heavy, repetitive cho ...
Serialism in the Works of Charles Ives
... (In the version in the piano part, the palindrome is actually complete.) The fugal entrances of the string parts, and the top notes of the piano part, in a different rhythm, all consist of repetitions of the pitch series. These five voices are in five different transpositions of the series, intended ...
... (In the version in the piano part, the palindrome is actually complete.) The fugal entrances of the string parts, and the top notes of the piano part, in a different rhythm, all consist of repetitions of the pitch series. These five voices are in five different transpositions of the series, intended ...
OTHER SCALES CHROMATIC SCALE The scale consisting of all
... The scale consisting of all twelve notes occurring between any two pitches an octave apart. The ascending form of the chromatic scale is usually written using sharps, and the descending version is usually written using flats. ...
... The scale consisting of all twelve notes occurring between any two pitches an octave apart. The ascending form of the chromatic scale is usually written using sharps, and the descending version is usually written using flats. ...
L 8-‐9 Musical Scales, Chords , and Intervals, The Pythagorean and
... sounds consonant (and has been the foundaIon of western music for several hundred years), and we measure the string lengths required for this triad. We find (demo) that the string lengths have ...
... sounds consonant (and has been the foundaIon of western music for several hundred years), and we measure the string lengths required for this triad. We find (demo) that the string lengths have ...
Elements of Music
... Pitches (notes): Pitch is the word used to describe the highness or lowness of a musical sound. Intervals: An interval is the distance between two pitches (notes). ...
... Pitches (notes): Pitch is the word used to describe the highness or lowness of a musical sound. Intervals: An interval is the distance between two pitches (notes). ...
File
... Augmented interval: when a perfect interval or major interval is made larger by one half step ...
... Augmented interval: when a perfect interval or major interval is made larger by one half step ...
Handout on Set Theory: Intervals and Atonality
... In traditional harmony, all augmented and diminished intervals are considered dissonant, while the perfect fifth and the perfect octave are consonant (the perfect fourth is generally considered a disso nance although it retains some consonant qualities). The other intervals are consonant or dissona ...
... In traditional harmony, all augmented and diminished intervals are considered dissonant, while the perfect fifth and the perfect octave are consonant (the perfect fourth is generally considered a disso nance although it retains some consonant qualities). The other intervals are consonant or dissona ...
Chord (music)

A chord, in music, is any harmonic set of three or more notes that is heard as if sounding simultaneously. These need not actually be played together: arpeggios and broken chords may, for many practical and theoretical purposes, constitute chords. Chords and sequences of chords are frequently used in modern Western, West African and Oceanian music, whereas they are absent from the music of many other parts of the world.In tonal Western classical music, the most frequently encountered chords are triads, so called because they consist of three distinct notes: further notes may be added to give tetrads such as seventh chords and added tone chords, as well as extended chords and tone clusters. Triads commonly found in the Western classical tradition are major, minor, augmented and diminished chords. The descriptions major, minor, augmented, and diminished are referred to collectively as chordal quality. Chords are also commonly classified by their root note—for instance, a C major triad consists of the pitch classes C, E, and G. Chords may also be classified by inversion, the way in which their pitches are vertically arranged.An ordered series of chords is called a chord progression. Although any chord may in principle be followed by any other chord, certain patterns of chords have been accepted as establishing key in common-practice harmony. To describe this, Western music theory has developed the practicing of numbering chords using Roman numerals which represent the number of diatonic steps up from the tonic note of the scale. Common ways of notating or representing chords in Western music other than conventional staff notation include Roman numerals, figured bass, macro symbols (sometimes used in modern musicology), and chord charts. Each of these systems is more likely to appear in certain contexts: figured bass notation was used prominently in notation of Baroque music, macro symbols are used in modern musicology, and chord charts are typically found in the lead sheets used in popular music.