* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year-9-Music
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
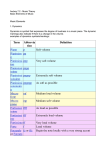
Year 9 Music Revision Notes 2015 Your Year 9 Music End of Year Listening Test will take place in your music lesson, in the week beginning 18 th May Listen to the musical examples named below. These musical examples can be found, along with these revision notes, in Shared Work > Music > Year 9 > 00Revision, or they can be played from music streaming or sharing sites such as Youtube. Piano Music in the Romantic Period Listen to Chopin Prelude in D flat ‘Raindrop’ and study the text below. Learn to hear these features in the music as you listen. Common features of piano music from the Romantic Period The performer uses a wide range of dynamics, from pianissimo (very soft) to fortissimo (very loud) The performer subtly uses crescendos (getting louder) and diminuendos (getting quieter) throughout. The performer subtly changes the tempo (speed) throughout, known as rubato. The performer plays legato (smoothly) using the sustain pedal. The performer plays a smooth melody with the right hand and broken chords with the left hand. Features of Chopin Prelude in D flat ‘Raindrop’ Section Section A Name (0:00-0:26) Tonality Texture Rhythm Dynamics Major Key (sounds ‘bright’) Section B (2:56-3:40) Section A, followed by Coda (4:31-End) Minor Key (sounds ‘dark’) Major Key (sounds ‘bright’) Mostly melody and accompaniment Pedal Note (a note is repeated continuously) At first, the melody is played by the left hand, the pedal note (repeating note) is played by the right hand. Later the right hand plays chords Mostly melody and accompaniment Pedal Note (a note is repeated continuously) Monophonic during coda (single line of music) Dotted quaver motif begins the theme (main melody) At first, the left hand plays crotchets (one-beat notes) Later the left hand plays minims (two-beat notes) Dotted quaver motif begins the theme (main melody) Mostly p (quiet) Subtle crescendos and diminuendos (getting gradually louder then softer) Dramatic crescendo (getting louder) From p (quiet) to ff (very loud) Then diminuendo (getting quieter) back to p Mostly p (quiet) Subtle crescendos and diminuendos (getting gradually louder then softer) Diminuendo at the end Minimalism Listen to Steve Reich’s Electric Counterpoint Movement 3 ‘Fast’ and study the text below. Learn to hear these features in the music as you listen. Common features of Minimalism Minimalism is a style of music using short musical ideas known as motifs or cells. These musical ideas are repeated many times creating ostinatos (repeating patterns). These patterns can be layered, to create contrapuntal (layered) textures. In minimalist pieces, complex, syncopated rhythms are common and it is normal for the music to change gradually over a long period of time. Features of Reich Electric Counterpoint Movement 3 ‘Fast’ Instruments & 7 electric guitar parts and 2 bass guitar parts recorded on tape. Technology 1 live guitar plays solo part Begins monophonic (one line of music). Parts are added one by one. Texture Then texture is layered & contrapuntal (independent lines of music played at the same time) Also imitative & canonic (lines of music are the same but starting at different times so as to overlap) Minimalist Layering Techniques Repetition Begins and ends in E minor. Tonality Middle section alternates between E minor and C minor. Listener hears a resultant melody when the guitars are layered. Melody Resultant melody is also played by the live guitar. Metre 3/2 (3 beats per bar) Rhythm Syncopated (off-beat) Bass guitars diminuendo (get softer) then drop out before the end of the piece. Dynamics At the end of the piece there is a crescendo Club Dance Music Listen to Moby’s Why Does My Heart Feel So Bad and study the text below. Learn to hear these features in the music as you listen. Common features of Club Dance Music A regular beat in a 4/4 time signature Use of technology including: Synthesisers: instruments which produce their sound electronically Sequencers: computer programmes which record, store and organise sounds to produce the finished piece of music Samples: sounds which have been recorded from other pieces of music / environments, to be replayed Use of studio effects including: Reverb: When a sound does not stop suddenly but takes time to die away Retriggering: When a sound is repeated in quick succession Echo: When a sound is repeated in quick succession, fading away Changes in EQ and filtering: sounds of different pitches are made louder or quieter, changing the balance between them Structure of Moby Why Does My Heart Feel So Bad Section Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Time 0:00 0:19 0:39 0:59 1:19 1:38 1:57 2:17 2:37 2:59 3:18 3:38 3:57 Bar Number Bar 1-8 Bar 9-16 Bar 17-24 Bar 25-32 Bar 33-40 Bar 41-48 Bar 48-56 Bar 57-64 Bar 1-8 Bar 1-8 Bar 1-8 Bar 1-8 Bar 1-8 Section INTRO VERSE 1 CHORUS 1 VERSE 2 CHORUS 2 Names BUILD – UP OUTRO BREAKDOWN Additional Additional hi-hat loop hi-hat loop Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string chords chords chords chords chords chords Am Em G D Am Em G D C Am C Am FCFC Am Em G D Am Em G D Male Vocal sample ‘Why does my heart’ Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth pad chords chords chords chords C Am C Am FCFC FCFC Am Em G D Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string Synth string & piano & piano & piano & piano & piano & piano & piano countercountercountercountercountercountercountermelody 1 melody 1 melody 1 melody 2 melody 3 melody 1 melody 1 Synth string Synth string & piano & piano countercountermelody 3 melody 3 Drum and Drum and Drum and Drum and Drum and Drum and Drum and shaker loop shaker loop shaker loop shaker loop shaker loop shaker loop shaker loop Drum and Drum and shaker loop shaker loop Male Vocal sample ‘Why does my heart’ Male Vocal sample ‘Why does my heart’ Male Female Female Male Male Vocal Vocal Vocal Vocal Vocal sample sample sample sample sample ‘Why does ‘These open ‘These open ‘Why does ‘Why does my heart’ doors’ doors’ my heart’ my heart’ retriggered Retriggered Retriggered with reverb with reverb and echo and echo Piano Piano Piano Piano Syncopated Syncopated Syncopated Syncopated Syncopated chords chords chords chords piano piano piano piano piano Am Em G D Am Em G D Am Em G D Am Em G D chords chords chords chords chords Am Em G D C Am C Am FCFC Am Em G D Am Em G D Bass AEGD Bass AEGD Bass CACA Bass FCFC Bass AEGD Bass AEGD Female Female Female Male Vocal Vocal Vocal Vocal sample sample sample sample ‘These open ‘These open ‘These open ‘Why does doors’ doors’ doors’ my heart’ With reverb retriggered retriggered & filtering/ EQ change Syncopated Syncopated piano piano chords chords FCFC FCFC Bass FCFC Bass FCFC Programme Music Listen to themes from Prokofiev’s Peter and the Wolf and study the text below. Learn to hear these features in the music as you listen. Definition Programme music is music that describes a story, a scene or an emotion through music alone (without the use of words or images). Features of Prokofiev Peter and the Wolf Theme Instrument Pitch Bird’s Theme Flute High Cat’s Theme Clarinet Quite low Duck’s Theme Oboe Grandfather’s Theme Peter’s Theme Bassoon Low Violins Wolf’s Theme French Horns Ascending then descending Low then ascends Tempo Allegro (fast) Andante (walking pace) Moderato (moderate) Key Larghetto (slow and broad) Andante (walking pace) Minor Other Features Grace notes, trills and fast arpeggios Staccato (detached) arpeggios Sustained notes, Legato (smooth) Cantabile (singing style) Heavy, accented dotted notes. Major Elegant dotted rhythms Andante (walking pace) Minor Crescendo (getting louder) from piano to forte. Chromatic notes. Major Major