Ragtime Inventing - Kinross High School
... 2. Annotate the score to highlight key features of the music. 3. Find out about the music of Michael Nyman, the compositional techniques that he uses and what has influenced him as a composer ...
... 2. Annotate the score to highlight key features of the music. 3. Find out about the music of Michael Nyman, the compositional techniques that he uses and what has influenced him as a composer ...
Doc 2
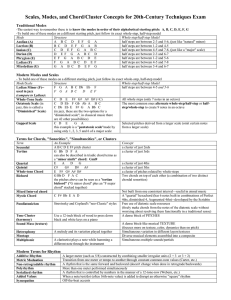
... (octave) or more) or “small” (less than an octave) Phrase: a complete musical idea with a beginning and end. Usually between 4-8 measures. Texture: how the different melodies are put together. Can be described as “thick” (lots of notes on top of each other) or “thin” (unison (all doing the same thin ...
... (octave) or more) or “small” (less than an octave) Phrase: a complete musical idea with a beginning and end. Usually between 4-8 measures. Texture: how the different melodies are put together. Can be described as “thick” (lots of notes on top of each other) or “thin” (unison (all doing the same thin ...
Music Music Functions: Physical
... Harmony- Pleasing combination of two or three tones played together in the background while a melody is being played. Harmony also refers to the study of chord progressions. ...
... Harmony- Pleasing combination of two or three tones played together in the background while a melody is being played. Harmony also refers to the study of chord progressions. ...
Purcell 1
... To study the background of the baroque solo concerto and place the Purcell trumpet sonata in context ...
... To study the background of the baroque solo concerto and place the Purcell trumpet sonata in context ...
Traditional composition techniques
... inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same notes, different rhythm; used constantly in dodecaphony microtones intervals smaller than a semitone non-tonal scales scale structures that are symmetric in con ...
... inversion mirrored contour; e.g., subject and inversion in Bartok's Music for Strings, Percussion and Celeste, first movement isomelos same notes, different rhythm; used constantly in dodecaphony microtones intervals smaller than a semitone non-tonal scales scale structures that are symmetric in con ...
Elements of Music
... it as a bass note. Bass players can usually stick to going with the second note. Another popular chord is a suspended chord. It would be written like Asus, Dsus, Esus A suspended chord is when the 3rd is raised. An Esus would have be made up of E, A, and B This is usually used as a prolongation of t ...
... it as a bass note. Bass players can usually stick to going with the second note. Another popular chord is a suspended chord. It would be written like Asus, Dsus, Esus A suspended chord is when the 3rd is raised. An Esus would have be made up of E, A, and B This is usually used as a prolongation of t ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Whole-Tone Scale Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two ...
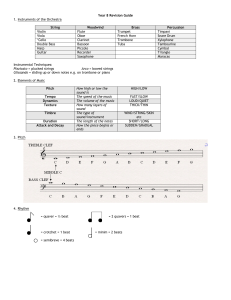
Year 7 Revision Guide
... A chord is 2 or more notes played at the same time. The chords used most often have 3 notes and are called TRIADS. *The fourth note in brackets can be added to make the chord sound jazzy. Musicians would use the BLUES SCALE to improvise (make up on the spot, without rehearsal) over the chord pattern ...
... A chord is 2 or more notes played at the same time. The chords used most often have 3 notes and are called TRIADS. *The fourth note in brackets can be added to make the chord sound jazzy. Musicians would use the BLUES SCALE to improvise (make up on the spot, without rehearsal) over the chord pattern ...
Music 170 Homework problem set 6 (due Nov. 3) 1. Two pipes, both
... 2. Three alpenhorns are tuned so that the second one is a perfect fifth above the first, and the third one is a perfect fifth above the second one. If the first one sounds at 100 Hz, at what frequency does the third, highest, one sound? 3. The harmonic overtone series (the ratios 1:2:3:...) defines ...
... 2. Three alpenhorns are tuned so that the second one is a perfect fifth above the first, and the third one is a perfect fifth above the second one. If the first one sounds at 100 Hz, at what frequency does the third, highest, one sound? 3. The harmonic overtone series (the ratios 1:2:3:...) defines ...
Higher Concepts - Dunblane High School Music Website
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for ...
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for ...
Higher Concepts Higher Music Listening 2014 Onwards Music
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for improvising. ...
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for improvising. ...
Revision Pack for: MUSIC AS
... tone‐picture". concerto. A concerto is a composition for a solo instrument, such as violin or keyboard, and Interrupted cadence V-VI This is considered a weak cadence because of the "hanging" orchestra. The full orchestra plays the ritornello as an introduction. (suspended) feel it invokes Romantic ...
... tone‐picture". concerto. A concerto is a composition for a solo instrument, such as violin or keyboard, and Interrupted cadence V-VI This is considered a weak cadence because of the "hanging" orchestra. The full orchestra plays the ritornello as an introduction. (suspended) feel it invokes Romantic ...
Higher Concepts - Garnock Academy
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for improvising. ...
... Term used to describe music based on a mode, a type of early scale used before major and minor keys were developed. Modes are used in jazz and pop music for improvising. ...
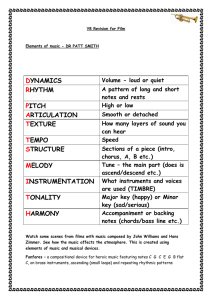
dynamics rhythm pitch articulation texture tempo
... Smooth or detached How many layers of sound you can hear Speed Sections of a piece (intro, chorus, A, B etc.) Tune – the main part (does is ascend/descend etc.) What instruments and voices are used (TIMBRE) Major key (happy) or Minor key (sad/serious) Accompaniment or backing notes (chords/bass line ...
... Smooth or detached How many layers of sound you can hear Speed Sections of a piece (intro, chorus, A, B etc.) Tune – the main part (does is ascend/descend etc.) What instruments and voices are used (TIMBRE) Major key (happy) or Minor key (sad/serious) Accompaniment or backing notes (chords/bass line ...
Slide 1
... Within a key, Major chords are assigned UPPERCASE Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc), while minor chords are assigned lowercase Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, etc) ...
... Within a key, Major chords are assigned UPPERCASE Roman numerals (I, II, III, etc), while minor chords are assigned lowercase Roman numerals (i, ii, iii, etc) ...
MUSIC 111 Class Notes 2
... • African American dance rhythms Jazz • polyrhythmic - simultaneous use of conflicting rhythmic patterns - straight notes • equal (metrical) - Metrical Patterns • simple securing patterns ...
... • African American dance rhythms Jazz • polyrhythmic - simultaneous use of conflicting rhythmic patterns - straight notes • equal (metrical) - Metrical Patterns • simple securing patterns ...
Romantic and impressionist harmony
... mass) a nice example with the remarkable progressions of F major, F# minor, C# major, D major, Eb minor, Bb major, B major, C minor and F major. The leading tone then becomes more important and enables the chromatic world of Liszt and Wagner with their complex chords and fast key interactions (which ...
... mass) a nice example with the remarkable progressions of F major, F# minor, C# major, D major, Eb minor, Bb major, B major, C minor and F major. The leading tone then becomes more important and enables the chromatic world of Liszt and Wagner with their complex chords and fast key interactions (which ...
Materials of Music Study Guide Medium Melody Harmony
... A melody is the line, or tune, in music, a concept that is shared by most cultures. Each melody is unique in its contour (how it moves up and down) and in its range, or span of pitches. An interval is the distance between any two pitches in a melody. A melody that moves in small, connected intervals ...
... A melody is the line, or tune, in music, a concept that is shared by most cultures. Each melody is unique in its contour (how it moves up and down) and in its range, or span of pitches. An interval is the distance between any two pitches in a melody. A melody that moves in small, connected intervals ...
Grade 4 Music I Can... Rhythm I can show that beats may be
... I can show that beats may be grouped into 4’s. I can show the duration of sixteenth notes y Melody I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the ...
... I can show that beats may be grouped into 4’s. I can show the duration of sixteenth notes y Melody I can tell that an interval is the space between two sounds. • I know that an interval may be changed by an accidental. • I can tell that intervals can give shape or contour to a melody I can tell the ...
Sample Grade 4 Theory Paper
... Circle five different mistakes in the following music, then write it out correctly. ...
... Circle five different mistakes in the following music, then write it out correctly. ...
Notes - Andre Mount
... Augmented 6th chords are called that because they’re characterized by an augmented 6th The interval expands outward to an octave o Part of a V chord “To generalize, the bass of an augmented 6th chord is a half step above 5 (6 in minor or b6 in major), one of the upper voices is a half step bel ...
... Augmented 6th chords are called that because they’re characterized by an augmented 6th The interval expands outward to an octave o Part of a V chord “To generalize, the bass of an augmented 6th chord is a half step above 5 (6 in minor or b6 in major), one of the upper voices is a half step bel ...
Summary of Tonal Harmony - Leon Couch`s Course Listings
... 1. All the rest of the non-chord tones are pt, nt, susp, with either the approach or the resolution disrupted. The only absolutely forbidden NCT is one with leaps on both sides of a dissonance; i.e., arpeggios must outline a chord. 2. The pedal point is considered dissonant by K&P while harmonies pr ...
... 1. All the rest of the non-chord tones are pt, nt, susp, with either the approach or the resolution disrupted. The only absolutely forbidden NCT is one with leaps on both sides of a dissonance; i.e., arpeggios must outline a chord. 2. The pedal point is considered dissonant by K&P while harmonies pr ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.