document - Far Western District
... In conjunction with the Far Western District’s efforts to provide MORE variety at our FWD conventions (in addition to the contests), Keith Eckhardt invited me to facilitate a one-hour class on “How To Read Music”. I had previously facilitated a series of one-hour classes for my fellow chapter membe ...
... In conjunction with the Far Western District’s efforts to provide MORE variety at our FWD conventions (in addition to the contests), Keith Eckhardt invited me to facilitate a one-hour class on “How To Read Music”. I had previously facilitated a series of one-hour classes for my fellow chapter membe ...
2 – First Species Counterpoint
... the preceding beat presented the 3rd of this tonic harmony. Had the 3rd of the tonic chord not just sounded the fifth would have been rather coarse sounding. Example 2-1b also uses the rather rare interval of a diminished 5th near the end. This interval can be very effective but it must resolve inwa ...
... the preceding beat presented the 3rd of this tonic harmony. Had the 3rd of the tonic chord not just sounded the fifth would have been rather coarse sounding. Example 2-1b also uses the rather rare interval of a diminished 5th near the end. This interval can be very effective but it must resolve inwa ...
Scales, Modes, and Chord/Cluster Concepts for 20th
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two options for a "d ...
... All whole steps (only 7 notes in an octave) Octatonic Scale (in C D Eb F Gb Ab A B C The most common ones alternate whole-step/half-step or halfjazz, this is called a C Db Eb E F# G A Bb C step/whole-step to create 9 notes in an octave "Diminished" Scale) (in jazz, these are the two options for a "d ...
BG Vocab
... 6. Octave: Range between one note and the same note repeated either lower or higher. (From the root “oct-” meaning “eight” because there are eight natural notes in an octave.) 7. Scale: an arrangement of notes in a system of ascending or descending pitch, usually within an octave 8. Chromatic scale: ...
... 6. Octave: Range between one note and the same note repeated either lower or higher. (From the root “oct-” meaning “eight” because there are eight natural notes in an octave.) 7. Scale: an arrangement of notes in a system of ascending or descending pitch, usually within an octave 8. Chromatic scale: ...
ECDL2006_thematic-similarities - Music
... First theme in Allegro of Mozart’s Clarinet Concerto in A, K622 Taken from the Barlow and Morgenstern dictionary ...
... First theme in Allegro of Mozart’s Clarinet Concerto in A, K622 Taken from the Barlow and Morgenstern dictionary ...
Music Vocabulary Lists Year 1
... Grave - Word to indicate the movement or entire composition is to be played very slow and serious. Grazioso - Word to indicate the movement or entire composition is to be played gracefully. Harmony - Pleasing combination of two or three tones played together in the background while a melody is bein ...
... Grave - Word to indicate the movement or entire composition is to be played very slow and serious. Grazioso - Word to indicate the movement or entire composition is to be played gracefully. Harmony - Pleasing combination of two or three tones played together in the background while a melody is bein ...
File - Humanities 1100
... Beat and Meter - In order to define meter, let's first define beats. Beats give music its regular rhythmic pattern. Beats are grouped together in a measure; the notes and rests corresponds to a certain number of beats. Meter refers to rhythmic patterns produced by grouping together strong and weak ...
... Beat and Meter - In order to define meter, let's first define beats. Beats give music its regular rhythmic pattern. Beats are grouped together in a measure; the notes and rests corresponds to a certain number of beats. Meter refers to rhythmic patterns produced by grouping together strong and weak ...
PPT only
... Sequential presentation of notes Fundamental = note at scale base, bottom note of chord ...
... Sequential presentation of notes Fundamental = note at scale base, bottom note of chord ...
STRATFORD PUBLIC SCHOOLS Music Department – Music Theory
... Identify four triad types aurally. Demonstrate understanding of 1st and 2nd inversion triads including inversion symbols. Identify triads on major and minor scale degrees using Roman Numerals, popular chord symbols, and scale degree names. • Perform triads on keyboard. • Write triads based on popula ...
... Identify four triad types aurally. Demonstrate understanding of 1st and 2nd inversion triads including inversion symbols. Identify triads on major and minor scale degrees using Roman Numerals, popular chord symbols, and scale degree names. • Perform triads on keyboard. • Write triads based on popula ...
Structure and Form File
... • Constant repetition of a fixed number of beats or melodic pattern • During each cycle these patterns can be repeated and developed through; – improvisation – changes in texture – dynamics ...
... • Constant repetition of a fixed number of beats or melodic pattern • During each cycle these patterns can be repeated and developed through; – improvisation – changes in texture – dynamics ...
playing gospel piano - Apostolic Faith Church
... Find someone else to play melody in upper register or on an instrument while you are practicing accompanying styles. Tips for Choosing Printed Music To begin, find very simple, notated hymns with chord symbols. God is So Good (Key of C) Deep and Wide (Key of C) Check out key signature. M ...
... Find someone else to play melody in upper register or on an instrument while you are practicing accompanying styles. Tips for Choosing Printed Music To begin, find very simple, notated hymns with chord symbols. God is So Good (Key of C) Deep and Wide (Key of C) Check out key signature. M ...
Music Terminology Articulation: How specific notes or passages are
... Energy: The intensity or vitality of expression. Very often composers will talk about building energy (for example, towards the climax of the work) and releasing energy (i.e. giving the listener a chance to take a breath before launching into the next thing). ...
... Energy: The intensity or vitality of expression. Very often composers will talk about building energy (for example, towards the climax of the work) and releasing energy (i.e. giving the listener a chance to take a breath before launching into the next thing). ...
Powerpoint
... vocal styles (mentioned previously in approaches to pitch) The music reaches an increasingly lower pitch at the end, appearing to fade away. ...
... vocal styles (mentioned previously in approaches to pitch) The music reaches an increasingly lower pitch at the end, appearing to fade away. ...
A Guide to Part Writing Involving Root Position Triads
... Important exception: In major mode, it's possible to resolve the leading tone down to the next available chord tone when it is in an inner voice (tenor or alto), circumventing the above procedure, and resulting in a normal doubling for the submediant triad. This is not acceptable in the minor mod ...
... Important exception: In major mode, it's possible to resolve the leading tone down to the next available chord tone when it is in an inner voice (tenor or alto), circumventing the above procedure, and resulting in a normal doubling for the submediant triad. This is not acceptable in the minor mod ...
Aural Revision Grade 7
... Folk Prelude: Identifiable as a folk song but harmonised, sometimes in several different ways) Neo Classicism: Based on traditionl classical form but with modern harmonies. Composers such as Prokofiev, Stravinsky, Ravel. ...
... Folk Prelude: Identifiable as a folk song but harmonised, sometimes in several different ways) Neo Classicism: Based on traditionl classical form but with modern harmonies. Composers such as Prokofiev, Stravinsky, Ravel. ...
Music Theory G10-12 - Ewing Public Schools
... Students will apply solfege syllables to each scale degree in a major scale while applying the correct hand signal for each syllable. Students will identify all musical intervals: m2-M10 Students will recognize and identify the triad qualities of Major, minor, augmented and diminished. Students will ...
... Students will apply solfege syllables to each scale degree in a major scale while applying the correct hand signal for each syllable. Students will identify all musical intervals: m2-M10 Students will recognize and identify the triad qualities of Major, minor, augmented and diminished. Students will ...
The Elements of Music
... This tells us how fast or slow the music is. Italian words are often used to describe it. Eg Moderato = moderate. Texture This is the layers of sounds in a piece of music. It may be thick with many different melodies all at once, or thin with just one melody on its ...
... This tells us how fast or slow the music is. Italian words are often used to describe it. Eg Moderato = moderate. Texture This is the layers of sounds in a piece of music. It may be thick with many different melodies all at once, or thin with just one melody on its ...
1 - Julianne Baird
... d. a shift from one key to another within the same composition 35. Improvisation is a. a technique used only in jazz and non western music b. music created at the same time it is performed c. the addition of ornaments not indicated in the printed music d. all of the above 36. A song in which several ...
... d. a shift from one key to another within the same composition 35. Improvisation is a. a technique used only in jazz and non western music b. music created at the same time it is performed c. the addition of ornaments not indicated in the printed music d. all of the above 36. A song in which several ...
1 - Julianne Baird
... d. a shift from one key to another within the same composition 35. Improvisation is a. a technique used only in jazz and non western music b. music created at the same time it is performed c. the addition of ornaments not indicated in the printed music d. all of the above 36. A song in which several ...
... d. a shift from one key to another within the same composition 35. Improvisation is a. a technique used only in jazz and non western music b. music created at the same time it is performed c. the addition of ornaments not indicated in the printed music d. all of the above 36. A song in which several ...
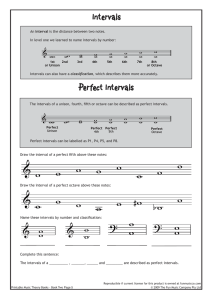
Intervals Perfect Intervals
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
... Intervals An Interval is the distance between two notes. In level one we learned to name intervals by number: ...
Harmony, Key, and Texture from 11/13/14 and
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
... • The interweaving of melody and harmony • Monophonic - one unaccompanied melody • Homophonic - one melody with some type of accompaniment (most common texture) • Polyphonic - two or more melodies at the same time.May be with or without accompaniment. This is "the crowning achievement of Western Mus ...
Figured Bass Basic Concepts
... c. the quality of the Roman numeral indicates the quality of the chord, just like in diatonic analysis. d. a sharp or flat before the Roman numeral raises or lowers the root of that chord. e. borrowed chords or other non-diatonic chords do not always need accidentals attached to the figures. For exa ...
... c. the quality of the Roman numeral indicates the quality of the chord, just like in diatonic analysis. d. a sharp or flat before the Roman numeral raises or lowers the root of that chord. e. borrowed chords or other non-diatonic chords do not always need accidentals attached to the figures. For exa ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.