Claude Debussy
... and his harmonies are rich (using dense, complex chords) and vague, creating a ‘wash’ of sound. Thus his music sounded very different from his late romantic contemporaries’, and laid the foundation for many developments in 20th century music. ...
... and his harmonies are rich (using dense, complex chords) and vague, creating a ‘wash’ of sound. Thus his music sounded very different from his late romantic contemporaries’, and laid the foundation for many developments in 20th century music. ...
Maths and music - Project Jugaad
... equal semitones in an octave of an ET scale and each octave is an exact factor of two in frequency. Therefore, the frequency change for each semitone is given by semitone12 = 2 or semitone = 21/12 = 1.05946. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . This defines the ET chromatic scale and allows the calcula ...
... equal semitones in an octave of an ET scale and each octave is an exact factor of two in frequency. Therefore, the frequency change for each semitone is given by semitone12 = 2 or semitone = 21/12 = 1.05946. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . This defines the ET chromatic scale and allows the calcula ...
Concepts for the Music Theory Sections of the Graduate Preliminary
... - No parallel 5ths or parallel octaves (also no "contrary" 5ths or octaves--this is when consecutive 5ths or octaves are created by contrary instead of parallel motion) - Resolve all "tendency tones" in the same voice--a leading-tone must resolves UP by half-step to the tonic; 7ths of "dominant 7th" ...
... - No parallel 5ths or parallel octaves (also no "contrary" 5ths or octaves--this is when consecutive 5ths or octaves are created by contrary instead of parallel motion) - Resolve all "tendency tones" in the same voice--a leading-tone must resolves UP by half-step to the tonic; 7ths of "dominant 7th" ...
a cappella Choral music performed without instrumental
... creating works through sound synthesis and manipulation. contrast Contrast of musical materials sustains our interest and feeds our love of change; it provides variety to a form. countermelody An accompanying melody sounded against the principal melody. crescendo The dynamic effect of gradually grow ...
... creating works through sound synthesis and manipulation. contrast Contrast of musical materials sustains our interest and feeds our love of change; it provides variety to a form. countermelody An accompanying melody sounded against the principal melody. crescendo The dynamic effect of gradually grow ...
The Musical Intervals Tutor
... You can also listen to the different sequences of intervals that make up various scales and modes by clicking Listen to Modes and Scales. And if you would like to test your knowledge of those sequences, click Take Test 3. ...
... You can also listen to the different sequences of intervals that make up various scales and modes by clicking Listen to Modes and Scales. And if you would like to test your knowledge of those sequences, click Take Test 3. ...
From Franz Liszt`s Late Piano Works to Analyze His
... The continuous use of the augmented triad The augmented triad, one of the extremely dissonant chords, is consisted of two kinds of three intervals to form chord structure to sound nervous and harsh so that few composers regard this as the primary chord to compose. In his late piano works, the augmen ...
... The continuous use of the augmented triad The augmented triad, one of the extremely dissonant chords, is consisted of two kinds of three intervals to form chord structure to sound nervous and harsh so that few composers regard this as the primary chord to compose. In his late piano works, the augmen ...
LABBS Harmony College 2003: Understanding the Barbershop Style
... homophonic texture. The melody is consistently sung by the lead, with the tenor harmonizing above the melody, the bass singing the lowest harmonizing notes, and the baritone completing the chord. The melody is not sung by the tenor except for an infrequent note or two to avoid awkward voice leading, ...
... homophonic texture. The melody is consistently sung by the lead, with the tenor harmonizing above the melody, the bass singing the lowest harmonizing notes, and the baritone completing the chord. The melody is not sung by the tenor except for an infrequent note or two to avoid awkward voice leading, ...
MUSICAL ELEMENTS
... • Tonality has a psychological aspect associated with it. – Music that is atonal can be disturbing to the listener. (Atonal has NO specific key.) -- The listener expects to hear certain sounds that complete the musical pattern. ...
... • Tonality has a psychological aspect associated with it. – Music that is atonal can be disturbing to the listener. (Atonal has NO specific key.) -- The listener expects to hear certain sounds that complete the musical pattern. ...
The Baroque 1/4
... Functional Harmony 1: Chord Progressions From about 1620, some important principles were formulated which came to dominate harmonic thought and practice. Tonality was the most important principle established at that time – by gradually replacing the modal system with major and minor scales. The cho ...
... Functional Harmony 1: Chord Progressions From about 1620, some important principles were formulated which came to dominate harmonic thought and practice. Tonality was the most important principle established at that time – by gradually replacing the modal system with major and minor scales. The cho ...
document - Far Western District
... has its roots as “ear music,” harmony singers would often use tense chords (minor, diminished, augmented, suspended) that simply BEGGED to be released to a major finish. Most often, the “Barbershop 7th” (Minor 7th, Dominant 7th) is used to generate this tension. We’ll investigate and experience this ...
... has its roots as “ear music,” harmony singers would often use tense chords (minor, diminished, augmented, suspended) that simply BEGGED to be released to a major finish. Most often, the “Barbershop 7th” (Minor 7th, Dominant 7th) is used to generate this tension. We’ll investigate and experience this ...
New Harmonic Resources
... Four arrangements of the mystic chord: a. As a series of stacked fourths (original form) b. As a scale: related to the whole-tone scale (with A-natural instead of A-flat) c. As a dominant thirteenth/sharp eleven chord (with added G) d. As a chord with mixed intervals ...
... Four arrangements of the mystic chord: a. As a series of stacked fourths (original form) b. As a scale: related to the whole-tone scale (with A-natural instead of A-flat) c. As a dominant thirteenth/sharp eleven chord (with added G) d. As a chord with mixed intervals ...
Musical Terms - Keating
... Notes are symbols that show a person how long to play and when to play. In music notation each note stands for a specific length of time for a tone to be held. ...
... Notes are symbols that show a person how long to play and when to play. In music notation each note stands for a specific length of time for a tone to be held. ...
1 Consonance and Dissonance in Theory, Practice and Science
... Pitch commonality is the degree to which two successive sounds have pitches in common, independent of context. By “pitch” we mean a subjective experience. Pitch is not physical frequency, nor is it a note in a score. The pitch that we experience at the missing fundamental is a pitch in this sense. I ...
... Pitch commonality is the degree to which two successive sounds have pitches in common, independent of context. By “pitch” we mean a subjective experience. Pitch is not physical frequency, nor is it a note in a score. The pitch that we experience at the missing fundamental is a pitch in this sense. I ...
Musical Terms Level 3
... A slur is a curved line used to indicate that notes should be played smoothly (legato) and in one breath. The notes are of different pitches and can be of different types. A slur can extended over two or several notes at a time, sometimes encompassing several bars of music ...
... A slur is a curved line used to indicate that notes should be played smoothly (legato) and in one breath. The notes are of different pitches and can be of different types. A slur can extended over two or several notes at a time, sometimes encompassing several bars of music ...
Introduction to Barbershop Harmony
... To maximize the effect of the natural overtone series, the roots and fifths of all chords are sung a little louder than the thirds and sevenths. In all cases, the melody is tuned to the tonal center, and the harmony parts are tuned to the melody part. Use of similar word sounds in good quality and b ...
... To maximize the effect of the natural overtone series, the roots and fifths of all chords are sung a little louder than the thirds and sevenths. In all cases, the melody is tuned to the tonal center, and the harmony parts are tuned to the melody part. Use of similar word sounds in good quality and b ...
01_front - Massey Research Online
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
... topics of scales, melody, voicings, harmony and rhythm are examined in separate chapters with over two hundred notated musical examples used to demonstrate the materials in their context. This thesis also seeks to explain the relationships between these elements and presents the material in a fonn a ...
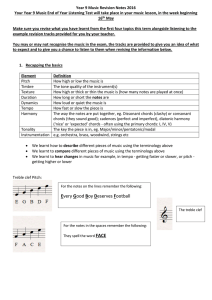
Year-9-Music
... o Ground Bass is both a way of composing and a type of composition. The ground bass can be developed in a variety of ways: o AUGMENTATION – The process of doubling the note values of a theme as a means of variation - the duration of the notes get longer o COUNTER MELODY – A melody that is played or ...
... o Ground Bass is both a way of composing and a type of composition. The ground bass can be developed in a variety of ways: o AUGMENTATION – The process of doubling the note values of a theme as a means of variation - the duration of the notes get longer o COUNTER MELODY – A melody that is played or ...
Rossini`s - The Spirit of Great Oak
... Synopsis of “Petite Messe Solennelle” Rossini’s mass was very solemn, the last of his Péchés de vieillesse (sins of old age). He dedicated it to the Countess Louise Pillet-Will and given its first performance at her private chapel in March 1864. Originally scored for two pianos, harmonium and 12 so ...
... Synopsis of “Petite Messe Solennelle” Rossini’s mass was very solemn, the last of his Péchés de vieillesse (sins of old age). He dedicated it to the Countess Louise Pillet-Will and given its first performance at her private chapel in March 1864. Originally scored for two pianos, harmonium and 12 so ...
Musicianship notes - University High School 2014
... x double sharp- raises pitch two half steps, or one full step b flat- lowers pitch one half step bb double flat- lowers pitch two half steps, or one full step natural- cancels out all sharps and flats, including key signature Enharmonic Equivalence Two pitches that sound the same, but are notated di ...
... x double sharp- raises pitch two half steps, or one full step b flat- lowers pitch one half step bb double flat- lowers pitch two half steps, or one full step natural- cancels out all sharps and flats, including key signature Enharmonic Equivalence Two pitches that sound the same, but are notated di ...
HIGH FREQUENCY VOCABULARY AND DEFINITIONS 5TH
... Theatrical performance combining music and drama Interval of eight notes, either up or down A short repeated rhythmic or melodic pattern Music based on a five tone scale Very soft Soft The highest pitched instrument in the woodwind family , ; in 4/4 time, receives one beat Single-reed instrument i ...
... Theatrical performance combining music and drama Interval of eight notes, either up or down A short repeated rhythmic or melodic pattern Music based on a five tone scale Very soft Soft The highest pitched instrument in the woodwind family , ; in 4/4 time, receives one beat Single-reed instrument i ...
modern jazz techniques
... two exceptions, every left-hand chord is quartal in nature, using two types of quartalbased chords. One is purely quartal, consisting of three notes separated by fourths. The second type is quartal in nature but includes a tritone between the lower two intervals (it is often written as an enharmonic ...
... two exceptions, every left-hand chord is quartal in nature, using two types of quartalbased chords. One is purely quartal, consisting of three notes separated by fourths. The second type is quartal in nature but includes a tritone between the lower two intervals (it is often written as an enharmonic ...
Impressionism - Mallaig High School Music Dept
... Notes which seem to clash when sounded together. ...
... Notes which seem to clash when sounded together. ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.