Ben Johnston Pantonality Generalized
... Ben Johnston’s artistic researches in extended just intonation by Marc Sabat What are the relationships between acoustics, physiology, cognition and specifically musical perceptions of sound in an artistic practice? How may experimental evidence gathered in any one of these fields approach the possi ...
... Ben Johnston’s artistic researches in extended just intonation by Marc Sabat What are the relationships between acoustics, physiology, cognition and specifically musical perceptions of sound in an artistic practice? How may experimental evidence gathered in any one of these fields approach the possi ...
Creates a response in the listener
... “Movement” is a self‐contained piece of music that is part of a larger set of ...
... “Movement” is a self‐contained piece of music that is part of a larger set of ...
Reference Guide to Music Literacy
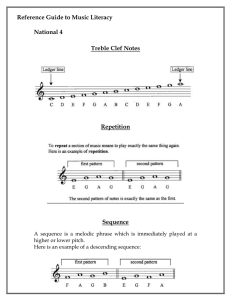
... Reference Guide to Music Literacy National 4 Treble Clef Notes ...
... Reference Guide to Music Literacy National 4 Treble Clef Notes ...
Elements of Music: Sound, Melody, Rhythm, and Harmony
... what he or she has heard before and relate that to what he or she hears in the present. Much folk and popular music is brief and repetitive with very little thematic development. More complex works—a Mozart string quartet, for example—have distinct themes that go through a period of development. The ...
... what he or she has heard before and relate that to what he or she hears in the present. Much folk and popular music is brief and repetitive with very little thematic development. More complex works—a Mozart string quartet, for example—have distinct themes that go through a period of development. The ...
Music History Lecture Notes
... Describing Sounds: Pitch • Refers to both its frequency and relative position in a musical scale – The answer to the question “what note is that?” ...
... Describing Sounds: Pitch • Refers to both its frequency and relative position in a musical scale – The answer to the question “what note is that?” ...
Babbitt`s Theorem - Theorem of the Day
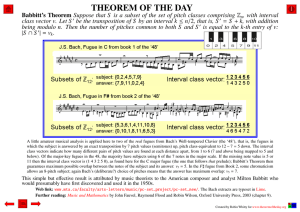
... below). Of the major-key fugues in the 48, the majority have subjects using 6 of the 7 notes in the major scale. If the missing note value is 5 or 11 then the interval class vector is (1 4 3 2 5 0), as found here for the C major fugue (the one that follows that prelude); Babbitt’s Theorem then guara ...
... below). Of the major-key fugues in the 48, the majority have subjects using 6 of the 7 notes in the major scale. If the missing note value is 5 or 11 then the interval class vector is (1 4 3 2 5 0), as found here for the C major fugue (the one that follows that prelude); Babbitt’s Theorem then guara ...
AP Music Theory
... - The viio triad, half-diminished seventh and fully diminished seventh chords - The leading tone relationship to dominant - Resolution to the tonic or tonic family - Analysis, dictation, and harmonization of these chords ** A Composition project assigned for UNIT FOUR is an original composition foll ...
... - The viio triad, half-diminished seventh and fully diminished seventh chords - The leading tone relationship to dominant - Resolution to the tonic or tonic family - Analysis, dictation, and harmonization of these chords ** A Composition project assigned for UNIT FOUR is an original composition foll ...
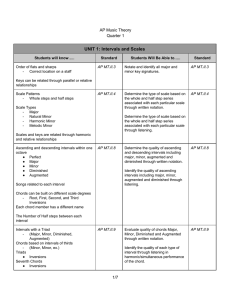
UNIT 1: Intervals and Scales
... Secondary triads can be found in either major, minor, diminished or augmented form depending on the scale represented. ...
... Secondary triads can be found in either major, minor, diminished or augmented form depending on the scale represented. ...
On Serial Music
... note before all twelve have been used would create a smoother line (see later for a discussion of this rule), he would. When writing a melody in a serial composition, he realised that structures such as the shape of phrases and the different characteristics of intervals between consecutive notes of ...
... note before all twelve have been used would create a smoother line (see later for a discussion of this rule), he would. When writing a melody in a serial composition, he realised that structures such as the shape of phrases and the different characteristics of intervals between consecutive notes of ...
CIS 3000 Intervals Tutorial
... instead of “major,” but the technicality behind it is not particularly relevant to us. The important thing to understand is that these intervals, especially the perfect fifth, have a relatively “empty” sound to them. While they are both usually considered consonant intervals, without the context of ...
... instead of “major,” but the technicality behind it is not particularly relevant to us. The important thing to understand is that these intervals, especially the perfect fifth, have a relatively “empty” sound to them. While they are both usually considered consonant intervals, without the context of ...
69s and pentatonics
... Used against a major chord or a dominant seventh built on the lowest note we get the 3 blues notes - the minor 7th, flattened 5th and the minor 3rd. Sometimes the major 3rd can also be used as indeed can the natural 5th. (If the natural 5th is used with a minor 3rd we have the minor pentatonic scal ...
... Used against a major chord or a dominant seventh built on the lowest note we get the 3 blues notes - the minor 7th, flattened 5th and the minor 3rd. Sometimes the major 3rd can also be used as indeed can the natural 5th. (If the natural 5th is used with a minor 3rd we have the minor pentatonic scal ...
Medieval and Renaissance Instrumental Music
... For I have loved you well and long, Delighting in your company. ...
... For I have loved you well and long, Delighting in your company. ...
About Diapason
... moves very gradually from one pitch position to another within the harmonic series, and as it moves, the bandwidth changes as well. For example, near the beginning and the end of the piece, the “diapason” includes harmonics from the 48th through 64th (thus defining an interval of a perfect fourth), ...
... moves very gradually from one pitch position to another within the harmonic series, and as it moves, the bandwidth changes as well. For example, near the beginning and the end of the piece, the “diapason” includes harmonics from the 48th through 64th (thus defining an interval of a perfect fourth), ...
Chapter 10 Harmonic Progression
... Harmonize each melody note with one chord. It is possible to repeat chords, but add inversions for variety Use first inversion chords to make a smoother bass line Shape the bass line carefully to make it a singable melodic line. Avoid overuse of ascending third and descending second progressions ...
... Harmonize each melody note with one chord. It is possible to repeat chords, but add inversions for variety Use first inversion chords to make a smoother bass line Shape the bass line carefully to make it a singable melodic line. Avoid overuse of ascending third and descending second progressions ...
essay - Dartmouth Math Home
... piano sonata, low chords approximate the sounds of drums, which have non-harmonic signals. His use of minor/major chords (chords containing both a minor and major third scale degree) can cause the ear to hear beats or combination tones that sound like pitches in between the two thirds. This could ei ...
... piano sonata, low chords approximate the sounds of drums, which have non-harmonic signals. His use of minor/major chords (chords containing both a minor and major third scale degree) can cause the ear to hear beats or combination tones that sound like pitches in between the two thirds. This could ei ...
Film Music
... * Animated Cartoons require more music than other film genres. Click tracks (an electronic metronome) were often used for accurate synchronisation of music to events. * Cartoons developed a range of associated musical cliches – pedal notes, the “walking” motif, the “calamity” motif, cluster chords a ...
... * Animated Cartoons require more music than other film genres. Click tracks (an electronic metronome) were often used for accurate synchronisation of music to events. * Cartoons developed a range of associated musical cliches – pedal notes, the “walking” motif, the “calamity” motif, cluster chords a ...
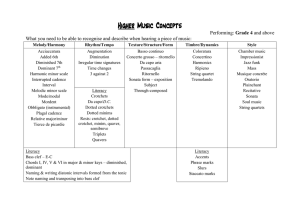
Higher Music Concepts
... Sonata form is the structure of the first movement of many sonatas, symphonies and often overtures. It contains three sections: exposition (introduction of two contrasting themes in related keys), development (the original ideas are built upon) and recapitulation (the original ideas are heard again, ...
... Sonata form is the structure of the first movement of many sonatas, symphonies and often overtures. It contains three sections: exposition (introduction of two contrasting themes in related keys), development (the original ideas are built upon) and recapitulation (the original ideas are heard again, ...
Hugo Wolf’s song ‘Das verlassene Mägdlein’ sean feit, feb 2011 Mörike Lieder
... its root? The missing root would then be F, forming an f minor chord. The progression then becomes (mixing between A major and a minor): I vi, the same progression that began the song in mm. 5-6, with the qualities reversed. This kind of overlapping parallelism is common in Wagner, and the use of mo ...
... its root? The missing root would then be F, forming an f minor chord. The progression then becomes (mixing between A major and a minor): I vi, the same progression that began the song in mm. 5-6, with the qualities reversed. This kind of overlapping parallelism is common in Wagner, and the use of mo ...
MUSIC OFFICE - SONGWRITING SESSIONS SESSION 1 – HARMONY Introduction
... chord lies not in the root note, but in its third and seventh. Let’s go back to working in C major. Chord V is a G dominant 7. The third of this chord is a B and the seventh is an F. The gap between these two notes is 6 semitones (also known as a ‘Tritone’, down to the fact there are 3 whole tones b ...
... chord lies not in the root note, but in its third and seventh. Let’s go back to working in C major. Chord V is a G dominant 7. The third of this chord is a B and the seventh is an F. The gap between these two notes is 6 semitones (also known as a ‘Tritone’, down to the fact there are 3 whole tones b ...
63. Familia Valera Miranda Se quema la chumbamba
... Diatonic G minor throughout, without any modulations. ...
... Diatonic G minor throughout, without any modulations. ...
On Ben Johnston`s Notation and the Performance
... reduction of natural relations to manageable ones. Its ubiquity in Western musical thinking, epitomized by the pianos which were once present in every home, and transferred by default to fixed-pitch percussion, modern organs and synthesizers, belies its own history as well as everyday musical experi ...
... reduction of natural relations to manageable ones. Its ubiquity in Western musical thinking, epitomized by the pianos which were once present in every home, and transferred by default to fixed-pitch percussion, modern organs and synthesizers, belies its own history as well as everyday musical experi ...
COURSE TITLE - Metropolitan Community College
... 5. Build major and minor scales. 6. Derive various key signatures from the major and minor scales. 7. Use your speaking voice to illustrate different dynamic levels and the tapping of your hand to differentiate different tempos. 8. Build triads and seventh chords on the staff and at the piano. 9. In ...
... 5. Build major and minor scales. 6. Derive various key signatures from the major and minor scales. 7. Use your speaking voice to illustrate different dynamic levels and the tapping of your hand to differentiate different tempos. 8. Build triads and seventh chords on the staff and at the piano. 9. In ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.