ZCHS Performing Arts Department 2015-2016
... Tie: two notes of the same pitch joined by a curved line over or under the note. Each note joined by a tie is held for it's full value but only the first note is played or sing Time signature appears at beginning of music, too number tells how many beats per measure, lower number indicates what type ...
... Tie: two notes of the same pitch joined by a curved line over or under the note. Each note joined by a tie is held for it's full value but only the first note is played or sing Time signature appears at beginning of music, too number tells how many beats per measure, lower number indicates what type ...
ap® music theory 2015 scoring guidelines
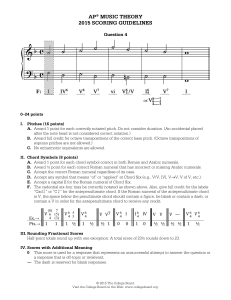
... A. Award 1 point for each correctly notated pitch. Do not consider duration. (An accidental placed after the note head is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enha ...
... A. Award 1 point for each correctly notated pitch. Do not consider duration. (An accidental placed after the note head is not considered correct notation.) B. Award full credit for octave transpositions of the correct bass pitch. (Octave transpositions of soprano pitches are not allowed.) C. No enha ...
Document
... C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, B Note that C7dim is the same as D#7dim, F#7dim and A7dim. This is an ambiguous chord and can resolve into many possible chords. There are only 4 diminished 7th chords. ...
... C, C#, D, D#, E, F, F#, G, G#, A, A#, B Note that C7dim is the same as D#7dim, F#7dim and A7dim. This is an ambiguous chord and can resolve into many possible chords. There are only 4 diminished 7th chords. ...
Elements of music - Texture, Tone Color
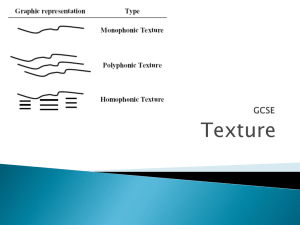
... Texture refers to the manner in which musical sounds/chords/lines/melodies are combined in a piece of music, and the relationship these parts have to one another. Monophony or Monophonic Texture Music with one note sounding at a time; a melody with no harmony or accompaniment Homophony - Homophonic ...
... Texture refers to the manner in which musical sounds/chords/lines/melodies are combined in a piece of music, and the relationship these parts have to one another. Monophony or Monophonic Texture Music with one note sounding at a time; a melody with no harmony or accompaniment Homophony - Homophonic ...
Vocabulary Guide - Heath Vocal Music
... Pitch - the highness of lowness of a tone Timbre - tone quality Interval - the distance between two notes in regards to pitch 2nd - step; neighbor notes 3rd - skip; from line to line or space to space Unison - all voice parts singing the same pitches ...
... Pitch - the highness of lowness of a tone Timbre - tone quality Interval - the distance between two notes in regards to pitch 2nd - step; neighbor notes 3rd - skip; from line to line or space to space Unison - all voice parts singing the same pitches ...
Aural Revision Grade 6
... Any Baroque or early Classical music had to make do without a sustain pedal, as it was written for the Harpsichord or Clavichord. Therefore we often have highly decorated cadences, and often there is ornamentation to fill out the gaps. Though you cannot presume that a piece with ornamentation is aut ...
... Any Baroque or early Classical music had to make do without a sustain pedal, as it was written for the Harpsichord or Clavichord. Therefore we often have highly decorated cadences, and often there is ornamentation to fill out the gaps. Though you cannot presume that a piece with ornamentation is aut ...
Music for Voices - misswardmusic.com
... A special kind of imitation – a musical phrase is ‘passed around’ between different groups of voices or instruments Often the groups are placed in different parts of the building or stage – creates a stereo effect ...
... A special kind of imitation – a musical phrase is ‘passed around’ between different groups of voices or instruments Often the groups are placed in different parts of the building or stage – creates a stereo effect ...
See more information on MUS - Barbershop Harmony Society
... the song’s lyrics, rhythm, melody, or harmony. The Music judge evaluates the performer’s choices of appropriate voicings and embellishment when used to enhance the song’s theme and delivery. Embellishment- The Music judge evaluates the effectiveness with which the performer uses embellishments for t ...
... the song’s lyrics, rhythm, melody, or harmony. The Music judge evaluates the performer’s choices of appropriate voicings and embellishment when used to enhance the song’s theme and delivery. Embellishment- The Music judge evaluates the effectiveness with which the performer uses embellishments for t ...
scottish - Gryffe Music
... Dotted Quaver - A note that lasts for ¾ of a beat. A dot after a note increases the length of the note by half of its original length, so without the dot this note lasts for ½ beat, adding the dot means it is ½ + ¼ = ¾ beats. ...
... Dotted Quaver - A note that lasts for ¾ of a beat. A dot after a note increases the length of the note by half of its original length, so without the dot this note lasts for ½ beat, adding the dot means it is ½ + ¼ = ¾ beats. ...
P5a - Piano Grade 5
... • There is generally one main mood, one main theme, and one main rhythmic pattern used throughout a Baroque composition. • It is usually performed with a constant rhythmic pulse. • Counterpoint (the simultaneous sounding of different melodic lines) and imitation are frequently used, so both hands ar ...
... • There is generally one main mood, one main theme, and one main rhythmic pattern used throughout a Baroque composition. • It is usually performed with a constant rhythmic pulse. • Counterpoint (the simultaneous sounding of different melodic lines) and imitation are frequently used, so both hands ar ...
Justin`s Quick Guide to Basic Music Theory and Playing by Ear
... up and down and do a happy dance. If not, you will need to put some more time into analyzing it. Recognition of keys takes practice. With enough practice, you will be able to tell the difference between your car keys and your house keys in a jiffy! (wait…nevermind). Those tricky musicians will somet ...
... up and down and do a happy dance. If not, you will need to put some more time into analyzing it. Recognition of keys takes practice. With enough practice, you will be able to tell the difference between your car keys and your house keys in a jiffy! (wait…nevermind). Those tricky musicians will somet ...
Appendix 1
... Cut time (Alla breve) The time signature C or 2/2 time; simple duple meter with the half note as the pulse note. D.C. al Fine It. “Da Capo” (“to the head”) directs the musician to return to the beginning and repeat, ending at the word Fine (the end). D.S. al Fine It. “Dal Segno” (“to the sign”) dire ...
... Cut time (Alla breve) The time signature C or 2/2 time; simple duple meter with the half note as the pulse note. D.C. al Fine It. “Da Capo” (“to the head”) directs the musician to return to the beginning and repeat, ending at the word Fine (the end). D.S. al Fine It. “Dal Segno” (“to the sign”) dire ...
Introduction to Music
... a. A statement followed by a contrasting statement b. The technique of combining several melodic lines into a meaningful whole c. The organization of musical ideas in time d. Constant repetition of a music idea ...
... a. A statement followed by a contrasting statement b. The technique of combining several melodic lines into a meaningful whole c. The organization of musical ideas in time d. Constant repetition of a music idea ...
Jefferson College Course Syllabus MSC101 Fundamentals of Music
... including scales, intervals, triads, and harmonization of simple melodies. The course is for both non-music majors and those preparing for Music Theory I and will partially fulfill the general education humanities requirement. (F, S, Su) ...
... including scales, intervals, triads, and harmonization of simple melodies. The course is for both non-music majors and those preparing for Music Theory I and will partially fulfill the general education humanities requirement. (F, S, Su) ...
Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... expression, technique, style, criteria, clarity, unity, expression, octave, thirds, melody, major, minor, chord Strategies for determining and singing harmonic parts Styles of music and strategies for recognizing them Listening techniques (ELA integration) Cycle of music composition and perf ...
... expression, technique, style, criteria, clarity, unity, expression, octave, thirds, melody, major, minor, chord Strategies for determining and singing harmonic parts Styles of music and strategies for recognizing them Listening techniques (ELA integration) Cycle of music composition and perf ...
Music for Small Ensemble
... Both pieces comprise three sections, each one repeated Melody and Rhythm Melodic lines move generally by step, with few large leaps – similar to vocal music, especially in the Pavane Opening motive of the Pavane (descending 4th from tonic to dominant, starting from a long note) is a symbol of ...
... Both pieces comprise three sections, each one repeated Melody and Rhythm Melodic lines move generally by step, with few large leaps – similar to vocal music, especially in the Pavane Opening motive of the Pavane (descending 4th from tonic to dominant, starting from a long note) is a symbol of ...
Music, Mathematics and Bach --------~--------
... music for small ensembles of instruments or voices survives in written form to this day. Around the 1600s another development took place, started by composers of what is called the 'Baroque' period which is the earliest period of 'classical' western music. As a reaction to the complexity of contrapu ...
... music for small ensembles of instruments or voices survives in written form to this day. Around the 1600s another development took place, started by composers of what is called the 'Baroque' period which is the earliest period of 'classical' western music. As a reaction to the complexity of contrapu ...
Appendix 1 Musical Terms
... Roman numerals Roman numerals are drawn below the staff to represent the number note in the scale (scale degree) on which a chord is based. For example, the roman numeral IV or iv represents the subdominant triad in a major and minor key, respectively. Root The note on which a chord is built; the ro ...
... Roman numerals Roman numerals are drawn below the staff to represent the number note in the scale (scale degree) on which a chord is based. For example, the roman numeral IV or iv represents the subdominant triad in a major and minor key, respectively. Root The note on which a chord is built; the ro ...
The Geometry of Musical Chords REPORTS
... The content of a collection of notes is often more important than their order. Chords can therefore be modeled as multisets of either pitches or pitch classes. (BChord[ will henceforth refer to a multiset of pitch classes unless otherwise noted.) The musical term Btransposition[ is synonymous with t ...
... The content of a collection of notes is often more important than their order. Chords can therefore be modeled as multisets of either pitches or pitch classes. (BChord[ will henceforth refer to a multiset of pitch classes unless otherwise noted.) The musical term Btransposition[ is synonymous with t ...
38. Schubert Der Doppelgänger Background information and performance circumstances 1
... • The second chord: B minor Vb without C sharp. • The third chord: D and F sharp in this context signify Ib without its root B. • The fourth chord: C sharp and F sharp signify V7c without E and A sharp. This chord sounds very bare, consisting entirely of perfect intervals – octaves, 4ths and 5ths. 2 ...
... • The second chord: B minor Vb without C sharp. • The third chord: D and F sharp in this context signify Ib without its root B. • The fourth chord: C sharp and F sharp signify V7c without E and A sharp. This chord sounds very bare, consisting entirely of perfect intervals – octaves, 4ths and 5ths. 2 ...
S3 Theory Matters Workbook
... Using the example, this would be C, D and E. So, C and E are a 3rd apart. Another example… What is the distance between G and C? Count G, A, B and C. There are 4 notes named so the distance between G and C is a 4th. The easiest way to do this is counting on your fingers, or using a diagram like the ...
... Using the example, this would be C, D and E. So, C and E are a 3rd apart. Another example… What is the distance between G and C? Count G, A, B and C. There are 4 notes named so the distance between G and C is a 4th. The easiest way to do this is counting on your fingers, or using a diagram like the ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.