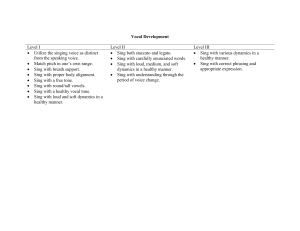
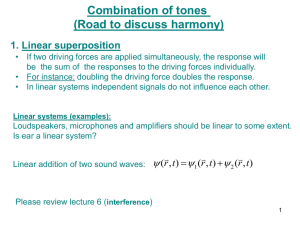
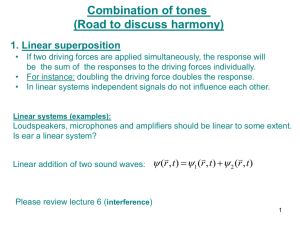
The Sound of It: Chords and “Sonority”
... 2 and 3 show that these were in use in the North Highlands by 1774. Melodies belong to the tonal system of keys whenever chord I (the tonic) moves to chord IV (the subdominant) and to chord V7 (pronounced “five seven”—the dominant seventh). If chord V7 doesn’t resolve to chord I, then a melody is not ...
... 2 and 3 show that these were in use in the North Highlands by 1774. Melodies belong to the tonal system of keys whenever chord I (the tonic) moves to chord IV (the subdominant) and to chord V7 (pronounced “five seven”—the dominant seventh). If chord V7 doesn’t resolve to chord I, then a melody is not ...
View - Ross Hamilton`s Music Education Resources
... tonic and dominant chords, with added 6ths or 7ths for colour. The chords are connected by stepwise voice leading in the lower treble notes of the piano part (G-Fs-E-D). The melody reaches its highest pitch in b.13, then quickly descends, like laughter. ø7 A half-diminished 7th chord (ii ) in b.14 l ...
... tonic and dominant chords, with added 6ths or 7ths for colour. The chords are connected by stepwise voice leading in the lower treble notes of the piano part (G-Fs-E-D). The melody reaches its highest pitch in b.13, then quickly descends, like laughter. ø7 A half-diminished 7th chord (ii ) in b.14 l ...
Course Description - W. David
... There are four basic tertian triads: major, minor, diminished and augmented. All but the augmented triad can be derived from the Major (or diatonic) scale. Triads (and all other larger tertian chords) are built by combining or stacking every other tone the scale above each individual degree (or scal ...
... There are four basic tertian triads: major, minor, diminished and augmented. All but the augmented triad can be derived from the Major (or diatonic) scale. Triads (and all other larger tertian chords) are built by combining or stacking every other tone the scale above each individual degree (or scal ...
Minor Scales
... Chromatic Intervals These intervals do not stick with the key signature. They use flats or sharps to alter the interval chromatically. In the key of C, any pitch can work as a chromatic interval. So you can have an interval between C and F#, and that is considered a chromatic interval! ...
... Chromatic Intervals These intervals do not stick with the key signature. They use flats or sharps to alter the interval chromatically. In the key of C, any pitch can work as a chromatic interval. So you can have an interval between C and F#, and that is considered a chromatic interval! ...
music 1010 - BEHS Choirbuzz
... C. are sounded one after the other B. is considered stable an restful D. form a melody 14. A combination of tones that is considered unstable and tense is called a A. consonance C. dissonance B. progression D. chord 15. Musical texture refers to A. how many different layers of sound are heard at the ...
... C. are sounded one after the other B. is considered stable an restful D. form a melody 14. A combination of tones that is considered unstable and tense is called a A. consonance C. dissonance B. progression D. chord 15. Musical texture refers to A. how many different layers of sound are heard at the ...
Sequential Chorus Curriculum for grades 6-8
... Music History and Interdisciplinary Application 6th grade Discuss the historical and cultural background of the works performed by the ensemble. Identify similarities and differences in the meanings of common terms used in the various fine arts. Describe in simple terms the similarities and d ...
... Music History and Interdisciplinary Application 6th grade Discuss the historical and cultural background of the works performed by the ensemble. Identify similarities and differences in the meanings of common terms used in the various fine arts. Describe in simple terms the similarities and d ...
Elements of Music: Sound, Melody, Rhythm, and Harmony
... conjunct and staccato passages as disjunct. Be sure to emphasize that melodic contour refers to the placement of pitches within a melody, and not to the way that melody is performed. 5. Probably the best way to illustrate harmony is to use the blues progression as an example of how chords provide a ...
... conjunct and staccato passages as disjunct. Be sure to emphasize that melodic contour refers to the placement of pitches within a melody, and not to the way that melody is performed. 5. Probably the best way to illustrate harmony is to use the blues progression as an example of how chords provide a ...
- MusicTeachers.co.uk
... evident in his mature piano works written after 1900, with their exploration of the instrument's percussive bell- and gong-like sonorities. Harmonically, Debussy's music incorporates both modality and tonality (earlier French composers such as Fauré had used modal aspects in their works) and he is r ...
... evident in his mature piano works written after 1900, with their exploration of the instrument's percussive bell- and gong-like sonorities. Harmonically, Debussy's music incorporates both modality and tonality (earlier French composers such as Fauré had used modal aspects in their works) and he is r ...
DCVLE - AP Central - The College Board
... 1. The chord must be spelled correctly. The bass pitch must be correct. 2. The fifth (but not the third) may be omitted from any root-position triad. 3. The fifth (but not the third or seventh) may be omitted from a root-position dominant seventh chord. 4. All inverted triads and inverted seventh ch ...
... 1. The chord must be spelled correctly. The bass pitch must be correct. 2. The fifth (but not the third) may be omitted from any root-position triad. 3. The fifth (but not the third or seventh) may be omitted from a root-position dominant seventh chord. 4. All inverted triads and inverted seventh ch ...
POTTER VOICE STUDIO INTERVALS , SCALES , KE Y
... An interval is the distance between two notes. Intervals are always counted from the lower note to the higher one, with the lower note being counted as one. Intervals come in different qualities and size. If the notes are sounded successively, it is a melodic interval. If sounded simultaneously, the ...
... An interval is the distance between two notes. Intervals are always counted from the lower note to the higher one, with the lower note being counted as one. Intervals come in different qualities and size. If the notes are sounded successively, it is a melodic interval. If sounded simultaneously, the ...
Context - Fulford School : VLE
... and falls back to the tonic. Fairly small melodic range of an octave (F sharp to F sharp), apart from the unwritten high B, which is usually put in by singers on the last note of verse 2. Largely based on a pentatonic scale (B D E F sharp A) with the C sharps at the end of the second phrase the only ...
... and falls back to the tonic. Fairly small melodic range of an octave (F sharp to F sharp), apart from the unwritten high B, which is usually put in by singers on the last note of verse 2. Largely based on a pentatonic scale (B D E F sharp A) with the C sharps at the end of the second phrase the only ...
Summary of Major scale and Accidentals
... The distance (interval) from the first C on the left to the last C is numbered from 1 -8 and each set is called an octave. This octave can begin with any of the eight letters and will end up with that same letter as the eight letter. For example, D E F G A B C D, F G A B C D E F and so on. The name ...
... The distance (interval) from the first C on the left to the last C is numbered from 1 -8 and each set is called an octave. This octave can begin with any of the eight letters and will end up with that same letter as the eight letter. For example, D E F G A B C D, F G A B C D E F and so on. The name ...
Elements of Music
... Harmony • In general, harmony refers to the combination of notes (or chords) played together and the relationship between a series of chords. But to give you a better understanding of harmony, let's first define melody. Melody refers to the tune of a song or piece of music. It is created by playing ...
... Harmony • In general, harmony refers to the combination of notes (or chords) played together and the relationship between a series of chords. But to give you a better understanding of harmony, let's first define melody. Melody refers to the tune of a song or piece of music. It is created by playing ...
Harmony 1
... SYLLABUS (brief outline and summary of topics, max. 10 sentences) Development of tonality-consonance and dissonance, manifestation of functional relationships; The role and importance of cadence in the affirmation of tonality; Dynamics of tonal changes and expanded tonality; Types of scale; Affirmat ...
... SYLLABUS (brief outline and summary of topics, max. 10 sentences) Development of tonality-consonance and dissonance, manifestation of functional relationships; The role and importance of cadence in the affirmation of tonality; Dynamics of tonal changes and expanded tonality; Types of scale; Affirmat ...
Elements of Music
... harmonic accompaniment or accompanied by a drone or percussion instrument(s). Homophonic – Melody with accompaniment. A melody line with a chordal accompaniment. Polyphonic – Two or more melody lines that are heard at the same time. All melody lines are of equal importance. Heterophonic – Two or mor ...
... harmonic accompaniment or accompanied by a drone or percussion instrument(s). Homophonic – Melody with accompaniment. A melody line with a chordal accompaniment. Polyphonic – Two or more melody lines that are heard at the same time. All melody lines are of equal importance. Heterophonic – Two or mor ...
GCSE Music Revision - The Hazeley Academy
... Turnaround = Chords change twice per bar (bar 10 of All Blues) Comping = short for ‘accompanying’. The piano ‘comps’ throughout until it’s solo 12 bar blues and alterations ...
... Turnaround = Chords change twice per bar (bar 10 of All Blues) Comping = short for ‘accompanying’. The piano ‘comps’ throughout until it’s solo 12 bar blues and alterations ...
Making Musical Decisions
... A transcriber assigns the music to a different set of players or singers, changing the medium of the music, but not the arrangement of the material ...
... A transcriber assigns the music to a different set of players or singers, changing the medium of the music, but not the arrangement of the material ...
How Do I Write a Listening Log
... How Do I Write a Listening Log??? Listening is a very important aspect of being a great musician! How do I sound compared to them? What can I do to improve my sound? Why do I like the Black Eyed Peas but not Taylor Swift? Music is around us all day everyday, so what are we really listening to?? ...
... How Do I Write a Listening Log??? Listening is a very important aspect of being a great musician! How do I sound compared to them? What can I do to improve my sound? Why do I like the Black Eyed Peas but not Taylor Swift? Music is around us all day everyday, so what are we really listening to?? ...
Experiencing Music - Petal School District
... A melody can move up or down, by step or skip. We memorize the sounds of the intervals to link the notes together. Perfect 4th – Perfect 5th – Major 6th – Octave - ...
... A melody can move up or down, by step or skip. We memorize the sounds of the intervals to link the notes together. Perfect 4th – Perfect 5th – Major 6th – Octave - ...
Scales, Voice
... Octave interval is simple ratio Fifth is a simple ratio Fourth is a simple ratio Major third is a simple ratio Minor third is a simple ratio ...
... Octave interval is simple ratio Fifth is a simple ratio Fourth is a simple ratio Major third is a simple ratio Minor third is a simple ratio ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.