Milhaud Describes Polytonality
... In the harmonic texture coming from atonal lines, we will always find chords pertaining to diatonic harmony (triads, 7ths, augmented triads, etc.), but they will be isolated, and none of the tones that precede or follow them will justify the existence of one or more definite tonalities. Horizontally ...
... In the harmonic texture coming from atonal lines, we will always find chords pertaining to diatonic harmony (triads, 7ths, augmented triads, etc.), but they will be isolated, and none of the tones that precede or follow them will justify the existence of one or more definite tonalities. Horizontally ...
Music Theory answers
... The fifth note of the tonic scale is called the Dominant The bottom note of a chord or first note of a scale that a chord is based on is called the Root or Tonic Three note chords are called Triads and are built using a Root, third, fifth. A tonic chord is built using the Root, third and fifth of t ...
... The fifth note of the tonic scale is called the Dominant The bottom note of a chord or first note of a scale that a chord is based on is called the Root or Tonic Three note chords are called Triads and are built using a Root, third, fifth. A tonic chord is built using the Root, third and fifth of t ...
Major Diatonic Chords
... We now have the following triad types: 1. The i and iv triads are minor (minor third + major third). 2. The III, V and VI are major triads. The III and VI are naturally major triads (that is, just by using notes from the scale they automatically come out as major triads). The V triad, however, would ...
... We now have the following triad types: 1. The i and iv triads are minor (minor third + major third). 2. The III, V and VI are major triads. The III and VI are naturally major triads (that is, just by using notes from the scale they automatically come out as major triads). The V triad, however, would ...
You Can Get It If You Really Want (p
... The vocal line uses a lot of melismas – one syllable spread across two or more notes – especially at the end of phrases. Melodic lines are short – one or two bar units, rather than longer phrases. ...
... The vocal line uses a lot of melismas – one syllable spread across two or more notes – especially at the end of phrases. Melodic lines are short – one or two bar units, rather than longer phrases. ...
AP-Music-Theory-Study-Guide
... • Cross relation (false relation)- simultaneous or adjacent occurrence of a note in its natural and chromatically inflected (#/b) form in different voices (sounds bad) Miscellaneous harmonic terms • Arpeggio, arpeggiation- notes that outline a chord • Consonance- pleasing to the ear, major and more ...
... • Cross relation (false relation)- simultaneous or adjacent occurrence of a note in its natural and chromatically inflected (#/b) form in different voices (sounds bad) Miscellaneous harmonic terms • Arpeggio, arpeggiation- notes that outline a chord • Consonance- pleasing to the ear, major and more ...
Music Theory answers
... Notes that are marked with sharps, flats or naturals that are not in the key signature are called accidentals What is rule for accidentals? Accidentals are carried through the measure they are in. What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear co ...
... Notes that are marked with sharps, flats or naturals that are not in the key signature are called accidentals What is rule for accidentals? Accidentals are carried through the measure they are in. What might indicate that the tonal center or key of a piece is changing? Accidentals start to appear co ...
Tonal Harmony Chapter 7 Harmonic Progression and the Sequence
... Harmonic Progression and the Sequence Introduction Tonal Harmony developed slowly out of the great polyphonic modal tradition of the Renaissance period (1430-1600) The “rule” of counterpoint resulted in certain recurring and recognizable combinations of chords (tonal harmony) which is the heart ...
... Harmonic Progression and the Sequence Introduction Tonal Harmony developed slowly out of the great polyphonic modal tradition of the Renaissance period (1430-1600) The “rule” of counterpoint resulted in certain recurring and recognizable combinations of chords (tonal harmony) which is the heart ...
A GUIDE TO THE TERMINOLOGY OF GERMAN HARMONY
... At this point German harmony still does not depart markedly from English harmony. Both traditions presume harmony to be “functional,” though the meaning of this term is less clear in English than in German. Both are ultimately descended from Rameau, though filtered through various theories of fundam ...
... At this point German harmony still does not depart markedly from English harmony. Both traditions presume harmony to be “functional,” though the meaning of this term is less clear in English than in German. Both are ultimately descended from Rameau, though filtered through various theories of fundam ...
Ch11 Lecture Part I
... – Listeners: Great difficulty perceiving octave relationships between tones when one or both tones are greater than 5 kHz ...
... – Listeners: Great difficulty perceiving octave relationships between tones when one or both tones are greater than 5 kHz ...
Theory Intro
... chord is tonic; V and vii are dominant; ii and IV are predominant. Ê Certain patterns of harmony are especially common (in ...
... chord is tonic; V and vii are dominant; ii and IV are predominant. Ê Certain patterns of harmony are especially common (in ...
Required Graduate Music Theory Examinations
... examinations in aural skills and written theory BEFORE classes begin. The date and time for these examinations is listed in the “Orientation Schedule” published by the Division of Music each year and em ...
... examinations in aural skills and written theory BEFORE classes begin. The date and time for these examinations is listed in the “Orientation Schedule” published by the Division of Music each year and em ...
the fundamental principles of harmony
... This treatise offers to both teacher and student a unique and powerful knowledge of the musical universe of chords, harmonic syntax, doublings, and spacings. Taught as the art of hearing and listening, Harmony is treated here with sensitivity and musicality. From thorough analysis of the norms and s ...
... This treatise offers to both teacher and student a unique and powerful knowledge of the musical universe of chords, harmonic syntax, doublings, and spacings. Taught as the art of hearing and listening, Harmony is treated here with sensitivity and musicality. From thorough analysis of the norms and s ...
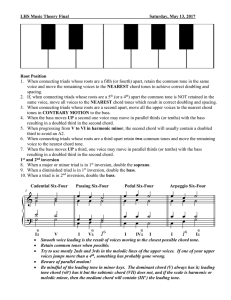
lhs music theory final exam review sheet
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
... 2. If, when connecting triads whose roots are a 5th (or a 4th) apart the common tone is NOT retained in the same voice, move all voices to the NEAREST chord tones which result in correct doubling and spacing. 3. When connecting triads whose roots are a second apart, move all the upper voices to the ...
Farmington High School Music Department
... A natural division of a melodic line, comparable to a sentence in language. Phrasing is an essential component in the expressive nature of music. Rhythm Everything which refers to the temporal quality (duration) of a musical sound. It is considered along with harmony and melody (motion) one of the t ...
... A natural division of a melodic line, comparable to a sentence in language. Phrasing is an essential component in the expressive nature of music. Rhythm Everything which refers to the temporal quality (duration) of a musical sound. It is considered along with harmony and melody (motion) one of the t ...
Matt Pike Music 122 Final Paper Ravel – String Quartet in F Major
... third relations serve different purposes. In the exposition, when the opening theme is played for the second time, in F, it is denied by an A major chord. A third relation of a major third, jammed into the middle of a passage with a definite tonal center. This third relation functions to disrupt the ...
... third relations serve different purposes. In the exposition, when the opening theme is played for the second time, in F, it is denied by an A major chord. A third relation of a major third, jammed into the middle of a passage with a definite tonal center. This third relation functions to disrupt the ...
The Elements of Music
... the vibration, the higher the pitch, the slower the vibration, the lower the pitch Each definite pitch is called a tone and has a specific frequency The distance in pitch between 2 notes is called an interval Question: How can you change the speed of vibration on an instrument? ...
... the vibration, the higher the pitch, the slower the vibration, the lower the pitch Each definite pitch is called a tone and has a specific frequency The distance in pitch between 2 notes is called an interval Question: How can you change the speed of vibration on an instrument? ...
Harmonic Progression - LearnMusicTheory.net
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
... A harmonic progression is a goal-directed succession of chords. Composers from the 1600s through the 1800s favored certain strong harmonic progressions. The strongest of all progressions involves the root of the chord moving down a fifth (or up a fourth), especially dominant (V) to tonic (I or i). ...
level 11 - Hlubek Piano Studio
... scherzando: a playful style of performance a cappella: unaccompanied trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of t ...
... scherzando: a playful style of performance a cappella: unaccompanied trill: alternation of two notes a second apart supertonic: second degree of the scale submediant: sixth degree of the scale deceptive cadence: a cadence consisting of V-vi chordal progression half cadence: a cadence consisting of t ...
Tonality vs. Atonality
... Characteristics of Traditional Harmony: • Tonality. A tonal center embodied in the tonic triad. • Tonality is established by the progression V-I and the resolution of the leading tone to the tonic pitch. Harmonic progressions point towards the tonic. • Functional harmony. Chords are polarized around ...
... Characteristics of Traditional Harmony: • Tonality. A tonal center embodied in the tonic triad. • Tonality is established by the progression V-I and the resolution of the leading tone to the tonic pitch. Harmonic progressions point towards the tonic. • Functional harmony. Chords are polarized around ...
Music Vocabulary Terms
... Music: Sounds organized in time Pitch: The highness or lowness of a sound, measured by frequency Staff: The five lines on which music is read Grand Staff: A full staff of both treble and bass clefs Bar Lines: The vertical lines on the staff, which breaks music into measures Measure or Bar: Sections ...
... Music: Sounds organized in time Pitch: The highness or lowness of a sound, measured by frequency Staff: The five lines on which music is read Grand Staff: A full staff of both treble and bass clefs Bar Lines: The vertical lines on the staff, which breaks music into measures Measure or Bar: Sections ...
Siyahamba is in the key of F major. Notice that the key signature at
... You may work in pairs to add the chords or have a go by yourself either adding single finger chords or full chords. ...
... You may work in pairs to add the chords or have a go by yourself either adding single finger chords or full chords. ...
Chord Symbols Handout
... make sure your m is lowercase in option 4. I usually opt for the first or second option here. Extensions Jazz musicians typically employ chords that have more than four notes. The notes above the seventh are known as extensions, and typically include the ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth of the chord. ...
... make sure your m is lowercase in option 4. I usually opt for the first or second option here. Extensions Jazz musicians typically employ chords that have more than four notes. The notes above the seventh are known as extensions, and typically include the ninth, eleventh, and thirteenth of the chord. ...
Music 181: Inversions of Intervals, Compound Intervals
... II. Compound intervals Any interval larger than an octave (8va) is a compound interval; intervals smaller than an octave are called simple intervals. Any compound interval can be reduced to a simple interval; in most musical contexts the compound interval and its simple counterpart are functionally ...
... II. Compound intervals Any interval larger than an octave (8va) is a compound interval; intervals smaller than an octave are called simple intervals. Any compound interval can be reduced to a simple interval; in most musical contexts the compound interval and its simple counterpart are functionally ...
Harmony

In music, harmony is the use of simultaneous pitches (tones, notes), or chords. The study of harmony involves chords and their construction and chord progressions and the principles of connection that govern them. Harmony is often said to refer to the ""vertical"" aspect of music, as distinguished from melodic line, or the ""horizontal"" aspect. Counterpoint, which refers to the interweaving of melodic lines, and polyphony, which refers to the relationship of separate independent voices, are thus sometimes distinguished from harmony.In popular and jazz harmony, chords are named by their root plus various terms and characters indicating their qualities. In many types of music, notably baroque, romantic, modern, and jazz, chords are often augmented with ""tensions"". A tension is an additional chord member that creates a relatively dissonant interval in relation to the bass. Typically, in the classical common practice period a dissonant chord (chord with tension) ""resolves"" to a consonant chord. Harmonization usually sounds pleasant to the ear when there is a balance between the consonant and dissonant sounds. In simple words, that occurs when there is a balance between ""tense"" and ""relaxed"" moments.